
最新刊期
卷 29 , 期 11 , 2025
- “在滑坡易发性评价领域,研究者融合InSAR监测结果和机器学习模型,提升了滑坡风险评估的准确性和现势性。”
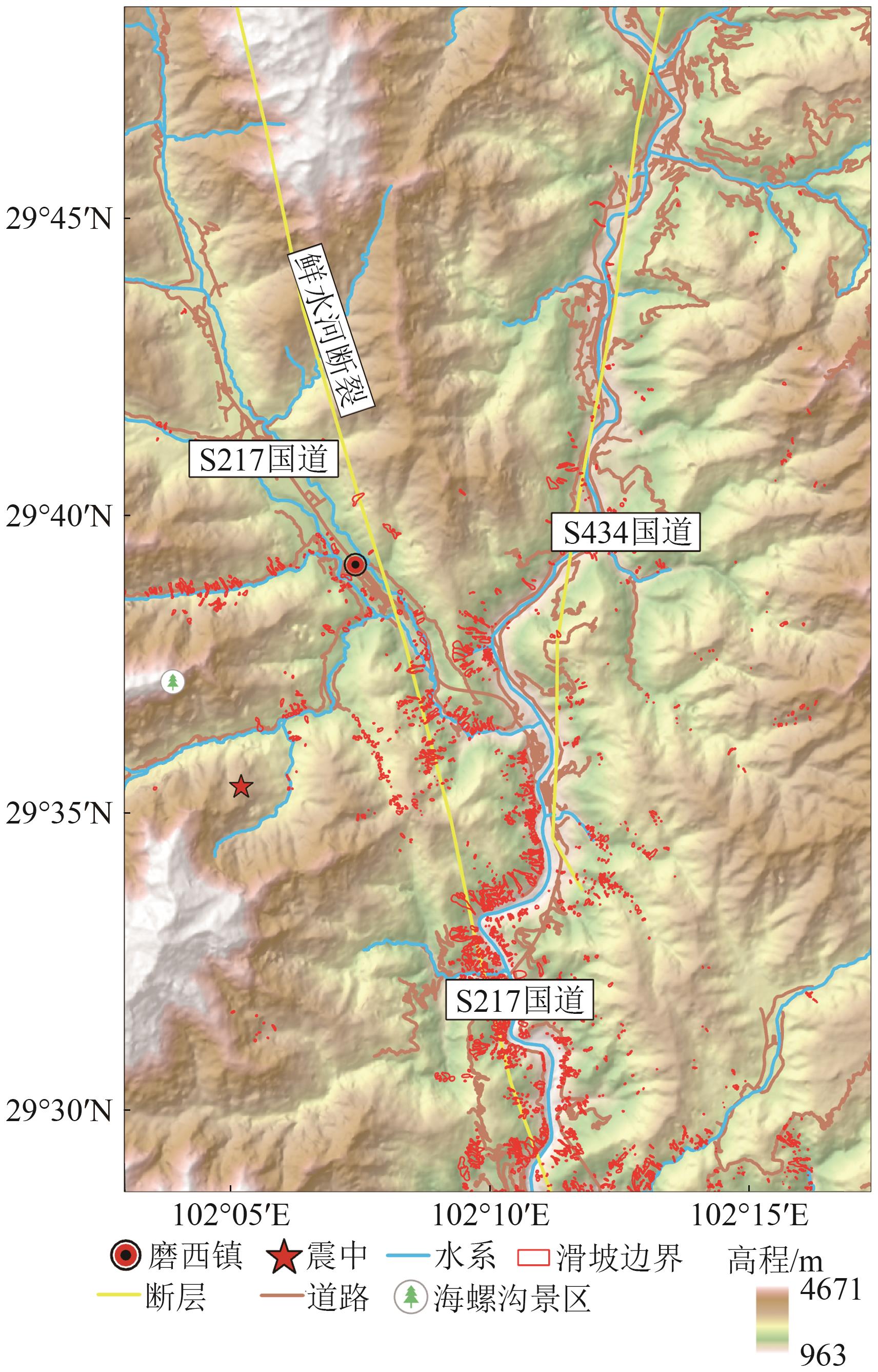 摘要:Landslide susceptibility assessment based on machine learning often faces challenges because of the precision of spatial geoinformation sample datasets and the model’s ability to fit disaster-causing mechanisms, resulting in misjudgment and omission of high-risk areas. In the aftermath of the Luding 9.5 earthquake, secondary landslides have occurred frequently, and highly developed vegetation limits the accuracy of remote sensing-based landslide cataloging, severely affecting the accurate assessment of post-disaster landslide susceptibility. Therefore, this study integrates LT-1 ascending/descending track time-series InSAR surface deformation monitoring results with existing historical landslide catalog data to enhance the timeliness and accuracy of landslide spatial distribution base data. Gradient boosting decision tree (GBDT) and extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) are selected as base learners to construct a stacking (GBDT-XGBoost) heterogeneous ensemble learning model for landslide susceptibility assessment. Through a comparative analysis of prediction accuracy, the model and algorithm optimization are completed, ultimately achieving precise, reliable, timely landslide susceptibility assessment and mapping. The experiment utilizes newly acquired ascending/descending track LT-1 satellite time-series SAR imagery datasets from 2023 to 2024. By extracting the surface deformation rate field by using stacking InSAR technology and conducting comprehensive landslide interpretation with Gaofen-2 satellite imagery, 36 new landslides are identified, expanding the historical landslide catalog dataset. On this basis, landslide susceptibility prediction is performed using three existing machine learning models. Comparative analysis of the accuracy and performance of the proposed heterogeneous ensemble learning model shows that the prediction performance and accuracy of each model improve because of the support of the LT dataset detecting landslide information. The stacking (GBDT-XGBoost) model has higher predictive performance and accuracy (area under the curve = 0.981, accuracy = 93.13%, recall = 92.82%, and F1-score = 0.932) compared with existing machine learning models. Moreover, the identified spatial distribution of landslides aligns closely with the high-risk areas predicted by the heterogeneous ensemble learning model. The proposed landslide cataloging method and landslide susceptibility assessment model help improve the accuracy and timeliness of landslide risk assessment and can provide a reference for disaster prevention, mitigation, and scientific reconstruction planning in relevant areas.关键词:remote sensing;Lutan-1;Luding earthquake;landslide interpretation;heterogeneous ensemble learning;landslide susceptibility assessment350|46|0更新时间:2025-12-30
摘要:Landslide susceptibility assessment based on machine learning often faces challenges because of the precision of spatial geoinformation sample datasets and the model’s ability to fit disaster-causing mechanisms, resulting in misjudgment and omission of high-risk areas. In the aftermath of the Luding 9.5 earthquake, secondary landslides have occurred frequently, and highly developed vegetation limits the accuracy of remote sensing-based landslide cataloging, severely affecting the accurate assessment of post-disaster landslide susceptibility. Therefore, this study integrates LT-1 ascending/descending track time-series InSAR surface deformation monitoring results with existing historical landslide catalog data to enhance the timeliness and accuracy of landslide spatial distribution base data. Gradient boosting decision tree (GBDT) and extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) are selected as base learners to construct a stacking (GBDT-XGBoost) heterogeneous ensemble learning model for landslide susceptibility assessment. Through a comparative analysis of prediction accuracy, the model and algorithm optimization are completed, ultimately achieving precise, reliable, timely landslide susceptibility assessment and mapping. The experiment utilizes newly acquired ascending/descending track LT-1 satellite time-series SAR imagery datasets from 2023 to 2024. By extracting the surface deformation rate field by using stacking InSAR technology and conducting comprehensive landslide interpretation with Gaofen-2 satellite imagery, 36 new landslides are identified, expanding the historical landslide catalog dataset. On this basis, landslide susceptibility prediction is performed using three existing machine learning models. Comparative analysis of the accuracy and performance of the proposed heterogeneous ensemble learning model shows that the prediction performance and accuracy of each model improve because of the support of the LT dataset detecting landslide information. The stacking (GBDT-XGBoost) model has higher predictive performance and accuracy (area under the curve = 0.981, accuracy = 93.13%, recall = 92.82%, and F1-score = 0.932) compared with existing machine learning models. Moreover, the identified spatial distribution of landslides aligns closely with the high-risk areas predicted by the heterogeneous ensemble learning model. The proposed landslide cataloging method and landslide susceptibility assessment model help improve the accuracy and timeliness of landslide risk assessment and can provide a reference for disaster prevention, mitigation, and scientific reconstruction planning in relevant areas.关键词:remote sensing;Lutan-1;Luding earthquake;landslide interpretation;heterogeneous ensemble learning;landslide susceptibility assessment350|46|0更新时间:2025-12-30 - “在合成孔径雷达干涉测量领域,研究人员提出了一种多尺度InSAR相位滤波方法,有效提升了相位细节保留与噪声抑制的平衡,为LT-1 A/B数字高程模型精确反演提供技术支撑。”
 摘要:Deep learning, with its powerful feature learning and nonlinear modeling capabilities, has been widely applied in the field of phase filtering for Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR). However, in high-noise and stripe-dense regions, existing methods still struggle to balance noise suppression with the preservation of detailed phase information. To address this, this paper proposes a multi-scale InSAR phase filtering method integrating an Adaptive Augmentation and dynamic Screening-based Technique Module (AASTM). This model constructs a multi-scale feature extraction and layer-by-layer fusion framework based on the U-Net architecture. The AASTM module is inserted at different scales to perform adaptive augmentation and dynamic screening of interferometric phase features, achieving a balance between phase detail preservation and noise suppression. Additionally, a rhombus-square grid method is employed to generate simulated training datasets covering high-noise and dense-stripe scenarios, further enhancing the network model’s robustness and generalization capability in complex environments. The filtering performance of the proposed method is experimentally validated using simulated data and LT-1 A/B dual-satellite SAR data, with comparisons against existing filtering techniques. Results demonstrate: On simulated data, the proposed method achieves an average reduction of approximately 20% in Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) compared to other filtering methods, an improvement of about 18% in Structural Similarity Index (SSI), and an increase of approximately 5% in peak signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Particularly in high-noise and dense stripe regions, the proposed method exhibits superior phase edge and detail retention capabilities. On LT-1 A/B field data, the proposed method achieves a residual error removal rate of 90.42% while better preserving phase detail information. In summary, the proposed method demonstrates significantly superior filtering accuracy compared to other methods, along with enhanced phase resolution and detail retention in dense stripe regions. It provides more reliable technical support for the precise inversion of LT-1 A/B digital elevation models.关键词:deep learning;synthetic aperture radar interferometry;phase filtering;adaptive enhancement;dynamic screening201|34|0更新时间:2025-12-30
摘要:Deep learning, with its powerful feature learning and nonlinear modeling capabilities, has been widely applied in the field of phase filtering for Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR). However, in high-noise and stripe-dense regions, existing methods still struggle to balance noise suppression with the preservation of detailed phase information. To address this, this paper proposes a multi-scale InSAR phase filtering method integrating an Adaptive Augmentation and dynamic Screening-based Technique Module (AASTM). This model constructs a multi-scale feature extraction and layer-by-layer fusion framework based on the U-Net architecture. The AASTM module is inserted at different scales to perform adaptive augmentation and dynamic screening of interferometric phase features, achieving a balance between phase detail preservation and noise suppression. Additionally, a rhombus-square grid method is employed to generate simulated training datasets covering high-noise and dense-stripe scenarios, further enhancing the network model’s robustness and generalization capability in complex environments. The filtering performance of the proposed method is experimentally validated using simulated data and LT-1 A/B dual-satellite SAR data, with comparisons against existing filtering techniques. Results demonstrate: On simulated data, the proposed method achieves an average reduction of approximately 20% in Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) compared to other filtering methods, an improvement of about 18% in Structural Similarity Index (SSI), and an increase of approximately 5% in peak signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Particularly in high-noise and dense stripe regions, the proposed method exhibits superior phase edge and detail retention capabilities. On LT-1 A/B field data, the proposed method achieves a residual error removal rate of 90.42% while better preserving phase detail information. In summary, the proposed method demonstrates significantly superior filtering accuracy compared to other methods, along with enhanced phase resolution and detail retention in dense stripe regions. It provides more reliable technical support for the precise inversion of LT-1 A/B digital elevation models.关键词:deep learning;synthetic aperture radar interferometry;phase filtering;adaptive enhancement;dynamic screening201|34|0更新时间:2025-12-30 - “陆地探测一号卫星系统研究取得进展,专家设计了卷积神经网络及损失函数,验证了利用双极化数据复原全极化信息的可行性,为SAR土地覆盖分类等应用提供新方向。”
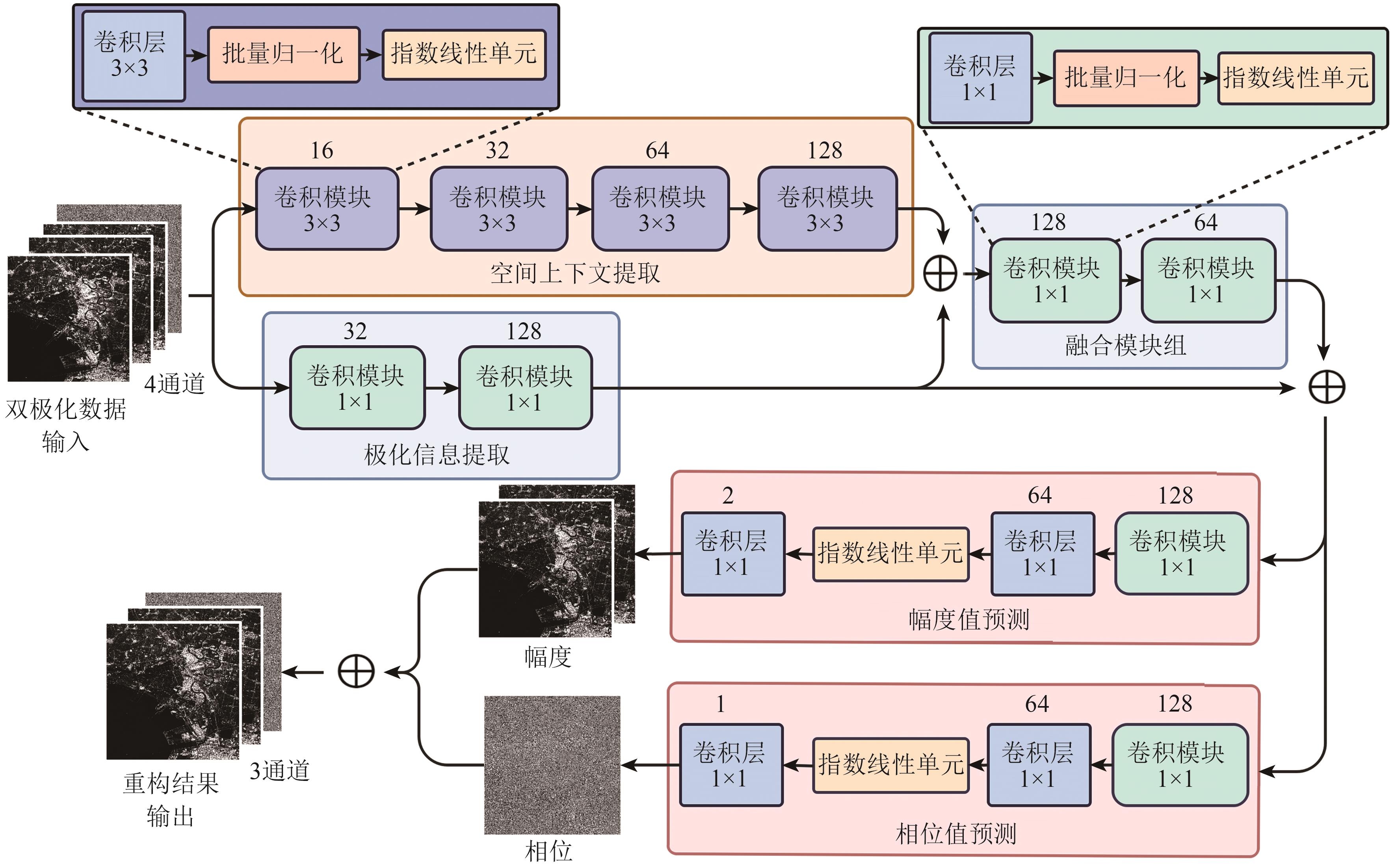 摘要:The LuTan-1 (LT-1) 01A/B satellite constellation, China’s first civilian L-band distributed Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) satellite system, is expected to further promote the widespread application of domestic radar data products. While LT-1’s dual-polarization mode supports high-resolution and wide-swath imaging, it lacks certain polarization information compared to full-polarization observation systems, which limits its applications such as land cover classification. To address this, this study designs a multi-head multi-branch Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and a tailored loss function for two commonly used dual-polarization modes of LT-1. The goal is to restore missing polarization information from dual-polarization inputs, thereby achieving full-polarization SAR data reconstruction. Considering the complementary nature of polarization and spatial features, as well as the distinct characteristics of amplitude and phase data, the network employs separate branches to extract pixel-level polarization information and local spatial features within receptive fields. Two independent heads predict amplitude and phase values to mitigate data crosstalk during output. Additionally, an amplitude/phase combined loss function incorporating phase periodicity is proposed to guide network training. Experiments conducted on two full-polarization SAR images acquired by LT-1 over urban areas in the UK demonstrate that, the proposed method achieves amplitude prediction errors of 1—2 dB and phase errors below 0.5 rad. These results surpass the reconstruction accuracy of a U-Net model with comparable parameter scale. The reconstructed data exhibit statistical distributions and polarization decomposition effects nearly identical to the ground-truth data, confirming effective preservation of full-polarization information. Furthermore, land cover classification experiments show that, classification maps using the reconstructed data achieve overall accuracy comparable to those using real full-polarization data, with a 5% improvement over dual-polarization based classification maps. This study preliminarily validates the feasibility of leveraging LT-1’s dual-polarization data to achieve high-resolution, wide-swath imaging while retaining full-polarization capabilities, providing richer input information for SAR land cover/use classification applications.关键词:SAR;LT-1;Dual Polarization;full polarization;CNN;Terrain Classification275|162|0更新时间:2025-12-30
摘要:The LuTan-1 (LT-1) 01A/B satellite constellation, China’s first civilian L-band distributed Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) satellite system, is expected to further promote the widespread application of domestic radar data products. While LT-1’s dual-polarization mode supports high-resolution and wide-swath imaging, it lacks certain polarization information compared to full-polarization observation systems, which limits its applications such as land cover classification. To address this, this study designs a multi-head multi-branch Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and a tailored loss function for two commonly used dual-polarization modes of LT-1. The goal is to restore missing polarization information from dual-polarization inputs, thereby achieving full-polarization SAR data reconstruction. Considering the complementary nature of polarization and spatial features, as well as the distinct characteristics of amplitude and phase data, the network employs separate branches to extract pixel-level polarization information and local spatial features within receptive fields. Two independent heads predict amplitude and phase values to mitigate data crosstalk during output. Additionally, an amplitude/phase combined loss function incorporating phase periodicity is proposed to guide network training. Experiments conducted on two full-polarization SAR images acquired by LT-1 over urban areas in the UK demonstrate that, the proposed method achieves amplitude prediction errors of 1—2 dB and phase errors below 0.5 rad. These results surpass the reconstruction accuracy of a U-Net model with comparable parameter scale. The reconstructed data exhibit statistical distributions and polarization decomposition effects nearly identical to the ground-truth data, confirming effective preservation of full-polarization information. Furthermore, land cover classification experiments show that, classification maps using the reconstructed data achieve overall accuracy comparable to those using real full-polarization data, with a 5% improvement over dual-polarization based classification maps. This study preliminarily validates the feasibility of leveraging LT-1’s dual-polarization data to achieve high-resolution, wide-swath imaging while retaining full-polarization capabilities, providing richer input information for SAR land cover/use classification applications.关键词:SAR;LT-1;Dual Polarization;full polarization;CNN;Terrain Classification275|162|0更新时间:2025-12-30 - “记者从中国南方地区建筑物变化检测研究中获悉,中国自主研制的陆地探测一号01组A/B卫星(LT-1A/1B)数据在变化检测领域具有应用潜力。研究基于LT-1数据,提出一种融合多时相合成孔径雷达(SAR)幅度特征和相干性信息的城区建筑物变化检测算法,通过建筑物识别、色域分割和相干性变化约束,获取城区建筑物变化区域并定位建筑物变化时段。实验结果验证了算法的可靠性,为城市规划和违建查处等领域提供解决方案。”
 摘要:Urban building change detection is an important part of land use, resource management, and urban planning. It plays an extremely important role in urban development, housing security and post-disaster reconstruction in earthquake areas. Optical image and SAR image are two commonly used data sources in urban building change detection. Optical images have the advantages of high resolution, high timeliness and convenient visual interpretation in change detection. However, optical images are difficult to use because of the influence of cloud, fog, and rain weather in southern China. SAR satellite is a side-looking imaging, and its imaging signal contains rich surface texture information, which is convenient for change detection and analysis. In SAR images, the change of ground objects can cause the change of amplitude information and coherence characteristics of SAR images, and buildings have certain imaging characteristics. China’s self-developed LT-1A/1B satellite has the advantages of high resolution, short return period, multipolarization, and all-day, all-weather operation. It can be used as an important supplement to optical images and has strong application potential in change detection. At present, the mining and utilization of SAR image timing information is not enough, and there are still some problems in the fusion of amplitude feature and coherence information. Therefore, it is of great significance to integrate the amplitude and coherence characteristics of multi-temporal SAR images to realize the change detection of urban buildings for the development of urban planning statistics. On the basis of LT-1 data, this study proposes an urban building change detection algorithm that combines multitemporal SAR amplitude and coherence information. The algorithm uses building recognition, color model conversion, and coherence change constraints to correlate multitemporal image pixel value changes to building changes, thereby obtaining urban building change areas and locating building change periods. Through the conversion of color model, the change characteristics of changing buildings in H component are distinguished, and the color gamut segmentation is classified and discussed to further determine the correspondence between building changes and H component sequences. The algorithm also analyzes the comparative changes of coherence before and after building changes, and obtains the corresponding relationship between building changes and coherence changes. With the amplitude and coherence information, the algorithm can locate the time period of change accurately and the misjudgment area is better eliminated. The local area of Hengqin Town, Zhuhai City, is employed as an example to conduct an experiment, and the results of building change detection in the study area are obtained using five scenes of LT-1 ascending images from June 23, 2023, to November 14, 2023. In addition, combined with the development of Hengqin, the results of building change detection in the northeast and central parts of Hengqin Town are verified against the construction periods of buildings. The findings show that the changes in 19 buildings in eight typical areas are consistent with the construction period of buildings, verifying the reliability of the algorithm. This work reveals the application ability and value of LT-1 data in urban building change detection. These data have a wide application prospect in urban planning and illegal construction investigation.关键词:SAR;building change detection;Amplitude;Color model conversion;coherence242|384|0更新时间:2025-12-30
摘要:Urban building change detection is an important part of land use, resource management, and urban planning. It plays an extremely important role in urban development, housing security and post-disaster reconstruction in earthquake areas. Optical image and SAR image are two commonly used data sources in urban building change detection. Optical images have the advantages of high resolution, high timeliness and convenient visual interpretation in change detection. However, optical images are difficult to use because of the influence of cloud, fog, and rain weather in southern China. SAR satellite is a side-looking imaging, and its imaging signal contains rich surface texture information, which is convenient for change detection and analysis. In SAR images, the change of ground objects can cause the change of amplitude information and coherence characteristics of SAR images, and buildings have certain imaging characteristics. China’s self-developed LT-1A/1B satellite has the advantages of high resolution, short return period, multipolarization, and all-day, all-weather operation. It can be used as an important supplement to optical images and has strong application potential in change detection. At present, the mining and utilization of SAR image timing information is not enough, and there are still some problems in the fusion of amplitude feature and coherence information. Therefore, it is of great significance to integrate the amplitude and coherence characteristics of multi-temporal SAR images to realize the change detection of urban buildings for the development of urban planning statistics. On the basis of LT-1 data, this study proposes an urban building change detection algorithm that combines multitemporal SAR amplitude and coherence information. The algorithm uses building recognition, color model conversion, and coherence change constraints to correlate multitemporal image pixel value changes to building changes, thereby obtaining urban building change areas and locating building change periods. Through the conversion of color model, the change characteristics of changing buildings in H component are distinguished, and the color gamut segmentation is classified and discussed to further determine the correspondence between building changes and H component sequences. The algorithm also analyzes the comparative changes of coherence before and after building changes, and obtains the corresponding relationship between building changes and coherence changes. With the amplitude and coherence information, the algorithm can locate the time period of change accurately and the misjudgment area is better eliminated. The local area of Hengqin Town, Zhuhai City, is employed as an example to conduct an experiment, and the results of building change detection in the study area are obtained using five scenes of LT-1 ascending images from June 23, 2023, to November 14, 2023. In addition, combined with the development of Hengqin, the results of building change detection in the northeast and central parts of Hengqin Town are verified against the construction periods of buildings. The findings show that the changes in 19 buildings in eight typical areas are consistent with the construction period of buildings, verifying the reliability of the algorithm. This work reveals the application ability and value of LT-1 data in urban building change detection. These data have a wide application prospect in urban planning and illegal construction investigation.关键词:SAR;building change detection;Amplitude;Color model conversion;coherence242|384|0更新时间:2025-12-30
ApplicationsofLuTan-1InterferometricSARSystem
- “海岸带遥感技术,全面监测资源生态环境,分析国内外研究现状,探讨科学技术问题,明确机遇挑战,为未来发展提供参考。”
 摘要:The coastal zone is an ecologically crucial zone where land and ocean interact, collecting a considerable amount of matter and energy. However, this area is currently facing unprecedented challenges due to intensified human activities, global climate change, and species invasion. Remote sensing science and technology provide effective means for the comprehensive and systematic monitoring of coastal zone resources, ecosystems, and environmental conditions. However, our understanding of key scientific issues relative to remote sensing applications in coastal zones remains unclear. Several issues and challenges are encountered in the design of remote sensing sensors, the interaction mechanisms between electromagnetic waves and surface objects, remote sensing data processing and information extraction, quantitative retrieval of ecological parameters, and the cross-application of remote sensing across various fields of coastal zones. Considering the uniqueness of coastal zones and the advantages of remote sensing technology, this paper analyzes the current status of domestic and foreign research on coastal remote sensing, using data from the Web of Science and CNKI databases. It explores the scientific and technological issues in coastal remote sensing, summarizes research progress, identifies opportunities and challenges, and discusses potential future development directions. Results show the following: (1) Considering the characteristics of high spatial and temporal heterogeneity, changing climate, and complex surface factors in the coastal zone, developing a new generation of remote sensing payloads is necessary. These payloads should feature specific spectral characteristics, observation modes, orbital modes, and orbital inclinations to provide support for large-scale, high-frequency monitoring and fine-scale detection of natural resources in the coastal zone. (2) Aiming to accurately analyze the physical and optical characteristics of the coastal zone environment, geoscience big data is integrated with numerical simulation technology to develop precise models of the scattering and absorption characteristics of atmospheric and marine materials and clarify radiation transmission process across the atmosphere-land-water interface. (3) Comprehensive methods should be developed to improve remote sensing image quality under complex coastal zone imaging conditions. through remote sensing AI model and cloud computing technology, to achieve high-precision and intelligent extraction of remote sensing information across the entire coastal zone. (4) Existing radiation transfer, light energy utilization, and process models should be optimized to analyze the radiation transfer mechanisms of coastal surface elements. A “mechanism-data” dual-driven quantitative inversion model of surface parameters, powered by an opportunistic AI model, is introduced to address inversion accuracy errors caused by differences in the radiation characteristics of multi-source sensors, as well inconsistencies in observation angles and observation times. (5) The cross-application of land-sea integration, ecological restoration, and disaster prevention and reduction in coastal zones has seen marked advancements, promoting deeper interdisciplinary integration and contributing to the development of a more comprehensive scientific and technological system. This paper can serve as a reference for understanding the key scientific challenges in coastal remote sensing and for identifying future directions in its development.关键词:remote sensing of coastal zone;scientific issues;design of sensors;interaction between ground objects and electromagnetic waves;information extraction;quantitative inversion of remote sensing parameters;practice of interdisciplinary;challenge and opportunity796|2487|0更新时间:2025-12-30
摘要:The coastal zone is an ecologically crucial zone where land and ocean interact, collecting a considerable amount of matter and energy. However, this area is currently facing unprecedented challenges due to intensified human activities, global climate change, and species invasion. Remote sensing science and technology provide effective means for the comprehensive and systematic monitoring of coastal zone resources, ecosystems, and environmental conditions. However, our understanding of key scientific issues relative to remote sensing applications in coastal zones remains unclear. Several issues and challenges are encountered in the design of remote sensing sensors, the interaction mechanisms between electromagnetic waves and surface objects, remote sensing data processing and information extraction, quantitative retrieval of ecological parameters, and the cross-application of remote sensing across various fields of coastal zones. Considering the uniqueness of coastal zones and the advantages of remote sensing technology, this paper analyzes the current status of domestic and foreign research on coastal remote sensing, using data from the Web of Science and CNKI databases. It explores the scientific and technological issues in coastal remote sensing, summarizes research progress, identifies opportunities and challenges, and discusses potential future development directions. Results show the following: (1) Considering the characteristics of high spatial and temporal heterogeneity, changing climate, and complex surface factors in the coastal zone, developing a new generation of remote sensing payloads is necessary. These payloads should feature specific spectral characteristics, observation modes, orbital modes, and orbital inclinations to provide support for large-scale, high-frequency monitoring and fine-scale detection of natural resources in the coastal zone. (2) Aiming to accurately analyze the physical and optical characteristics of the coastal zone environment, geoscience big data is integrated with numerical simulation technology to develop precise models of the scattering and absorption characteristics of atmospheric and marine materials and clarify radiation transmission process across the atmosphere-land-water interface. (3) Comprehensive methods should be developed to improve remote sensing image quality under complex coastal zone imaging conditions. through remote sensing AI model and cloud computing technology, to achieve high-precision and intelligent extraction of remote sensing information across the entire coastal zone. (4) Existing radiation transfer, light energy utilization, and process models should be optimized to analyze the radiation transfer mechanisms of coastal surface elements. A “mechanism-data” dual-driven quantitative inversion model of surface parameters, powered by an opportunistic AI model, is introduced to address inversion accuracy errors caused by differences in the radiation characteristics of multi-source sensors, as well inconsistencies in observation angles and observation times. (5) The cross-application of land-sea integration, ecological restoration, and disaster prevention and reduction in coastal zones has seen marked advancements, promoting deeper interdisciplinary integration and contributing to the development of a more comprehensive scientific and technological system. This paper can serve as a reference for understanding the key scientific challenges in coastal remote sensing and for identifying future directions in its development.关键词:remote sensing of coastal zone;scientific issues;design of sensors;interaction between ground objects and electromagnetic waves;information extraction;quantitative inversion of remote sensing parameters;practice of interdisciplinary;challenge and opportunity796|2487|0更新时间:2025-12-30 - “在海岸带遥感领域,AI技术与深度学习模型的结合,推动了水淹监测、水边线提取等应用的发展,为解决实际问题提供新方案。”
 摘要:Over the past four decades, remote sensing technology has made remarkable progress, leading to unprecedented resolution and coverage in coastal zone observations, and ushering in the era of big data. However, when addressing practical challenges, a major issue lies in the effective processing and accurate analysis of large-scale coastal remote sensing data. Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly developed in recent years, leading to the emergence of numerous Deep Learning (DL) models and their extensive application in big data analytics and real-world problem solving. The integration of AI with coastal remote sensing has driven progress in various application fields, introducing considerable value and benefits to society.This paper reviews major AI-driven advancements in coastal zone remote sensing, placing emphasis on model efficiency for coastal flood monitoring, waterline extraction, raft aquaculture zone management, green tide monitoring, and coastal wetland monitoring. For instance, AI algorithms can process Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data in real time to assess flood extent. Thus, these models can accurately detect inundated areas and track their progression, offering timely information to support emergency response efforts.The article highlights waterline extraction as another crucial application of AI in coastal zone remote sensing. Aiming to achieve accurate and automated waterline delineation, AI-based algorithms can efficiently analyze large volumes of remote sensing data. They are especially effective in complex coastal environments, facilitating the detection of subtle changes in dynamic shorelines. Through the integration of multi-source data, AI also enables real-time monitoring and forecasting of coastal erosion, supporting effective coastal management and protection.AI has also demonstrated remarkable potential in monitoring the distribution and temporal dynamics of raft aquaculture zones, contributing to highly efficient resource management. Deep learning models can accurately outline aquaculture boundaries and monitor water quality and facility conditions. Thus, AI enhances aquaculture oversight, optimizes resource allocation, and helps mitigate environmental pressures by leveraging remote sensing data and real-time analytics.Moreover, AI plays a crucial role in green tide monitoring. Through spectral analysis, deep learning algorithms enable the rapid detection of algal bloom regions and mapping of their spatial spread with high precision, even under large-scale, data-intensive conditions. These capabilities support timely environmental assessments and the development of early warning systems to reduce ecological risks.In coastal wetland monitoring, AI enables rapid classification and change detection using multi-sensor and multi-temporal observations. Deep learning models help effectively track wetland dynamics, evaluate ecosystem health, and identify degradation patterns, thereby supporting biodiversity conservation and ecological restoration planning.Finally, this review outlines future directions for AI in terms of coastal remote sensing. With continuous advancements in computational capacity and algorithm design, AI applications are also expected to become highly accurate, scalable, and indispensable. They can offer critical support for addressing climate change, coastal erosion, and sustainable coastal management challenges.关键词:Coastal Zone Remote Sensing;artificial intelligence;image processing;Flood Monitoring;Waterline Delineation;Raft Aquaculture Zone Monitoring;Green Tide Detection;Coastal Wetland Monitoring341|710|0更新时间:2025-12-30
摘要:Over the past four decades, remote sensing technology has made remarkable progress, leading to unprecedented resolution and coverage in coastal zone observations, and ushering in the era of big data. However, when addressing practical challenges, a major issue lies in the effective processing and accurate analysis of large-scale coastal remote sensing data. Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly developed in recent years, leading to the emergence of numerous Deep Learning (DL) models and their extensive application in big data analytics and real-world problem solving. The integration of AI with coastal remote sensing has driven progress in various application fields, introducing considerable value and benefits to society.This paper reviews major AI-driven advancements in coastal zone remote sensing, placing emphasis on model efficiency for coastal flood monitoring, waterline extraction, raft aquaculture zone management, green tide monitoring, and coastal wetland monitoring. For instance, AI algorithms can process Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data in real time to assess flood extent. Thus, these models can accurately detect inundated areas and track their progression, offering timely information to support emergency response efforts.The article highlights waterline extraction as another crucial application of AI in coastal zone remote sensing. Aiming to achieve accurate and automated waterline delineation, AI-based algorithms can efficiently analyze large volumes of remote sensing data. They are especially effective in complex coastal environments, facilitating the detection of subtle changes in dynamic shorelines. Through the integration of multi-source data, AI also enables real-time monitoring and forecasting of coastal erosion, supporting effective coastal management and protection.AI has also demonstrated remarkable potential in monitoring the distribution and temporal dynamics of raft aquaculture zones, contributing to highly efficient resource management. Deep learning models can accurately outline aquaculture boundaries and monitor water quality and facility conditions. Thus, AI enhances aquaculture oversight, optimizes resource allocation, and helps mitigate environmental pressures by leveraging remote sensing data and real-time analytics.Moreover, AI plays a crucial role in green tide monitoring. Through spectral analysis, deep learning algorithms enable the rapid detection of algal bloom regions and mapping of their spatial spread with high precision, even under large-scale, data-intensive conditions. These capabilities support timely environmental assessments and the development of early warning systems to reduce ecological risks.In coastal wetland monitoring, AI enables rapid classification and change detection using multi-sensor and multi-temporal observations. Deep learning models help effectively track wetland dynamics, evaluate ecosystem health, and identify degradation patterns, thereby supporting biodiversity conservation and ecological restoration planning.Finally, this review outlines future directions for AI in terms of coastal remote sensing. With continuous advancements in computational capacity and algorithm design, AI applications are also expected to become highly accurate, scalable, and indispensable. They can offer critical support for addressing climate change, coastal erosion, and sustainable coastal management challenges.关键词:Coastal Zone Remote Sensing;artificial intelligence;image processing;Flood Monitoring;Waterline Delineation;Raft Aquaculture Zone Monitoring;Green Tide Detection;Coastal Wetland Monitoring341|710|0更新时间:2025-12-30 - “在滨海湿地生态保护领域,专家提出了基于卫星影像的互花米草清除状态和治理方式识别方法,为湿地管理决策提供重要参考。”
 摘要:Controlling the invasive plant Spartina alterniflora is a crucial aspect of ecological protection and restoration in coastal wetlands in China. Over the past decades, S. alterniflora has rapidly colonized tidal flats and estuarine areas, and led to a remarkable decline in biodiversity, degradation of wetland ecosystem services, and caused increased challenges for coastal management. Multiple coastal provinces in China are currently implementing S. alterniflora control projects, adopting methods such as physical removal and chemical control. The former is effective but prone to recurrence, while the latter is cost-effective but may have negative environmental impacts. Timely monitoring of S. alterniflora control dynamics and identification of the control methods are crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of control projects and assessing their environmental impacts. This study focuses on the S. alterniflora area in the coastal wetlands of Zhejiang and Shanghai and aims to introduce a method based on time-series optical satellite imagery to identify the removal status and control methods (unremoved/physical removal/chemical control) of S. alterniflora and estimate the dates of physical removal.A novel framework based on dense time-series optical satellite imagery (Sentinel-2 MSI and Landsat 8 OLI) is proposed. Specifically, a time-series spectral index dataset was constructed through the fusion of Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8 observations, followed by cloud masking and spectral harmonization to ensure consistency. First, periods that are affected by control measures were identified using a sliding window combined with a rule-based decision approach, and unremoved pixels were separated from those experiencing removal. Subsequently, a random forest classifier was trained using field survey data and high-resolution validation imagery to distinguish physical removal from chemical control. The exact removal dates for physically removed areas were further estimated by analyzing rapid decline in vegetation indexes, including NDVI, EVI, and LSWI, as well as abrupt increments in DFI.The results indicate that this method achieved high classification accuracy for control status and control method classification, revealing an overall accuracy of 98.8% and a Kappa coefficient of 0.979. The Mean Absolute Error of estimated physical removal dates was only 3.91 days, and date recognition accuracy was 93.67%. Spatial analysis revealed substantial differences between regions: in 2023, Shanghai achieved a removal rate of 4.2%, with nearly equal proportions of physical and chemical control, while Zhejiang achieved a substantially higher removal rate of 62.7%, dominated by physical removal operations.The proposed framework not only provides a reliable means of tracking S. alterniflora control projects but also facilitates differentiation of control strategies at regional scales. Such information is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of invasive species control, supporting ecological restoration planning, and minimizing unintended environmental impacts. Furthermore, the methodology is scalable and can be extended to other coastal provinces or adapted for monitoring different invasive species across various environmental conditions.关键词:optical remote sensing;species invasion;time series analysis;wetland restoration;vegetation dynamic229|517|0更新时间:2025-12-30
摘要:Controlling the invasive plant Spartina alterniflora is a crucial aspect of ecological protection and restoration in coastal wetlands in China. Over the past decades, S. alterniflora has rapidly colonized tidal flats and estuarine areas, and led to a remarkable decline in biodiversity, degradation of wetland ecosystem services, and caused increased challenges for coastal management. Multiple coastal provinces in China are currently implementing S. alterniflora control projects, adopting methods such as physical removal and chemical control. The former is effective but prone to recurrence, while the latter is cost-effective but may have negative environmental impacts. Timely monitoring of S. alterniflora control dynamics and identification of the control methods are crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of control projects and assessing their environmental impacts. This study focuses on the S. alterniflora area in the coastal wetlands of Zhejiang and Shanghai and aims to introduce a method based on time-series optical satellite imagery to identify the removal status and control methods (unremoved/physical removal/chemical control) of S. alterniflora and estimate the dates of physical removal.A novel framework based on dense time-series optical satellite imagery (Sentinel-2 MSI and Landsat 8 OLI) is proposed. Specifically, a time-series spectral index dataset was constructed through the fusion of Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8 observations, followed by cloud masking and spectral harmonization to ensure consistency. First, periods that are affected by control measures were identified using a sliding window combined with a rule-based decision approach, and unremoved pixels were separated from those experiencing removal. Subsequently, a random forest classifier was trained using field survey data and high-resolution validation imagery to distinguish physical removal from chemical control. The exact removal dates for physically removed areas were further estimated by analyzing rapid decline in vegetation indexes, including NDVI, EVI, and LSWI, as well as abrupt increments in DFI.The results indicate that this method achieved high classification accuracy for control status and control method classification, revealing an overall accuracy of 98.8% and a Kappa coefficient of 0.979. The Mean Absolute Error of estimated physical removal dates was only 3.91 days, and date recognition accuracy was 93.67%. Spatial analysis revealed substantial differences between regions: in 2023, Shanghai achieved a removal rate of 4.2%, with nearly equal proportions of physical and chemical control, while Zhejiang achieved a substantially higher removal rate of 62.7%, dominated by physical removal operations.The proposed framework not only provides a reliable means of tracking S. alterniflora control projects but also facilitates differentiation of control strategies at regional scales. Such information is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of invasive species control, supporting ecological restoration planning, and minimizing unintended environmental impacts. Furthermore, the methodology is scalable and can be extended to other coastal provinces or adapted for monitoring different invasive species across various environmental conditions.关键词:optical remote sensing;species invasion;time series analysis;wetland restoration;vegetation dynamic229|517|0更新时间:2025-12-30 - “桂林会仙喀斯特湿地研究取得新进展,基于LiDAR点云语义分割的3D植被制图分析方法为湿地生态保护和管理提供新手段。”
 摘要:As a critical link between terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, wetlands provide essential ecological services and are vital for biodiversity conservation. However, the complex vertical layering of vegetation and unique hydrological conditions in karst wetlands pose remarkable challenges for effective vegetation distribution monitoring, thereby limiting deeper insights into wetland ecology. Aiming to address this issue, this paper proposes and implements a 3D vegetation mapping and analysis method based on LiDAR point cloud semantic segmentation, using the Huixian Karst Wetland of International Importance in Guilin, China, as the study area. This method adopts a deep learning point cloud semantic segmentation algorithm, DWS-KP-FCNN, to perform detailed 3D mapping of wetland vegetation. Several post-processing methods are applied to refine the 3D mapping results and improve their quantification potential. Based on the 3D vegetation map, the proposed method quantifies the volume distribution, proximity to water, and inundation frequency of each vegetation type, revealing the relationship between vegetation distribution and wetland hydrology. Results of the study reveal the following: (1) The deep learning algorithm, DWS-KP-FCNN, accurately identifies and classifies various vegetation types from LiDAR point clouds, effectively addressing challenges such as vegetation overlap and water body detection through post-processing techniques. Thus, this algorithm ultimately produces fine-grained high-precision 3D vegetation distribution maps. (2) Using the 3D vegetation distribution map, a quantitative analysis of vegetation volume, proximity to water, and inundation frequency reveals clear distribution patterns along the hydrological gradient. These patterns include vegetation clustering, mutual shading, optimal proximity to water, inundation frequency ranges, and the sensitivity of vegetation to hydrological changes. (3) Using a hierarchical clustering algorithm, the study area is divided into zones featuring distinct vegetation patterns based on proximity to water and inundation frequency. In shallow and near-water areas, karst wetland endemics, such as some bamboo and shrub species, are dominant, contributing to high species diversity and ecological value. Conversely, deeper zones reveal dense populations of invasive species such as water hyacinth, thereby posing potential management challenges that require effective control measures. These findings emphasize variations in vegetation communities across hydrological environments and provide valuable data for targeted wetland ecosystem management.Overall, the 3D vegetation mapping method, based on LiDAR point cloud semantic segmentation, offers an efficient, accurate, and comprehensive remote sensing approach for monitoring vegetation in karst wetlands, offering substantial benefits for ecological protection and management.关键词:karst wetland;UAV LiDAR;3D vegetation mapping;point cloud semantic segmentation;deep learning;vegetation distribution pattern46|22|0更新时间:2025-12-30
摘要:As a critical link between terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, wetlands provide essential ecological services and are vital for biodiversity conservation. However, the complex vertical layering of vegetation and unique hydrological conditions in karst wetlands pose remarkable challenges for effective vegetation distribution monitoring, thereby limiting deeper insights into wetland ecology. Aiming to address this issue, this paper proposes and implements a 3D vegetation mapping and analysis method based on LiDAR point cloud semantic segmentation, using the Huixian Karst Wetland of International Importance in Guilin, China, as the study area. This method adopts a deep learning point cloud semantic segmentation algorithm, DWS-KP-FCNN, to perform detailed 3D mapping of wetland vegetation. Several post-processing methods are applied to refine the 3D mapping results and improve their quantification potential. Based on the 3D vegetation map, the proposed method quantifies the volume distribution, proximity to water, and inundation frequency of each vegetation type, revealing the relationship between vegetation distribution and wetland hydrology. Results of the study reveal the following: (1) The deep learning algorithm, DWS-KP-FCNN, accurately identifies and classifies various vegetation types from LiDAR point clouds, effectively addressing challenges such as vegetation overlap and water body detection through post-processing techniques. Thus, this algorithm ultimately produces fine-grained high-precision 3D vegetation distribution maps. (2) Using the 3D vegetation distribution map, a quantitative analysis of vegetation volume, proximity to water, and inundation frequency reveals clear distribution patterns along the hydrological gradient. These patterns include vegetation clustering, mutual shading, optimal proximity to water, inundation frequency ranges, and the sensitivity of vegetation to hydrological changes. (3) Using a hierarchical clustering algorithm, the study area is divided into zones featuring distinct vegetation patterns based on proximity to water and inundation frequency. In shallow and near-water areas, karst wetland endemics, such as some bamboo and shrub species, are dominant, contributing to high species diversity and ecological value. Conversely, deeper zones reveal dense populations of invasive species such as water hyacinth, thereby posing potential management challenges that require effective control measures. These findings emphasize variations in vegetation communities across hydrological environments and provide valuable data for targeted wetland ecosystem management.Overall, the 3D vegetation mapping method, based on LiDAR point cloud semantic segmentation, offers an efficient, accurate, and comprehensive remote sensing approach for monitoring vegetation in karst wetlands, offering substantial benefits for ecological protection and management.关键词:karst wetland;UAV LiDAR;3D vegetation mapping;point cloud semantic segmentation;deep learning;vegetation distribution pattern46|22|0更新时间:2025-12-30 - “在海陆交接区域,记者报道了一种基于机载海洋激光雷达的海陆混合波形识别方法,为提取水边线位置提供新途径。”
 摘要:Ocean-Land Interfaces (OLIs) are instantaneous boundaries between fluctuating ocean surfaces and land and provide fundamental information for scientific research on ocean hydrology, ocean-land resource management, and sea level rise. However, detecting OLIs with high accuracy and resolution in automated manners is a challenging task. Airborne oceanic LiDARs (AOLs) are high-resolution, efficient, and flexible measurement systems that can be used for integrated ocean and land measurements. In areas where the ocean meets land, both ocean and land may exist in the laser spot of AOL, resulting in mixed ocean-land waveforms. If these mixed waveforms can be accurately identified, they can be used to detect the precise location of the ocean-land interface.Considering the existence of mixed ocean-land waveforms, a mixed waveform method based on AOL mixed ocean-land waveforms is proposed for ocean-land interface determination in this paper. First, the waveform features of the AOL infrared lasers are extracted, and principal component analysis is performed to reduce redundant features. Second, the waveform features are used to classify the AOL waveforms to obtain a membership matrix, and the Otsu method is used to determine the mixed ocean-land waveforms. Third, the DBSCAN algorithm is used to identify and eliminate misclassified mixed waveforms. Fourth, the PAEK algorithm is applied to smooth the laser points corresponding to the mixed ocean-land waveforms and output the ocean-land interface. Finally, the expression of the infrared laser-radar equation for mixed ocean and land is provided, and a method combining theoretical analysis and measured data verification is used to analyze the differences between ocean, land, and mixed ocean and land waveforms.The correctness and effectiveness of the methods proposed in this paper were verified via raw AOL datasets collected by the Optech CZMIL system. Compared with the traditional AOL elevation threshold method, the proposed AOL mixed waveform method reduced the mean and standard deviation of the ocean-land interface bias by 24.07% and 9.76%, respectively, and improved the SSIM index by 0.031, providing a new approach for detecting the ocean-land interface on tidal flats via AOL.The coexistence of water and land within AOL laser spots generates mixed ocean-land waveforms, and identifying these mixed waveforms has important theoretical and practical value. This study proposes an identification method for infrared laser mixed waveforms based on waveform fuzzy classification and Otsu threshold determination and an ocean-land interface extraction method using those identified mixed waveforms. Furthermore, this study extends the laser-radar equation by proposing an infrared laser-radar equation for infrared laser interactions with mixed ocean and land, providing a theoretical basis for studying mixed infrared laser waveforms. On the basis of this equation, a differential analysis was conducted on the ocean, land, and mixed ocean-land waveforms. The correctness and practicality of the infrared laser-radar equation for mixed ocean and land were verified via visualization analysis results of raw waveform data.关键词:Airborne oceanic LiDAR;infrared laser;ocean-land waveform classification;mixed ocean-land waveform;ocean-land interface295|471|0更新时间:2025-12-30
摘要:Ocean-Land Interfaces (OLIs) are instantaneous boundaries between fluctuating ocean surfaces and land and provide fundamental information for scientific research on ocean hydrology, ocean-land resource management, and sea level rise. However, detecting OLIs with high accuracy and resolution in automated manners is a challenging task. Airborne oceanic LiDARs (AOLs) are high-resolution, efficient, and flexible measurement systems that can be used for integrated ocean and land measurements. In areas where the ocean meets land, both ocean and land may exist in the laser spot of AOL, resulting in mixed ocean-land waveforms. If these mixed waveforms can be accurately identified, they can be used to detect the precise location of the ocean-land interface.Considering the existence of mixed ocean-land waveforms, a mixed waveform method based on AOL mixed ocean-land waveforms is proposed for ocean-land interface determination in this paper. First, the waveform features of the AOL infrared lasers are extracted, and principal component analysis is performed to reduce redundant features. Second, the waveform features are used to classify the AOL waveforms to obtain a membership matrix, and the Otsu method is used to determine the mixed ocean-land waveforms. Third, the DBSCAN algorithm is used to identify and eliminate misclassified mixed waveforms. Fourth, the PAEK algorithm is applied to smooth the laser points corresponding to the mixed ocean-land waveforms and output the ocean-land interface. Finally, the expression of the infrared laser-radar equation for mixed ocean and land is provided, and a method combining theoretical analysis and measured data verification is used to analyze the differences between ocean, land, and mixed ocean and land waveforms.The correctness and effectiveness of the methods proposed in this paper were verified via raw AOL datasets collected by the Optech CZMIL system. Compared with the traditional AOL elevation threshold method, the proposed AOL mixed waveform method reduced the mean and standard deviation of the ocean-land interface bias by 24.07% and 9.76%, respectively, and improved the SSIM index by 0.031, providing a new approach for detecting the ocean-land interface on tidal flats via AOL.The coexistence of water and land within AOL laser spots generates mixed ocean-land waveforms, and identifying these mixed waveforms has important theoretical and practical value. This study proposes an identification method for infrared laser mixed waveforms based on waveform fuzzy classification and Otsu threshold determination and an ocean-land interface extraction method using those identified mixed waveforms. Furthermore, this study extends the laser-radar equation by proposing an infrared laser-radar equation for infrared laser interactions with mixed ocean and land, providing a theoretical basis for studying mixed infrared laser waveforms. On the basis of this equation, a differential analysis was conducted on the ocean, land, and mixed ocean-land waveforms. The correctness and practicality of the infrared laser-radar equation for mixed ocean and land were verified via visualization analysis results of raw waveform data.关键词:Airborne oceanic LiDAR;infrared laser;ocean-land waveform classification;mixed ocean-land waveform;ocean-land interface295|471|0更新时间:2025-12-30 - “本报道介绍了黄河口湿地盐沼物候监测的研究进展,专家采用面向对象方法,有效降低了高分辨率遥感影像的椒盐噪声,为盐沼湿地高分辨率物候提取提供解决方案。”
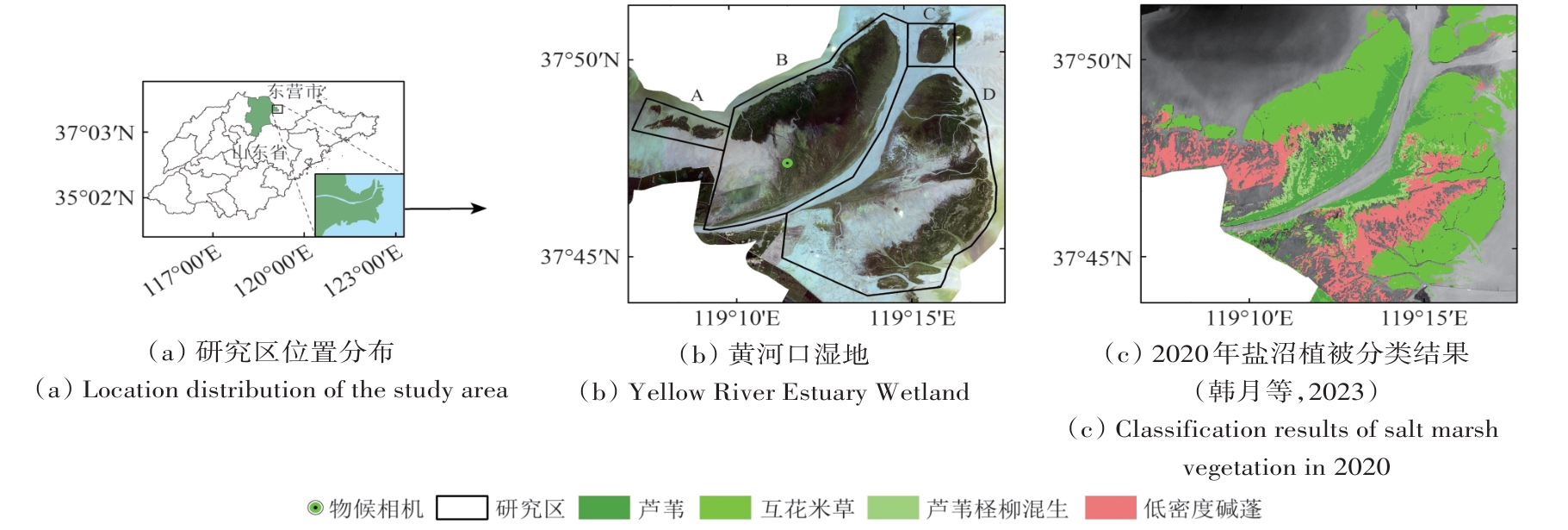 摘要:Accurate monitoring of salt marsh vegetation phenology is crucial for understanding the carbon cycle in “blue carbon” ecosystems. High spatiotemporal resolution satellite remote sensing technology facilitates detailed monitoring of vegetation phenology; however, the presence of “salt-and-pepper” noise is an inevitable challenge. This study focuses on the Yellow River Estuary Wetland and adopts an object-oriented method combined with high-resolution remote sensing data to investigate coastal salt marsh phenology. First, multiscale segmentation is applied to Jilin-1 images to extract salt marsh vegetation objects, serving as basic units for phenological parameter extraction. Using time-series NDVI from PlanetScope images, phenological parameters, including the start date of the growing season (SOS), end date of the growing season (EOS), and length of the growing season (LOS), are extracted using S–G(Savitzky-Golay) filtering, a double-logistic model, and dynamic thresholding methods. Results are assessed from the following three aspects: (1) the fitting accuracy of the time-series NDVI, (2) the spatial heterogeneity of the extracted phenological parameters, and (3) consistency with observations from a phenological camera. Results indicate the following: (1) Compared to pixel-based approaches, the object-based time-series NDVI fitting achieves lower root mean square error (RMSE), mean absolute error (MAE), and mean absolute percentage error (MAPE). Specifically, the area with RMSE<0.05, MAPE<15%, and MAE<0.035 increased by 11.46%, 12.93%, and 10.72%, respectively, demonstrating improved fitting accuracy at the object scale. (2) The extracted phenological parameters are similar for object- and pixel-based approaches, which capture the spatial heterogeneity of salt marsh vegetation phenology. Conversely, object-based parameters are spatially smoother, mitigating the small-scale variability in pixel-level phenological parameters. Spatial heterogeneity analysis through semi-variogram functions reveals substantially lower nugget (C0) and partial sill (C) values for object-based parameters than those for pixel-based parameters. (3) Object-based phenological parameters exhibit a high degree of consistency with those obtained from the phenological camera (with SOS matching exactly, and EOS and LOS differing by only one day), whereas pixel-level parameters exhibit remarkable variations. This study reveals that object-oriented image analysis effectively reduces salt-and-pepper noise in high-resolution remote sensing images and holds strong potential for high-resolution phenology extraction in salt marsh wetlands.关键词:Saltmarsh wetlands;phenology;Jilin-1;PlanetScope;high resolution316|673|0更新时间:2025-12-30
摘要:Accurate monitoring of salt marsh vegetation phenology is crucial for understanding the carbon cycle in “blue carbon” ecosystems. High spatiotemporal resolution satellite remote sensing technology facilitates detailed monitoring of vegetation phenology; however, the presence of “salt-and-pepper” noise is an inevitable challenge. This study focuses on the Yellow River Estuary Wetland and adopts an object-oriented method combined with high-resolution remote sensing data to investigate coastal salt marsh phenology. First, multiscale segmentation is applied to Jilin-1 images to extract salt marsh vegetation objects, serving as basic units for phenological parameter extraction. Using time-series NDVI from PlanetScope images, phenological parameters, including the start date of the growing season (SOS), end date of the growing season (EOS), and length of the growing season (LOS), are extracted using S–G(Savitzky-Golay) filtering, a double-logistic model, and dynamic thresholding methods. Results are assessed from the following three aspects: (1) the fitting accuracy of the time-series NDVI, (2) the spatial heterogeneity of the extracted phenological parameters, and (3) consistency with observations from a phenological camera. Results indicate the following: (1) Compared to pixel-based approaches, the object-based time-series NDVI fitting achieves lower root mean square error (RMSE), mean absolute error (MAE), and mean absolute percentage error (MAPE). Specifically, the area with RMSE<0.05, MAPE<15%, and MAE<0.035 increased by 11.46%, 12.93%, and 10.72%, respectively, demonstrating improved fitting accuracy at the object scale. (2) The extracted phenological parameters are similar for object- and pixel-based approaches, which capture the spatial heterogeneity of salt marsh vegetation phenology. Conversely, object-based parameters are spatially smoother, mitigating the small-scale variability in pixel-level phenological parameters. Spatial heterogeneity analysis through semi-variogram functions reveals substantially lower nugget (C0) and partial sill (C) values for object-based parameters than those for pixel-based parameters. (3) Object-based phenological parameters exhibit a high degree of consistency with those obtained from the phenological camera (with SOS matching exactly, and EOS and LOS differing by only one day), whereas pixel-level parameters exhibit remarkable variations. This study reveals that object-oriented image analysis effectively reduces salt-and-pepper noise in high-resolution remote sensing images and holds strong potential for high-resolution phenology extraction in salt marsh wetlands.关键词:Saltmarsh wetlands;phenology;Jilin-1;PlanetScope;high resolution316|673|0更新时间:2025-12-30 - “最新研究揭示长岛植被固碳量变化特征,为“零碳岛”建设提供理论依据。”
 摘要:Islands feature unique geographical characteristics and distinct ecosystems. Analyzing the temporal dynamics of carbon sequestration in island ecosystems is critical for supporting the development of low-carbon and ecological islands. This study uses GF-1 and Sentinel-2 multispectral satellite imagery to classify vegetation types across the Changdao Archipelago. Combined with topographic and geomorphological subdivision data, these datasets were analyzed using a carbon sequestration rate approach to quantify vegetation carbon storage capacity during 2015—2022. The methodology further examines spatiotemporal change patterns, identifies the drivers behind vegetation carbon sink enhancement, and evaluates the potential for afforestation-induced carbon sequestration. Results show the following: (1) From 2015 to 2022, vegetation coverage in Changdao exhibited an overall declining trend. Areas dominated by pure Pinusthunbergii stands and mixed forests decreased, while pure Robinia pseudoacacia stands and shrublands increased. In the southern area of the North Five Islands, vegetation coverage declined substantially, demonstrating the transition of extensive shrublands to non-forest grasslands, which represents a primary form of vegetation degradation. (2) Interannual vegetation carbon sequestration in Changdao showed a fluctuating but increasing trend, revealing a “multicore growth and banded weakening” spatial pattern. Substantial north-south differences were observed in the inflection points of vegetation carbon sequestration across islands. “Stable zones” of vegetation carbon sequestration exhibited continuous enhancement, with key sequestration inflection points occurring in 2016 and 2019. Additionally, vegetation carbon sequestration demonstrated notable variations with elevation and slope gradients. (3) Key factors that influence carbon sequestration variation included the spread of pine wilt disease, extreme climate events, drought stress, and tree aging. The afforestation suitability index across Changdao ranged from 17.96 to 81.98, with the North Five Islands identified as the priority area for afforestation efforts. This study provides theoretical and empirical support for the development of Changdao as a “zero-carbon island.”关键词:island city;vegetation types;Carbon sequestration;Carbon sink enhancement potential;Changdao31|26|0更新时间:2025-12-30
摘要:Islands feature unique geographical characteristics and distinct ecosystems. Analyzing the temporal dynamics of carbon sequestration in island ecosystems is critical for supporting the development of low-carbon and ecological islands. This study uses GF-1 and Sentinel-2 multispectral satellite imagery to classify vegetation types across the Changdao Archipelago. Combined with topographic and geomorphological subdivision data, these datasets were analyzed using a carbon sequestration rate approach to quantify vegetation carbon storage capacity during 2015—2022. The methodology further examines spatiotemporal change patterns, identifies the drivers behind vegetation carbon sink enhancement, and evaluates the potential for afforestation-induced carbon sequestration. Results show the following: (1) From 2015 to 2022, vegetation coverage in Changdao exhibited an overall declining trend. Areas dominated by pure Pinusthunbergii stands and mixed forests decreased, while pure Robinia pseudoacacia stands and shrublands increased. In the southern area of the North Five Islands, vegetation coverage declined substantially, demonstrating the transition of extensive shrublands to non-forest grasslands, which represents a primary form of vegetation degradation. (2) Interannual vegetation carbon sequestration in Changdao showed a fluctuating but increasing trend, revealing a “multicore growth and banded weakening” spatial pattern. Substantial north-south differences were observed in the inflection points of vegetation carbon sequestration across islands. “Stable zones” of vegetation carbon sequestration exhibited continuous enhancement, with key sequestration inflection points occurring in 2016 and 2019. Additionally, vegetation carbon sequestration demonstrated notable variations with elevation and slope gradients. (3) Key factors that influence carbon sequestration variation included the spread of pine wilt disease, extreme climate events, drought stress, and tree aging. The afforestation suitability index across Changdao ranged from 17.96 to 81.98, with the North Five Islands identified as the priority area for afforestation efforts. This study provides theoretical and empirical support for the development of Changdao as a “zero-carbon island.”关键词:island city;vegetation types;Carbon sequestration;Carbon sink enhancement potential;Changdao31|26|0更新时间:2025-12-30 - “在遥感影像样本生成领域,专家提出了基于样本自动增广与自适应迁移的长时序遥感影像样本生成方法,有效提升了分类效率和样本质量。”
 摘要:Generating samples from long-term remote sensing imagery is crucial for land cover classification, surface change monitoring, and land use pattern analysis. However, traditional supervised classification methods require extensive labeled samples, thereby increasing time and labor costs while limiting classification accuracy and reliability. Aiming to overcome these challenges, this study proposes a generation method for long-term remote sensing imagery samples based on the combination of automatic sample augmentation and adaptive transfer. The objective is to achieve “one-time sample annotation with multiple reuses” to enhance efficiency and applicability in large-scale remote sensing classification tasks.The proposed method comprises two key components sample automatic augmentation and adaptive sample transfer. First, a local clustering algorithm is used to identify potential sample pixels based on spectral similarity, thereby expanding the labeled dataset. Change analysis between bi-temporal remote sensing images is then conducted to identify transferable samples, and a domain similarity rule is adopted to ensure consistency across different temporal images. This approach ensures the effective reuse of sample information from one time period to another, reducing the need for repeated manual annotations. The above steps are integrated into an interactive algorithm, thereby allowing sequential image processing in long-term remote sensing datasets. The proposed method was validated using Landsat 8 OLI time-series imagery of the Hangzhou Bay area, spanning from 2013 to 2022.Experimental results demonstrate the following1) The proposed automatic sample augmentation strategy effectively increases the quantity and quality of training samples, leading to improved classification performance and accuracy. 2) The adaptive sample transfer strategy facilitates successful sample migration across different temporal images, thereby eliminating the need for annual manual labeling and markedly enhancing sample generation efficiency. 3) The proposed approach is also robust across multiple classifiers, including support vector machine and k-Nearest Neighbor, indicating its broad applicability in classification tasks involving remote sensing.The proposed method presents a considerable advancement in long-term remote sensing image classification by successfully supplementing and transferring samples, thereby reducing annotation costs and enhancing classification efficiency. Through the combination of automatic augmentation and adaptive transfer, this approach presents a scalable solution for large-scale, long-term remote sensing image classification, ensuring reliable and cost-effective land cover analysis. The experimental results highlight the effectiveness of the proposed method in enhancing classification accuracy and efficiency, making it a valuable tool for remote sensing applications.关键词:sample generation method;land cover classification;sample automatic augmentation;sample adaptive transfer;Hangzhou Bay;long-term remote sensing imagery43|19|0更新时间:2025-12-30
摘要:Generating samples from long-term remote sensing imagery is crucial for land cover classification, surface change monitoring, and land use pattern analysis. However, traditional supervised classification methods require extensive labeled samples, thereby increasing time and labor costs while limiting classification accuracy and reliability. Aiming to overcome these challenges, this study proposes a generation method for long-term remote sensing imagery samples based on the combination of automatic sample augmentation and adaptive transfer. The objective is to achieve “one-time sample annotation with multiple reuses” to enhance efficiency and applicability in large-scale remote sensing classification tasks.The proposed method comprises two key components sample automatic augmentation and adaptive sample transfer. First, a local clustering algorithm is used to identify potential sample pixels based on spectral similarity, thereby expanding the labeled dataset. Change analysis between bi-temporal remote sensing images is then conducted to identify transferable samples, and a domain similarity rule is adopted to ensure consistency across different temporal images. This approach ensures the effective reuse of sample information from one time period to another, reducing the need for repeated manual annotations. The above steps are integrated into an interactive algorithm, thereby allowing sequential image processing in long-term remote sensing datasets. The proposed method was validated using Landsat 8 OLI time-series imagery of the Hangzhou Bay area, spanning from 2013 to 2022.Experimental results demonstrate the following1) The proposed automatic sample augmentation strategy effectively increases the quantity and quality of training samples, leading to improved classification performance and accuracy. 2) The adaptive sample transfer strategy facilitates successful sample migration across different temporal images, thereby eliminating the need for annual manual labeling and markedly enhancing sample generation efficiency. 3) The proposed approach is also robust across multiple classifiers, including support vector machine and k-Nearest Neighbor, indicating its broad applicability in classification tasks involving remote sensing.The proposed method presents a considerable advancement in long-term remote sensing image classification by successfully supplementing and transferring samples, thereby reducing annotation costs and enhancing classification efficiency. Through the combination of automatic augmentation and adaptive transfer, this approach presents a scalable solution for large-scale, long-term remote sensing image classification, ensuring reliable and cost-effective land cover analysis. The experimental results highlight the effectiveness of the proposed method in enhancing classification accuracy and efficiency, making it a valuable tool for remote sensing applications.关键词:sample generation method;land cover classification;sample automatic augmentation;sample adaptive transfer;Hangzhou Bay;long-term remote sensing imagery43|19|0更新时间:2025-12-30
CoastalZoneRemoteSensing
-
Application efficiency of multisource optical remote sensing data for marine oil spill monitoring AI导读
“最新研究进展显示,多源卫星光学遥感数据联合工作能提升中国近海溢油监测效能,为溢油污染精细化监测提供技术支撑。” 摘要:Oil spills are critical targets in marine environmental monitoring. In the process of weathering (e.g., spreading, drifting, emulsification evaporation, and dissolution), oils that spill into the ocean can form various weathered oils and exhibit different visual characteristics, including non-emulsified oil slicks, water-in-oil (WO) emulsions, and oil-in-water (OW) emulsions. Optical remote sensing provides comprehensive spectral signatures and band information for the identification, classification, and quantification of different types of oil spill pollution. Multisource optical satellite monitoring plays a key role in remote sensing of oil spills because single-satellite detection has limitations, such as insufficient spatiotemporal resolution, inadequate spectral band settings, and susceptibility to environmental interference. However, utilizing the advantages of multisource monitoring to improve oil spill detection efficiency remains a challenge. This study builds a comprehensive remote sensing dataset from 2019 to 2023 that includes HY-1 C/D coastal zone imager (CZI), GF-1/6 wide field of view, HJ-2 A/B charge-coupled device wide-field imager, Sentinel-2 multispectral instrument (MSI), Landsat-8 operational land imager, and Aqua/Terra moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer satellites. With the HY-1C/D CZI payload as a benchmark, the detection capabilities, effective data coverage, and quantitative estimation abilities of various satellites are analyzed to clarify the efficiency of multisource satellite optical remote sensing in oil spill monitoring and to extend its application to precise monitoring in offshore China. Results reveal that (1) the key performance parameter for detecting surface oil spills is spatial resolution. A high spatial resolution contributes to the ability to identify small-scale oil spills and distinguish between emulsions. Near-infrared and short-wave infrared bands are crucial for classifying, unmixing, and estimating emulsified oils, such as WO and OW emulsions. (2) The HY-1 C/D satellites have substantially improved the image coverage of China’s offshore oil spill events (achieving coverage twice every three days), and their effective data are over four times that of other optical satellites. (3) Compared with Sentinel-2 MSI data, Chinese satellite data can achieve reliable results in oil spill identification and classification (R2>0.8), but the ability to quantitatively estimate oil spill concentrations is limited because of differences in spectral band settings. The spatial resolution and scale effects of optical remote sensing images can introduce uncertainty in area estimation, and coarse resolutions are prone to bias. Moreover, the case study reveals the spatial and temporal distributions of the oil spill. Multisource satellite optical remote sensing can track oil spill events promptly and produce effective information, thus providing new insights into the assessment and ma关键词:oil spill;emulsified oil;optical remote sensing;HY-1C/D;offshore China;monitoring effectiveness67|16|0更新时间:2025-12-30
摘要:Oil spills are critical targets in marine environmental monitoring. In the process of weathering (e.g., spreading, drifting, emulsification evaporation, and dissolution), oils that spill into the ocean can form various weathered oils and exhibit different visual characteristics, including non-emulsified oil slicks, water-in-oil (WO) emulsions, and oil-in-water (OW) emulsions. Optical remote sensing provides comprehensive spectral signatures and band information for the identification, classification, and quantification of different types of oil spill pollution. Multisource optical satellite monitoring plays a key role in remote sensing of oil spills because single-satellite detection has limitations, such as insufficient spatiotemporal resolution, inadequate spectral band settings, and susceptibility to environmental interference. However, utilizing the advantages of multisource monitoring to improve oil spill detection efficiency remains a challenge. This study builds a comprehensive remote sensing dataset from 2019 to 2023 that includes HY-1 C/D coastal zone imager (CZI), GF-1/6 wide field of view, HJ-2 A/B charge-coupled device wide-field imager, Sentinel-2 multispectral instrument (MSI), Landsat-8 operational land imager, and Aqua/Terra moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer satellites. With the HY-1C/D CZI payload as a benchmark, the detection capabilities, effective data coverage, and quantitative estimation abilities of various satellites are analyzed to clarify the efficiency of multisource satellite optical remote sensing in oil spill monitoring and to extend its application to precise monitoring in offshore China. Results reveal that (1) the key performance parameter for detecting surface oil spills is spatial resolution. A high spatial resolution contributes to the ability to identify small-scale oil spills and distinguish between emulsions. Near-infrared and short-wave infrared bands are crucial for classifying, unmixing, and estimating emulsified oils, such as WO and OW emulsions. (2) The HY-1 C/D satellites have substantially improved the image coverage of China’s offshore oil spill events (achieving coverage twice every three days), and their effective data are over four times that of other optical satellites. (3) Compared with Sentinel-2 MSI data, Chinese satellite data can achieve reliable results in oil spill identification and classification (R2>0.8), but the ability to quantitatively estimate oil spill concentrations is limited because of differences in spectral band settings. The spatial resolution and scale effects of optical remote sensing images can introduce uncertainty in area estimation, and coarse resolutions are prone to bias. Moreover, the case study reveals the spatial and temporal distributions of the oil spill. Multisource satellite optical remote sensing can track oil spill events promptly and produce effective information, thus providing new insights into the assessment and ma关键词:oil spill;emulsified oil;optical remote sensing;HY-1C/D;offshore China;monitoring effectiveness67|16|0更新时间:2025-12-30 - “本报道聚焦湖泊富营养化监测,研究了三种营养状态遥感估算方法,为湖泊环境管理提供重要参考。”
 摘要:Lakes are an important part of terrestrial ecosystems. The eutrophication of lakes has become a major ecological and environmental problem in China and even globally, which is one of the key causes of lake ecosystem degradation. Effective monitoring of lake eutrophication provides an important approach to accurately grasping the ecological dynamics of lakes and strictly controlling environmental pollution in lakes. It is of great significance to determine the trophic level and quantify the trophic state of lakes for remote sensing monitoring of lake eutrophication.In this study, we focused on the Trophic State Index (TSI), and evaluated the performance and reliability of three remote sensing methods for trophic state estimation developed for national lakes based on simultaneous field data: Forel-Ule index (FUI), total non-water absorption (atw) and Algal Biomass Index (ABI) on Landsat-8 and Sentinel-3 satellites. The fitting coefficients of the empirical models were corrected based on field data, and the accuracy before and after the algorithm corrections were compared to assess stability. The effects of the surface reflectance products and the remote sensing reflectance corrected by the atmospheric correction algorithms on the TSI inversion were further compared to examine the sensitivity of these algorithms.Our results show that the FUI algorithm has good identification accuracy for eutrophic water bodies with lower requirements for sensor band settings (visible bands). However, it only provides qualitative judgement. The atw algorithm has good identification accuracy for mesotrophic lakes with higher requirements for sensor band settings and atmospheric corrections. The ABI algorithm provides a reliable performance of eutrophication, with good stability of satellite remote sensing data at different levels. The ABI algorithm can figure out different degrees of eutrophic waters, but relies on shortwave infrared for optical classification of water bodies. The ABI algorithm shows the best accuracy with an overall accuracy of 71% and 73% for Landsat-8 and Sentinel-3, respectively, which is better than atw (56% and 63%) and FUI (49% and 52%) algorithm.To sum up, the FUI algorithm is preferred for the qualitative investigation of lake eutrophication to quickly and roughly grasp the trophic level, and the ABI or atw algorithm is further applied for precise quantification. It is recommended to choose one remote sensing evaluation method according to different application scenarios, which can improve the consistency and comparability of lake trophic state assessment. This study can provide an important basis for the future specification of remote sensing monitoring of lake eutrophication.关键词:lake eutrophication;trophic state;Forel-Ule index;total non-water absorption;algal biomass;atmospheric corrections;water classification165|97|0更新时间:2025-12-30
摘要:Lakes are an important part of terrestrial ecosystems. The eutrophication of lakes has become a major ecological and environmental problem in China and even globally, which is one of the key causes of lake ecosystem degradation. Effective monitoring of lake eutrophication provides an important approach to accurately grasping the ecological dynamics of lakes and strictly controlling environmental pollution in lakes. It is of great significance to determine the trophic level and quantify the trophic state of lakes for remote sensing monitoring of lake eutrophication.In this study, we focused on the Trophic State Index (TSI), and evaluated the performance and reliability of three remote sensing methods for trophic state estimation developed for national lakes based on simultaneous field data: Forel-Ule index (FUI), total non-water absorption (atw) and Algal Biomass Index (ABI) on Landsat-8 and Sentinel-3 satellites. The fitting coefficients of the empirical models were corrected based on field data, and the accuracy before and after the algorithm corrections were compared to assess stability. The effects of the surface reflectance products and the remote sensing reflectance corrected by the atmospheric correction algorithms on the TSI inversion were further compared to examine the sensitivity of these algorithms.Our results show that the FUI algorithm has good identification accuracy for eutrophic water bodies with lower requirements for sensor band settings (visible bands). However, it only provides qualitative judgement. The atw algorithm has good identification accuracy for mesotrophic lakes with higher requirements for sensor band settings and atmospheric corrections. The ABI algorithm provides a reliable performance of eutrophication, with good stability of satellite remote sensing data at different levels. The ABI algorithm can figure out different degrees of eutrophic waters, but relies on shortwave infrared for optical classification of water bodies. The ABI algorithm shows the best accuracy with an overall accuracy of 71% and 73% for Landsat-8 and Sentinel-3, respectively, which is better than atw (56% and 63%) and FUI (49% and 52%) algorithm.To sum up, the FUI algorithm is preferred for the qualitative investigation of lake eutrophication to quickly and roughly grasp the trophic level, and the ABI or atw algorithm is further applied for precise quantification. It is recommended to choose one remote sensing evaluation method according to different application scenarios, which can improve the consistency and comparability of lake trophic state assessment. This study can provide an important basis for the future specification of remote sensing monitoring of lake eutrophication.关键词:lake eutrophication;trophic state;Forel-Ule index;total non-water absorption;algal biomass;atmospheric corrections;water classification165|97|0更新时间:2025-12-30 - “新疆光伏电站分布及植被影响研究取得新进展,基于深度学习模型筛选出最优识别模型,为光伏选址和生态评估提供数据支持。”
 摘要:Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, endowed with abundant land and solar energy resources, has emerged as a national leader in terms of installed photovoltaic (PV) capacity, driven by the growing demand for renewable energy and advancements in PV technology. Accurate, real-time identification of PV station distribution and quantitative analysis of its effects on the spatial aggregation of surrounding vegetation provide crucial data and informed decision-making support for PV siting in Xinjiang.This study employs deep learning semantic segmentation models constructed by combining three architectures (UNet, pyramid scene parsing network, and DeepLabV3+) with four backbone networks (ResNet-34, ResNet-50, ResNet-101, and ResNet-152), as well as alternative DeepLabV3+ backbones including MobileNetV2, DarkNet53, VGG16, and DenseNet121 in different combinations. The objective is to determine the optimal model for PV station detection and map the spatial distribution of PV stations across Xinjiang. Global Moran’s I values are calculated as a time series within buffer zones divided into equal intervals (ranging from 30 m to 600 m around the PV stations) to assess the effect of PV station construction on vegetation spatial aggregation.Results reveal that (1) the UNet-ResNet50 model demonstrates superior performance in PV station recognition, achieving an accuracy of 98.64% (improvement of 0.09 percentage points), an F1 score of 95% (improvement of 0.4 percentage points), and an intersection over union value of 90.47% (improvement of 0.57 percentage points). These exceptional recognition capabilities are primarily attributable to the high accuracy of the PV sample set and the model’s outstanding feature extraction and depth balancing abilities. (2) With Sentinel-2 remote sensing images and the UNet-ResNet50 model, the 2020 PV stations in Xinjiang are extracted and classified into vegetation-covered and bare-land PV stations, with area proportions of 30% and 70%, respectively. (3) Within different buffer zones ranging from 30 m to 210 m from a PV station, the Global Moran’s I of vegetation shows a remarkable downward trend from 2012 to 2020. In the buffer zones 210—600 m from a PV station, decrease in the Global Moran’s I of vegetation slows down substantially. The closer the location is to a PV station, the greater the influence on the spatial aggregation of vegetation is and the more evident the decrement in the time series is.Therefore, remote sensing monitoring of PV stations and their surrounding buffer zones offers critical data and technical support for construction planning, precise operational management, and assessment of ecological effects associated with PV stations.关键词:photovoltaic station;semantic segmentation model;vegetation spatial aggregation;Global Moran’s Index672|774|0更新时间:2025-12-30
摘要:Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, endowed with abundant land and solar energy resources, has emerged as a national leader in terms of installed photovoltaic (PV) capacity, driven by the growing demand for renewable energy and advancements in PV technology. Accurate, real-time identification of PV station distribution and quantitative analysis of its effects on the spatial aggregation of surrounding vegetation provide crucial data and informed decision-making support for PV siting in Xinjiang.This study employs deep learning semantic segmentation models constructed by combining three architectures (UNet, pyramid scene parsing network, and DeepLabV3+) with four backbone networks (ResNet-34, ResNet-50, ResNet-101, and ResNet-152), as well as alternative DeepLabV3+ backbones including MobileNetV2, DarkNet53, VGG16, and DenseNet121 in different combinations. The objective is to determine the optimal model for PV station detection and map the spatial distribution of PV stations across Xinjiang. Global Moran’s I values are calculated as a time series within buffer zones divided into equal intervals (ranging from 30 m to 600 m around the PV stations) to assess the effect of PV station construction on vegetation spatial aggregation.Results reveal that (1) the UNet-ResNet50 model demonstrates superior performance in PV station recognition, achieving an accuracy of 98.64% (improvement of 0.09 percentage points), an F1 score of 95% (improvement of 0.4 percentage points), and an intersection over union value of 90.47% (improvement of 0.57 percentage points). These exceptional recognition capabilities are primarily attributable to the high accuracy of the PV sample set and the model’s outstanding feature extraction and depth balancing abilities. (2) With Sentinel-2 remote sensing images and the UNet-ResNet50 model, the 2020 PV stations in Xinjiang are extracted and classified into vegetation-covered and bare-land PV stations, with area proportions of 30% and 70%, respectively. (3) Within different buffer zones ranging from 30 m to 210 m from a PV station, the Global Moran’s I of vegetation shows a remarkable downward trend from 2012 to 2020. In the buffer zones 210—600 m from a PV station, decrease in the Global Moran’s I of vegetation slows down substantially. The closer the location is to a PV station, the greater the influence on the spatial aggregation of vegetation is and the more evident the decrement in the time series is.Therefore, remote sensing monitoring of PV stations and their surrounding buffer zones offers critical data and technical support for construction planning, precise operational management, and assessment of ecological effects associated with PV stations.关键词:photovoltaic station;semantic segmentation model;vegetation spatial aggregation;Global Moran’s Index672|774|0更新时间:2025-12-30
Ecology and Environment
- “环境减灾二号06星成功发射并组网运行,通过积分法和交叉辐射定标方法,有效获取了卫星条带模式的绝对定标常数,为定量化应用提供基础。”
 摘要:The HJ-2 06 satellite was successfully launched on August 9, 2023, and forms a coordinated earth observation system with its twin satellite HJ-2 05. As important components of China’s civil space infrastructure, these S-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR) satellites enable critical quantitative applications, such as soil moisture monitoring and ocean current observation. Radiometric calibration is the fundamental prerequisite for these applications because it establishes the precise functional relationship between SAR images and target backscatter coefficients. The HJ-2 06 satellite aims to achieve an absolute radiometric calibration accuracy of 2.00 dB through radiometric calibration.In this study, the radiometric calibration method of the HJ-2 06 satellite was introduced. Compared with the peak method, the integral method demonstrated superior stability and was thus adopted to derive the calibration constants for different beams of the HJ-2 06 satellite. To reduce the influence of random errors, absolute calibration constants of all beams were uniformly analyzed. The results were further validated using incidence normalized backscatter coefficients from the Amazon rainforest, a benchmark for other SAR satellites. During the on-orbit testing period of the HJ-2 06 satellite, absolute radiometric calibration of the strip mode was performed at Suniteyouqi, Inner Mongolia. Operational constraints, including limited revisit cycles and on-orbit testing duration, make simultaneous calibration and validation particularly challenging. To overcome this limitation, we proposed an innovative cross calibration technique that utilizes point targets as references between HJ-2 05 and HJ-2 06 satellites. The basis of the method is that the change of the radar cross section of point targets can be ignored when observed by the same beams between satellite constellations. The absolute calibration constants of the calibrated satellite were calculated by extracting the energy difference of point targets between satellite constellations. Cross radiometric calibration using corner reflectors as point targets was completed in Queensland, Australia.Experiment results showed that the differences in the absolute calibration constant among the beams of the HJ-2 06 satellite are not more than 1.42 dB, and the calibration constants within the beams remain within 0.53 dB, surpassing the design specifications. Furthermore, the cross radiometric calibration accuracy of single beam between HJ-2 05 and HJ-2 06 satellites is better than 1.33 dB. The difference between the average results of cross calibration and the average results of radiometric calibration was 0.38 dB, demonstrating excellent radiometric consistency within the satellite constellation.Comprehensive calibration constants were successfully derived for different operational beams of the HJ-2 06 satellite, and the findings showed that cross radiometric calibration on the basis of point targets can serve as a supplementary means to verify the results of SAR field calibration, indicating that the results of cross radiometric calibration tend to stabilize with increasing frequency. By averaging the cross calibration results of all beams, the random error is effectively reduced. Cross radiometric calibration plays a pivotal role in ensuring the consistency of SAR payload radiation between satellite constellations. The derived absolute calibration constants were successfully implemented in the HJ-2 06 satellite’s ground processing system, establishing a robust foundation for subsequent application verification and operational deployment.关键词:HJ-2 05/06 satellites;radiometric calibration;integral method;Cross radiometric calibration;Point targets426|256|0更新时间:2025-12-30
摘要:The HJ-2 06 satellite was successfully launched on August 9, 2023, and forms a coordinated earth observation system with its twin satellite HJ-2 05. As important components of China’s civil space infrastructure, these S-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR) satellites enable critical quantitative applications, such as soil moisture monitoring and ocean current observation. Radiometric calibration is the fundamental prerequisite for these applications because it establishes the precise functional relationship between SAR images and target backscatter coefficients. The HJ-2 06 satellite aims to achieve an absolute radiometric calibration accuracy of 2.00 dB through radiometric calibration.In this study, the radiometric calibration method of the HJ-2 06 satellite was introduced. Compared with the peak method, the integral method demonstrated superior stability and was thus adopted to derive the calibration constants for different beams of the HJ-2 06 satellite. To reduce the influence of random errors, absolute calibration constants of all beams were uniformly analyzed. The results were further validated using incidence normalized backscatter coefficients from the Amazon rainforest, a benchmark for other SAR satellites. During the on-orbit testing period of the HJ-2 06 satellite, absolute radiometric calibration of the strip mode was performed at Suniteyouqi, Inner Mongolia. Operational constraints, including limited revisit cycles and on-orbit testing duration, make simultaneous calibration and validation particularly challenging. To overcome this limitation, we proposed an innovative cross calibration technique that utilizes point targets as references between HJ-2 05 and HJ-2 06 satellites. The basis of the method is that the change of the radar cross section of point targets can be ignored when observed by the same beams between satellite constellations. The absolute calibration constants of the calibrated satellite were calculated by extracting the energy difference of point targets between satellite constellations. Cross radiometric calibration using corner reflectors as point targets was completed in Queensland, Australia.Experiment results showed that the differences in the absolute calibration constant among the beams of the HJ-2 06 satellite are not more than 1.42 dB, and the calibration constants within the beams remain within 0.53 dB, surpassing the design specifications. Furthermore, the cross radiometric calibration accuracy of single beam between HJ-2 05 and HJ-2 06 satellites is better than 1.33 dB. The difference between the average results of cross calibration and the average results of radiometric calibration was 0.38 dB, demonstrating excellent radiometric consistency within the satellite constellation.Comprehensive calibration constants were successfully derived for different operational beams of the HJ-2 06 satellite, and the findings showed that cross radiometric calibration on the basis of point targets can serve as a supplementary means to verify the results of SAR field calibration, indicating that the results of cross radiometric calibration tend to stabilize with increasing frequency. By averaging the cross calibration results of all beams, the random error is effectively reduced. Cross radiometric calibration plays a pivotal role in ensuring the consistency of SAR payload radiation between satellite constellations. The derived absolute calibration constants were successfully implemented in the HJ-2 06 satellite’s ground processing system, establishing a robust foundation for subsequent application verification and operational deployment.关键词:HJ-2 05/06 satellites;radiometric calibration;integral method;Cross radiometric calibration;Point targets426|256|0更新时间:2025-12-30 - “在光学遥感影像处理领域,Cloud-Harmonizer去云方法利用SAR与光学影像的互补性,有效修复云区信息,为多模态遥感数据融合应用提供有益参考。”
 摘要:Conventional cloud removal methods often fail to fully restore details in occluded areas, thereby degrading image quality. Thus, cloud occlusion remains a persistent challenge in optical remote sensing imagery. Clouds not only obscure critical ground information but also introduce noise and artifacts during reconstruction, limiting the imagery’s utility for applications such as land cover monitoring, disaster assessment, and environmental studies. Aiming to address this issue, this paper presents a cloud removal approach based on multimodal feature consistency fusion (Cloud-Harmonizer). The proposed framework leverages the complementary characteristics and consistency between Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and optical imagery for the effective restoration of cloud-occluded regions and the generation of high-quality reconstructed optical images. Compared to traditional methods that rely solely on temporal or spatial interpolation, the proposed approach capitalizes on the inherent advantages of SAR data (which is unaffected by cloud cover) to support the reconstruction process and ensure the authenticity of restored areas. Through the integration of multimodal data, the method aims to improve structural and spectral recovery in cloud-affected images.The Cloud-Harmonizer framework comprises three core modules for feature extraction, alignment, and fusion of SAR and optical images. The multimodal feature consistency module maps features from the two modalities into a shared vector space and generates modality difference attention to help identify cloud-affected regions. This approach ensures compatibility between the feature representations of twomodalities, facilitating precise identification of occlusions. The consistency-constrained compensation module uses difference attention to guide SAR data in compensating for missing features in optical imagery, facilitating reconstruction that aligns with the actual scene. The multimodal collaborative adaptive fusion module adopts self-attention-based adaptive fusion strategies to optimize the integration of the two modalities and enhance overall reconstruction quality. Accurate compensation and robust feature fusion under various environmental conditions, including dense cloud coverage and complex terrain, are achieved using this modular design. The framework dynamically adjusts the fusion process using input data characteristics, increasing its suitability for diverse remote sensing scenarios.Experiments conducted on the SEN12MS-CR dataset validate the effectiveness of the proposed method. The Cloud-Harmonizer framework achieves a peak signal-to-noise ratio of 30.0408, a structural similarity index of 0.9004, and a spectral angle mapper of 7.6068, demonstrating remarkable improvements over existing cloud removal methods. These quantitative results indicate the capability of the model to recover detailed information while maintaining structural and spectral consistency in reconstructed images. Comparative analyses with existing methods indicate that the proposed approach effectively preserves textures, edges, and other details while minimizing artifacts in cloud-occluded regions. Qualitative evaluations further confirm the natural visual appearance of reconstructed images, validating the robustness of the proposed framework.Experimental results demonstrate the potential of the Cloud-Harmonizer framework for cloud removal and feature restoration in optical remote sensing imagery. Through the effective application of multimodal data fusion, the proposed method addresses cloud occlusion challenges while maintaining feature consistency between SAR and optical modalities. The approach benefits from the complementary characteristics of both data types, achieving accurate reconstruction of occluded areas while maintaining image quality. The modular and adaptive design of the framework establishes a basis for the exploration of highly sophisticated fusion strategies and the extension of applications to other remote sensing challenges. Considering the growing demand for high-quality remote sensing data, Cloud-Harmonizer may serve as a viable solution for improving the usability of optical imagery in cloud-prone environments.关键词:cloud removal in remote sensing imagery;multi-modal data fusion;multi-modal feature consistency629|1172|0更新时间:2025-12-30
摘要:Conventional cloud removal methods often fail to fully restore details in occluded areas, thereby degrading image quality. Thus, cloud occlusion remains a persistent challenge in optical remote sensing imagery. Clouds not only obscure critical ground information but also introduce noise and artifacts during reconstruction, limiting the imagery’s utility for applications such as land cover monitoring, disaster assessment, and environmental studies. Aiming to address this issue, this paper presents a cloud removal approach based on multimodal feature consistency fusion (Cloud-Harmonizer). The proposed framework leverages the complementary characteristics and consistency between Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and optical imagery for the effective restoration of cloud-occluded regions and the generation of high-quality reconstructed optical images. Compared to traditional methods that rely solely on temporal or spatial interpolation, the proposed approach capitalizes on the inherent advantages of SAR data (which is unaffected by cloud cover) to support the reconstruction process and ensure the authenticity of restored areas. Through the integration of multimodal data, the method aims to improve structural and spectral recovery in cloud-affected images.The Cloud-Harmonizer framework comprises three core modules for feature extraction, alignment, and fusion of SAR and optical images. The multimodal feature consistency module maps features from the two modalities into a shared vector space and generates modality difference attention to help identify cloud-affected regions. This approach ensures compatibility between the feature representations of twomodalities, facilitating precise identification of occlusions. The consistency-constrained compensation module uses difference attention to guide SAR data in compensating for missing features in optical imagery, facilitating reconstruction that aligns with the actual scene. The multimodal collaborative adaptive fusion module adopts self-attention-based adaptive fusion strategies to optimize the integration of the two modalities and enhance overall reconstruction quality. Accurate compensation and robust feature fusion under various environmental conditions, including dense cloud coverage and complex terrain, are achieved using this modular design. The framework dynamically adjusts the fusion process using input data characteristics, increasing its suitability for diverse remote sensing scenarios.Experiments conducted on the SEN12MS-CR dataset validate the effectiveness of the proposed method. The Cloud-Harmonizer framework achieves a peak signal-to-noise ratio of 30.0408, a structural similarity index of 0.9004, and a spectral angle mapper of 7.6068, demonstrating remarkable improvements over existing cloud removal methods. These quantitative results indicate the capability of the model to recover detailed information while maintaining structural and spectral consistency in reconstructed images. Comparative analyses with existing methods indicate that the proposed approach effectively preserves textures, edges, and other details while minimizing artifacts in cloud-occluded regions. Qualitative evaluations further confirm the natural visual appearance of reconstructed images, validating the robustness of the proposed framework.Experimental results demonstrate the potential of the Cloud-Harmonizer framework for cloud removal and feature restoration in optical remote sensing imagery. Through the effective application of multimodal data fusion, the proposed method addresses cloud occlusion challenges while maintaining feature consistency between SAR and optical modalities. The approach benefits from the complementary characteristics of both data types, achieving accurate reconstruction of occluded areas while maintaining image quality. The modular and adaptive design of the framework establishes a basis for the exploration of highly sophisticated fusion strategies and the extension of applications to other remote sensing challenges. Considering the growing demand for high-quality remote sensing data, Cloud-Harmonizer may serve as a viable solution for improving the usability of optical imagery in cloud-prone environments.关键词:cloud removal in remote sensing imagery;multi-modal data fusion;multi-modal feature consistency629|1172|0更新时间:2025-12-30 - “在遥感图像语义分割领域,专家提出了基于去纠缠的分割模型,有效提升了分割性能,为解决地物光谱混淆问题提供新方案。”
 摘要:Remote sensing semantic segmentation refers to the task of classifying pixels in remote sensing images into predefined object categories, such as vehicles, buildings, and vegetation. As a prominent research topic in remote sensing, semantic segmentation provides critical support for land-use classification, urban planning, and disaster monitoring. Due to the significant differences in target sizes and the complex and variable backgrounds in remote sensing images, there are phenomena such as target spectral confusion and blurred feature boundaries, which increase the difficulty of the semantic segmentation task. To address the semantic segmentation difficulties caused by feature interdependencies under varying illumination conditions in urban environments, this paper proposes a disentanglement-based semantic segmentation model comprising a Light-Reflectance Disentanglement Network (LRD-Net) and a Multi-modal Semantic Segmentation Network (MSS-Net).The proposed method consists of several steps. First, based on the Retinex theory, we design the LRD-Net network to decompose the illumination and reflectance features in optical images. The model utilizes a Weight Sharing Transformer (WS-Transformer) to extract global contextual information and spatial local contextual information. Secondly, we design a simple and effective multi-scale noise module to adaptively enhance the illumination component, improving the model’s robustness in disentangling. Next, we construct a Significant feature Enhancement module (SE) composed of channel attention and convolutional layers to increase the differentiation of features extracted by LRD-Net, resulting in a more accurate representation of surface illumination features. Finally, the disentangled features are fused using MSS-Net to generate semantic segmentation results, effectively leveraging multi-modal features that contain illumination and reflection information. Additionally, we design an Edge feature Extraction module (EE) to enhance the representation capability of edge features, thereby improving the accuracy of object prediction and the integrity of overall contours. During the training process, a loss function based on the Retinex theory is constructed to better perceive changes in illumination and the reflective characteristics of surfaces.Experiments are conducted on the general datasets ISPRS Vaihingen and ISPRS Potsdam. The results of the feature disentanglement effect indicate that the model effectively captures the variations in shadows and the distribution of illumination intensity in the extracted illumination feature heatmaps, achieving an efficient disentanglement of illumination components and invariant reflectance. Compared to the primary model, the experimental results show that the evaluation metric mIoU reaches 84.60% and 87.42%, respectively. Additionally, the model demonstrates better performance in terms of average F1 score and overallaccuracy The experimental findings suggest that the proposed model outperforms other models in the task of semantic segmentation of remote sensing images. Moreover, the ablation experiment results indicate that the proposed WS module, SE module, and EE module can effectively enhance the performance of semantic segmentation.The proposed disentanglement-based model significantly improves edge processing capability and overall segmentation accuracy through enhanced edge feature extraction and illumination-reflectance disentanglement. Results indicate the model is well-suited for segmenting buildings, low vegetation, and trees, given its superior performance on target scale imbalance and spectral variations challenges. It effectively addresses decreased recognition accuracy of remote sensing images under varying lighting conditions. Future work will explore integrating large remote sensing models with disentanglement theory to further advance segmentation precision.关键词:semantic segmentation;Image decomposition;Retinex theory;Transformer364|677|0更新时间:2025-12-30
摘要:Remote sensing semantic segmentation refers to the task of classifying pixels in remote sensing images into predefined object categories, such as vehicles, buildings, and vegetation. As a prominent research topic in remote sensing, semantic segmentation provides critical support for land-use classification, urban planning, and disaster monitoring. Due to the significant differences in target sizes and the complex and variable backgrounds in remote sensing images, there are phenomena such as target spectral confusion and blurred feature boundaries, which increase the difficulty of the semantic segmentation task. To address the semantic segmentation difficulties caused by feature interdependencies under varying illumination conditions in urban environments, this paper proposes a disentanglement-based semantic segmentation model comprising a Light-Reflectance Disentanglement Network (LRD-Net) and a Multi-modal Semantic Segmentation Network (MSS-Net).The proposed method consists of several steps. First, based on the Retinex theory, we design the LRD-Net network to decompose the illumination and reflectance features in optical images. The model utilizes a Weight Sharing Transformer (WS-Transformer) to extract global contextual information and spatial local contextual information. Secondly, we design a simple and effective multi-scale noise module to adaptively enhance the illumination component, improving the model’s robustness in disentangling. Next, we construct a Significant feature Enhancement module (SE) composed of channel attention and convolutional layers to increase the differentiation of features extracted by LRD-Net, resulting in a more accurate representation of surface illumination features. Finally, the disentangled features are fused using MSS-Net to generate semantic segmentation results, effectively leveraging multi-modal features that contain illumination and reflection information. Additionally, we design an Edge feature Extraction module (EE) to enhance the representation capability of edge features, thereby improving the accuracy of object prediction and the integrity of overall contours. During the training process, a loss function based on the Retinex theory is constructed to better perceive changes in illumination and the reflective characteristics of surfaces.Experiments are conducted on the general datasets ISPRS Vaihingen and ISPRS Potsdam. The results of the feature disentanglement effect indicate that the model effectively captures the variations in shadows and the distribution of illumination intensity in the extracted illumination feature heatmaps, achieving an efficient disentanglement of illumination components and invariant reflectance. Compared to the primary model, the experimental results show that the evaluation metric mIoU reaches 84.60% and 87.42%, respectively. Additionally, the model demonstrates better performance in terms of average F1 score and overallaccuracy The experimental findings suggest that the proposed model outperforms other models in the task of semantic segmentation of remote sensing images. Moreover, the ablation experiment results indicate that the proposed WS module, SE module, and EE module can effectively enhance the performance of semantic segmentation.The proposed disentanglement-based model significantly improves edge processing capability and overall segmentation accuracy through enhanced edge feature extraction and illumination-reflectance disentanglement. Results indicate the model is well-suited for segmenting buildings, low vegetation, and trees, given its superior performance on target scale imbalance and spectral variations challenges. It effectively addresses decreased recognition accuracy of remote sensing images under varying lighting conditions. Future work will explore integrating large remote sensing models with disentanglement theory to further advance segmentation precision.关键词:semantic segmentation;Image decomposition;Retinex theory;Transformer364|677|0更新时间:2025-12-30 - “在机载LiDAR点云分割领域,研究者提出了LAE-Transformer网络,有效提升了小尺度目标分割精度,为该领域研究提供了新方向。”
 摘要:Existing semantic segmentation algorithms that are based on deep learning for airborne LiDAR point clouds encounter specific challenges when they deal with complex scenes. These challenges include insufficient utilization of local topological information, limited capability in multiscale feature representation, and low segmentation accuracy for small-scale objects, such as trucks, poles, and fences. These issues directly hinder the deployment of airborne LiDAR systems in practical applications. An airborne LiDAR point cloud segmentation network incorporating local-aware enhancement, namely, LAE-Transformer, is proposed in this study to address the aforementioned challenges. It aims to improve the accuracy and reliability of semantic segmentation tasks for airborne LiDAR point clouds by effectively utilizing local topological information and multiscale features.The proposed LAE-Transformer adopts an encoder–decoder structure with skip connections and incorporates four major innovations. First, the local topological information enhancement module is introduced to extract shallow topological features by using a K-nearest neighbor (KNN) approach. This module constructs a local geometric structure graph that allows the model to capture the fine-grained spatial variations and geometric edges of objects. Second, during the encoding phase, a combination of downsampling layers and Regional Point Transformer (RPT) modules is employed to extract deep semantic features while expanding the receptive field. The RPT modules utilize self-attention mechanisms to model intra- and inter-region dependencies, substantially improving the model’s ability to represent features at multiple scales. Third, during the decoding phase, a dynamic residual connection module is incorporated to adaptively fuse features from different semantic layers, thus ensuring the continuity and integrity of spatial information in the upsampling process. Last, a mixed pooling layer that integrates max pooling and attention pooling is designed to aggregate local salient features and global contextual information, effectively reducing information loss and maintaining rich feature diversity during processing.Extensive experiments are conducted on two publicly available benchmark datasets DALES and LASDU. The proposed LAE-Transformer achieves remarkable improvements in segmentation performance compared with several state-of-the-art models. Specifically, it attains an overall accuracy of 97.8% and 87.2% and mean Intersection over Union (IoU) scores of 80.8% and 68.5% on DALES and LASDU datasets, respectively. In addition, the model demonstrates substantial advantages in segmenting small-scale objects. On the DALES dataset, it achieves IoU scores of 42.1% for trucks, 75.4% for poles, and 63.8% for fences, outperforming widely used methods, such as point Transformer. These results strongly validate the model’s superior accuracy, robustness, and generalization capabilities in handling complex airborne LiDAR scenes.The proposed LAE-Transformer effectively overcomes the limitations of current semantic segmentation models by integrating local topological feature enhancement, multiscale Transformer-based feature extraction, dynamic residual connections, and a mixed pooling mechanism. These innovations allow the network to efficiently extract and fuse local and global features, thereby improving the segmentation accuracy for small-scale objects and the overall reliability of semantic segmentation in airborne LiDAR point cloud. The method’s practical value and potential for deployment in airborne LiDAR applications across complex environments are also validated.关键词:airborne LiDAR point cloud;deep learning;semantic segmentation;self-attention mechanism;local-aware enhancement;complex scenes;small-scale objects;Transformer215|183|0更新时间:2025-12-30
摘要:Existing semantic segmentation algorithms that are based on deep learning for airborne LiDAR point clouds encounter specific challenges when they deal with complex scenes. These challenges include insufficient utilization of local topological information, limited capability in multiscale feature representation, and low segmentation accuracy for small-scale objects, such as trucks, poles, and fences. These issues directly hinder the deployment of airborne LiDAR systems in practical applications. An airborne LiDAR point cloud segmentation network incorporating local-aware enhancement, namely, LAE-Transformer, is proposed in this study to address the aforementioned challenges. It aims to improve the accuracy and reliability of semantic segmentation tasks for airborne LiDAR point clouds by effectively utilizing local topological information and multiscale features.The proposed LAE-Transformer adopts an encoder–decoder structure with skip connections and incorporates four major innovations. First, the local topological information enhancement module is introduced to extract shallow topological features by using a K-nearest neighbor (KNN) approach. This module constructs a local geometric structure graph that allows the model to capture the fine-grained spatial variations and geometric edges of objects. Second, during the encoding phase, a combination of downsampling layers and Regional Point Transformer (RPT) modules is employed to extract deep semantic features while expanding the receptive field. The RPT modules utilize self-attention mechanisms to model intra- and inter-region dependencies, substantially improving the model’s ability to represent features at multiple scales. Third, during the decoding phase, a dynamic residual connection module is incorporated to adaptively fuse features from different semantic layers, thus ensuring the continuity and integrity of spatial information in the upsampling process. Last, a mixed pooling layer that integrates max pooling and attention pooling is designed to aggregate local salient features and global contextual information, effectively reducing information loss and maintaining rich feature diversity during processing.Extensive experiments are conducted on two publicly available benchmark datasets DALES and LASDU. The proposed LAE-Transformer achieves remarkable improvements in segmentation performance compared with several state-of-the-art models. Specifically, it attains an overall accuracy of 97.8% and 87.2% and mean Intersection over Union (IoU) scores of 80.8% and 68.5% on DALES and LASDU datasets, respectively. In addition, the model demonstrates substantial advantages in segmenting small-scale objects. On the DALES dataset, it achieves IoU scores of 42.1% for trucks, 75.4% for poles, and 63.8% for fences, outperforming widely used methods, such as point Transformer. These results strongly validate the model’s superior accuracy, robustness, and generalization capabilities in handling complex airborne LiDAR scenes.The proposed LAE-Transformer effectively overcomes the limitations of current semantic segmentation models by integrating local topological feature enhancement, multiscale Transformer-based feature extraction, dynamic residual connections, and a mixed pooling mechanism. These innovations allow the network to efficiently extract and fuse local and global features, thereby improving the segmentation accuracy for small-scale objects and the overall reliability of semantic segmentation in airborne LiDAR point cloud. The method’s practical value and potential for deployment in airborne LiDAR applications across complex environments are also validated.关键词:airborne LiDAR point cloud;deep learning;semantic segmentation;self-attention mechanism;local-aware enhancement;complex scenes;small-scale objects;Transformer215|183|0更新时间:2025-12-30 - “在遥感图像语义分割领域,专家提出了基于三分支集成网络的高分辨率遥感图像语义分割算法,有效提高了遥感图像分割的准确率。”
 摘要:Remote sensing images, characterized by wide coverage, multispectral information, and complex spatial structures, provide critical geospatial data for environmental monitoring, urban planning, and other applications. However, traditional interpretation methods struggle to address the growing challenges posed by expanding image coverage, diverse object categories, and intricate feature interactions. Although deep learning has shown promise in extracting multilevel semantic features for image segmentation, existing networks often suffer from suboptimal feature fusion and oversimplified feature representations. This study aims to develop a novel segmentation algorithm that effectively integrates semantic and spatial information while addressing feature consistency and overfitting issues in small-scale remote sensing datasets, thereby improving segmentation accuracy and robustness. The study proposes a three-branch integrated network for high-resolution remote sensing image segmentation. First, two dedicated branches separately extract semantic and spatial features to maximize their distinct characteristics. A third consistency branch is introduced to learn semantic-spatial consistency features, mitigating oversimplification during fusion. Second, a multiscale feature fusion module dynamically weighs and integrates outputs from all three branches, enhancing feature representation adaptability. Last, a spatial consistency-aware random cropping strategy is designed to alleviate overfitting caused by limited training data. This augmentation method generates diverse yet spatially coherent image patches by preserving key object structures during random cropping, thereby ensuring effective model generalization.The proposed algorithm achieves state-of-the-art performance on the ISPRS Potsdam and Vaihingen datasets, with mean intersection over union scores of 87.84% and 87.49%, respectively. It excels in segmenting complex scenarios, such as buildings with similar spectral profiles and non-opaque surfaces, by leveraging pixel-level spatial relationships and weighted multiscale features. Edge segmentation accuracy is notably improved; smooth boundaries are produced, and classification errors are reduced. However, interbranch feature interaction remains limited, as evidenced by occasional inconsistencies in regions with overlapping spectral signatures. While the model demonstrates robustness to dataset scale, its computational efficiency requires further optimization for real-time applications.This work presents a three-branch network architecture that effectively addresses feature fusion challenges in remote sensing image segmentation. By decoupling semantic and spatial feature extraction while enforcing consistency constraints, the algorithm achieves remarkable accuracy improvements over conventional methods. The spatial consistency-aware data augmentation further enhances model generalizability. Current limitations include insufficient cross-branch communication and high computational overhead. Future research should focus on designing lightweight interactive modules to strengthen feature exchange between branches and exploring Transformer-based architectures to capture long-range dependencies. These advancements could increase precision in large-scale remote sensing applications, such as disaster assessment and land-use monitoring.关键词:High resolution remote sensing image;semantic segmentation;Multi-scale fusion;Data enhancement;Multi-branch feature extraction;Spatial consistency204|413|0更新时间:2025-12-30
摘要:Remote sensing images, characterized by wide coverage, multispectral information, and complex spatial structures, provide critical geospatial data for environmental monitoring, urban planning, and other applications. However, traditional interpretation methods struggle to address the growing challenges posed by expanding image coverage, diverse object categories, and intricate feature interactions. Although deep learning has shown promise in extracting multilevel semantic features for image segmentation, existing networks often suffer from suboptimal feature fusion and oversimplified feature representations. This study aims to develop a novel segmentation algorithm that effectively integrates semantic and spatial information while addressing feature consistency and overfitting issues in small-scale remote sensing datasets, thereby improving segmentation accuracy and robustness. The study proposes a three-branch integrated network for high-resolution remote sensing image segmentation. First, two dedicated branches separately extract semantic and spatial features to maximize their distinct characteristics. A third consistency branch is introduced to learn semantic-spatial consistency features, mitigating oversimplification during fusion. Second, a multiscale feature fusion module dynamically weighs and integrates outputs from all three branches, enhancing feature representation adaptability. Last, a spatial consistency-aware random cropping strategy is designed to alleviate overfitting caused by limited training data. This augmentation method generates diverse yet spatially coherent image patches by preserving key object structures during random cropping, thereby ensuring effective model generalization.The proposed algorithm achieves state-of-the-art performance on the ISPRS Potsdam and Vaihingen datasets, with mean intersection over union scores of 87.84% and 87.49%, respectively. It excels in segmenting complex scenarios, such as buildings with similar spectral profiles and non-opaque surfaces, by leveraging pixel-level spatial relationships and weighted multiscale features. Edge segmentation accuracy is notably improved; smooth boundaries are produced, and classification errors are reduced. However, interbranch feature interaction remains limited, as evidenced by occasional inconsistencies in regions with overlapping spectral signatures. While the model demonstrates robustness to dataset scale, its computational efficiency requires further optimization for real-time applications.This work presents a three-branch network architecture that effectively addresses feature fusion challenges in remote sensing image segmentation. By decoupling semantic and spatial feature extraction while enforcing consistency constraints, the algorithm achieves remarkable accuracy improvements over conventional methods. The spatial consistency-aware data augmentation further enhances model generalizability. Current limitations include insufficient cross-branch communication and high computational overhead. Future research should focus on designing lightweight interactive modules to strengthen feature exchange between branches and exploring Transformer-based architectures to capture long-range dependencies. These advancements could increase precision in large-scale remote sensing applications, such as disaster assessment and land-use monitoring.关键词:High resolution remote sensing image;semantic segmentation;Multi-scale fusion;Data enhancement;Multi-branch feature extraction;Spatial consistency204|413|0更新时间:2025-12-30
Models and Methods
0

