
最新刊期
卷 29 , 期 3 , 2025
-
Seven principles for the application of artificial intelligence in remote sensing interpretation AI导读
“中国遥感卫星技术快速发展,人工智能技术与遥感大数据融合,推动新质生产力发展。专家总结了人工智能在遥感科学的应用现状,分析不足,展望未来,提出七大准则。” 摘要:Over the past decade, China’s remote sensing satellite technology has advanced rapidly. The integration of remote sensing big data with new-generation Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies has become a driving force for social development. This paper outlines the progress in interdisciplinary research between remote sensing science and AI technologies, analyzes the current shortcomings in intelligent interpretation of remote sensing data, forecasts the future development of intelligent interpretation and application of remote sensing big data, and summarizes seven principles for developing new-generation AI in remote sensing interpretation. The new generation of remote sensing AI technology should comprehensively consider the geometric and physical characteristics of remote sensing. By integrating geographical knowledge and utilizing remote sensing big data collected from various sensors and time periods, it should learn from standardized and semantic remote sensing ontology databases in a hierarchical “pixel-object-scene” manner. This approach enables deep mining of multi-dimensional surface dynamic information from remote sensing images, achieving a unified framework for simultaneous land cover classification, data fusion, and change detection. Ultimately, it produces high-precision and reliable remote sensing interpretation products with quality diagnostics, providing robust data support for interdisciplinary research and decision-making involving remote sensing, thereby promoting the development of new quality productive forces.关键词:remote sensing intelligent interpretation;earth observation;big data;artificial intelligence;remote sensing image processing393|160|0更新时间:2025-04-21
摘要:Over the past decade, China’s remote sensing satellite technology has advanced rapidly. The integration of remote sensing big data with new-generation Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies has become a driving force for social development. This paper outlines the progress in interdisciplinary research between remote sensing science and AI technologies, analyzes the current shortcomings in intelligent interpretation of remote sensing data, forecasts the future development of intelligent interpretation and application of remote sensing big data, and summarizes seven principles for developing new-generation AI in remote sensing interpretation. The new generation of remote sensing AI technology should comprehensively consider the geometric and physical characteristics of remote sensing. By integrating geographical knowledge and utilizing remote sensing big data collected from various sensors and time periods, it should learn from standardized and semantic remote sensing ontology databases in a hierarchical “pixel-object-scene” manner. This approach enables deep mining of multi-dimensional surface dynamic information from remote sensing images, achieving a unified framework for simultaneous land cover classification, data fusion, and change detection. Ultimately, it produces high-precision and reliable remote sensing interpretation products with quality diagnostics, providing robust data support for interdisciplinary research and decision-making involving remote sensing, thereby promoting the development of new quality productive forces.关键词:remote sensing intelligent interpretation;earth observation;big data;artificial intelligence;remote sensing image processing393|160|0更新时间:2025-04-21
Scholar's View Point
-
Progress of research on volcano hotspot identification algorithms using satellite infrared data AI导读
“卫星红外数据识别火山热点技术取得新进展,为全球火山活动监测提供安全低成本方案。” 摘要:Volcano monitoring is essential for predicting volcanic eruptions and implementing early warning measures. Traditional ground-based monitoring methods cannot fully cover all volcanoes. Satellite remote sensing technology, with its advantages of global coverage and high temporal and spatial resolutions, is an important complement for near-real-time monitoring of volcanic activities, especially for the detection of lava flows and volcanic thermal anomalies.This study presents the current status of typical sensors used for infrared remote sensing of volcanic hotspots and summarizes the methodology for detecting volcanic hotspots by using satellite infrared data. First, the history of thermal infrared satellite data monitoring and satellite system development is summarized. Notably, various types of algorithms and satellite systems have been applied to make the monitoring of volcanic activities at the global scale efficient and accurate. Second, the development of volcanic hotspot identification algorithms is analyzed, and existing volcanic hotspot identification algorithms are classified into four categories in accordance with the different characteristics of the volcano used and its surrounding features (spatial/temporal). The four algorithm categories are spatial feature, temporal feature, comprehensive feature, and artificial intelligence algorithms. The spatial feature algorithms are categorized into fixed and dynamic threshold methods on the basis of different methods of threshold selection (fixed/dynamic threshold). On the basis of the classification above, we describe the current status of the volcanic hotspot identification algorithms and summarize their data, scope of application, and application limitations to provide a comprehensive classification and assessment for understanding and improving volcano hotspot detection technology. Such classification and assessment are crucial for the development of future volcano thermal remote sensing theories and technologies.Subsequent research should improve the adaptability of the algorithms to different volcanic environments, combine the advantages of traditional algorithms and artificial intelligence, and utilize historical data and time-series analyses to identify volcanic hotspots accurately. In addition, the fusion of high-resolution and multispectral satellite data can improve the spatial and spectral resolutions of volcanic activity monitoring, thus capturing the microfeatures of volcanoes accurately. These improvements will enhance the comprehensiveness and accuracy of volcanic hotspot monitoring and provide reliable support for the monitoring, early warning, and prevention of geologic hazards.关键词:volcanic lava flows;thermal remote sensing;infrared satellite data;volcano monitoring;thermal anomalies;hotspot automatic detection;algorithm classification;disaster prevention and reduction336|573|0更新时间:2025-04-21
摘要:Volcano monitoring is essential for predicting volcanic eruptions and implementing early warning measures. Traditional ground-based monitoring methods cannot fully cover all volcanoes. Satellite remote sensing technology, with its advantages of global coverage and high temporal and spatial resolutions, is an important complement for near-real-time monitoring of volcanic activities, especially for the detection of lava flows and volcanic thermal anomalies.This study presents the current status of typical sensors used for infrared remote sensing of volcanic hotspots and summarizes the methodology for detecting volcanic hotspots by using satellite infrared data. First, the history of thermal infrared satellite data monitoring and satellite system development is summarized. Notably, various types of algorithms and satellite systems have been applied to make the monitoring of volcanic activities at the global scale efficient and accurate. Second, the development of volcanic hotspot identification algorithms is analyzed, and existing volcanic hotspot identification algorithms are classified into four categories in accordance with the different characteristics of the volcano used and its surrounding features (spatial/temporal). The four algorithm categories are spatial feature, temporal feature, comprehensive feature, and artificial intelligence algorithms. The spatial feature algorithms are categorized into fixed and dynamic threshold methods on the basis of different methods of threshold selection (fixed/dynamic threshold). On the basis of the classification above, we describe the current status of the volcanic hotspot identification algorithms and summarize their data, scope of application, and application limitations to provide a comprehensive classification and assessment for understanding and improving volcano hotspot detection technology. Such classification and assessment are crucial for the development of future volcano thermal remote sensing theories and technologies.Subsequent research should improve the adaptability of the algorithms to different volcanic environments, combine the advantages of traditional algorithms and artificial intelligence, and utilize historical data and time-series analyses to identify volcanic hotspots accurately. In addition, the fusion of high-resolution and multispectral satellite data can improve the spatial and spectral resolutions of volcanic activity monitoring, thus capturing the microfeatures of volcanoes accurately. These improvements will enhance the comprehensiveness and accuracy of volcanic hotspot monitoring and provide reliable support for the monitoring, early warning, and prevention of geologic hazards.关键词:volcanic lava flows;thermal remote sensing;infrared satellite data;volcano monitoring;thermal anomalies;hotspot automatic detection;algorithm classification;disaster prevention and reduction336|573|0更新时间:2025-04-21 - “地理学第二定律揭示空间数据异质性,地理加权回归技术应运而生,覆盖描述性、探索性、解释性和预测模拟等分析需求。专家系统梳理技术框架,为空间异质性量化分析提供新思路。”
 摘要:Spatial heterogeneity or nonstationarity in spatial data and relationships has elicited increasing attention in the field of spatial statistics. To explore this fundamental phenomenon, researchers have extensively developed place- or location-specific methods and local statistical techniques that assume data relationships to be spatially variant. In line with the principle of spatial dependence depicted by the first law of geography, the Geographically Weighted (GW) regression technique was proposed to incorporate spatial weights into location-wise regression model calibrations to highlight spatial heterogeneities in data relationships by outputting spatially varying coefficient estimates. With this distance-decaying schema for calculating spatial weights, a series of GW models has been proposed for fine-scaled spatial analysis in descriptive, explanatory, interpretive, and predictive scenarios, including GW descriptive statistics, basic GW regression and extensions, GW discriminant analysis, GW principal component analysis, GW machine learning, and GW artificial neural network. These GW models form a continually evolving technical framework for identifying spatially nonstationary features or patterns in various disciplines or fields, including geography, social science, biology, public health, and environment science.In this study, we systematically sorted the theoretical and technical frameworks of GW models. First, we summarized the essence and rules for applying the family of GW models, including catering for spatially heterogeneous or nonstationary features and relationships in geographic variables and outputting location-dependent metrics or estimates by calculating the spatial weight matrix and the distance-decaying principle of spatial dependence presented by Tobler’s first law of geography. With regard to the common and fundamental parts of GW models, we conducted hypothesis tests on spatial heterogeneity or nonstationarity, provided a general definition of distance metrics in geography, calculated spatial weights, and performed bandwidth optimization.With regard to descriptive, explanatory, interpretive, and predictive scenarios, the potential usages of each GW model were discussed from four analysis perspectives. We recommend the use of univariate GW descriptive statistics, such as GW average, GW quantile, GW standard deviation, and GW skewness, to help users grasp the spatially heterogeneous distribution of a geographic variable. For exploratory data analysis with multivariate spatial data, the GW correlation coefficient and GW principal component analysis are recommended. GW regression and its rich extensions, especially multiscale GW regression, are powerful tools in interpretive analysis and have been widely applied. When data relationships are studied comprehensively, accurate predictions are usually obtained in data analytics. The usages of GW regression and geographically and temporally weighted regression in predictions are straightforward, and the prediction accuracy is further improved when artificial intelligence technologies, such as GW machine learning, GW artificial neural network, and geographically neural network weighted regression, are incorporated.The increasing popularity of GW models has resulted in the development of several software packages, standalone programs, and toolkits, including the R package GWmodel and GWmodelS, which are new, free, user-friendly, high-performance standalone software that incorporate spatial data management and mapping tools and GW model functions. However, further improvement is needed before GW models can become all-around, quantitative, analytical frameworks for spatial heterogeneity because of drawbacks in theoretical foundation, technical completeness, complementarity, and evolution to spatiotemporal dimensions.关键词:spatial heterogeneity;Spatial dependence;Quantitive analysis;Spatial non-stationarity;spatial statistics440|787|0更新时间:2025-04-21
摘要:Spatial heterogeneity or nonstationarity in spatial data and relationships has elicited increasing attention in the field of spatial statistics. To explore this fundamental phenomenon, researchers have extensively developed place- or location-specific methods and local statistical techniques that assume data relationships to be spatially variant. In line with the principle of spatial dependence depicted by the first law of geography, the Geographically Weighted (GW) regression technique was proposed to incorporate spatial weights into location-wise regression model calibrations to highlight spatial heterogeneities in data relationships by outputting spatially varying coefficient estimates. With this distance-decaying schema for calculating spatial weights, a series of GW models has been proposed for fine-scaled spatial analysis in descriptive, explanatory, interpretive, and predictive scenarios, including GW descriptive statistics, basic GW regression and extensions, GW discriminant analysis, GW principal component analysis, GW machine learning, and GW artificial neural network. These GW models form a continually evolving technical framework for identifying spatially nonstationary features or patterns in various disciplines or fields, including geography, social science, biology, public health, and environment science.In this study, we systematically sorted the theoretical and technical frameworks of GW models. First, we summarized the essence and rules for applying the family of GW models, including catering for spatially heterogeneous or nonstationary features and relationships in geographic variables and outputting location-dependent metrics or estimates by calculating the spatial weight matrix and the distance-decaying principle of spatial dependence presented by Tobler’s first law of geography. With regard to the common and fundamental parts of GW models, we conducted hypothesis tests on spatial heterogeneity or nonstationarity, provided a general definition of distance metrics in geography, calculated spatial weights, and performed bandwidth optimization.With regard to descriptive, explanatory, interpretive, and predictive scenarios, the potential usages of each GW model were discussed from four analysis perspectives. We recommend the use of univariate GW descriptive statistics, such as GW average, GW quantile, GW standard deviation, and GW skewness, to help users grasp the spatially heterogeneous distribution of a geographic variable. For exploratory data analysis with multivariate spatial data, the GW correlation coefficient and GW principal component analysis are recommended. GW regression and its rich extensions, especially multiscale GW regression, are powerful tools in interpretive analysis and have been widely applied. When data relationships are studied comprehensively, accurate predictions are usually obtained in data analytics. The usages of GW regression and geographically and temporally weighted regression in predictions are straightforward, and the prediction accuracy is further improved when artificial intelligence technologies, such as GW machine learning, GW artificial neural network, and geographically neural network weighted regression, are incorporated.The increasing popularity of GW models has resulted in the development of several software packages, standalone programs, and toolkits, including the R package GWmodel and GWmodelS, which are new, free, user-friendly, high-performance standalone software that incorporate spatial data management and mapping tools and GW model functions. However, further improvement is needed before GW models can become all-around, quantitative, analytical frameworks for spatial heterogeneity because of drawbacks in theoretical foundation, technical completeness, complementarity, and evolution to spatiotemporal dimensions.关键词:spatial heterogeneity;Spatial dependence;Quantitive analysis;Spatial non-stationarity;spatial statistics440|787|0更新时间:2025-04-21
Reviews
- “风场测量雷达作为风云系列气象卫星的首部主动遥感仪器,其在轨状态良好,性能指标达到预期,为全球海面风场等参数测量提供解决方案。”
 摘要:The wind radar (WindRAD) onboard the Fengyun-3E (FY-3E) meteorological satellite is the first active remote sensing instrument of Chinese Fengyun series satellites and the first spaceborne dual-frequency and dual-polarization scatterometer in the world. Spaceborne scatterometer is important remote sensing instrument for measuring meteorological and ocean parameters to obtain geophysical parameters, such as wind speed and wind direction, on the global ocean surface through backscattering measurement of the earth system. WindRAD uses an advanced fan beam with a conical scanning system and primarily aims to measure the sea surface wind vector under all weather conditions and throughout the day with high precision and resolution. In addition, WindRAD can measure soil moisture, sea ice, and other geophysical parameters. This study aims to provide a preliminary evaluation of the in-orbit state and performance of WindRAD after its launch. The observation principle, signal characteristics, and main performance indicators of WindRAD are introduced, and a detailed data preprocessing method, that is, Level 1 processing, is proposed to generate the backscattering coefficient of the global land and sea surface. On the basis of WindRAD in-orbit test after its launch in 2021, the performance of the instrument is preliminarily analyzed. The key telemetry parameters, including rotation speed, internal calibration value, and temperatures of important components, are assessed. Azimuth resolution, range resolution, observation swath width, radiometric resolution, and internal calibration accuracy are evaluated using actual WindRAD remote sensing data and the parameters measured before the launch. Analysis results show that WindRAD works steadily in orbit, and all of the performance indicators meet expectations. WindRAD can provide high-quality backscattering coefficient data at C and Ku bands for product retrieval. This work paves the way for the remote sensing, assimilation, and weather forecast applications of WindRAD. WindRAD observation data are received and processed in the FY-3E satellite ground system. The operational data are available to users worldwide and can be obtained from the FENGYUN Satellite Data Center of National Satellite Meteorological Center, China Meteorological Administration (http://satellite.nsmc.org.cn/PortalSite/Data/DataView.aspx).关键词:remote sensing;Wind Radar;scatterometer;instrument performance;in-orbit test;radiometric resolution;data preprocessing;FY-3470|397|0更新时间:2025-04-21
摘要:The wind radar (WindRAD) onboard the Fengyun-3E (FY-3E) meteorological satellite is the first active remote sensing instrument of Chinese Fengyun series satellites and the first spaceborne dual-frequency and dual-polarization scatterometer in the world. Spaceborne scatterometer is important remote sensing instrument for measuring meteorological and ocean parameters to obtain geophysical parameters, such as wind speed and wind direction, on the global ocean surface through backscattering measurement of the earth system. WindRAD uses an advanced fan beam with a conical scanning system and primarily aims to measure the sea surface wind vector under all weather conditions and throughout the day with high precision and resolution. In addition, WindRAD can measure soil moisture, sea ice, and other geophysical parameters. This study aims to provide a preliminary evaluation of the in-orbit state and performance of WindRAD after its launch. The observation principle, signal characteristics, and main performance indicators of WindRAD are introduced, and a detailed data preprocessing method, that is, Level 1 processing, is proposed to generate the backscattering coefficient of the global land and sea surface. On the basis of WindRAD in-orbit test after its launch in 2021, the performance of the instrument is preliminarily analyzed. The key telemetry parameters, including rotation speed, internal calibration value, and temperatures of important components, are assessed. Azimuth resolution, range resolution, observation swath width, radiometric resolution, and internal calibration accuracy are evaluated using actual WindRAD remote sensing data and the parameters measured before the launch. Analysis results show that WindRAD works steadily in orbit, and all of the performance indicators meet expectations. WindRAD can provide high-quality backscattering coefficient data at C and Ku bands for product retrieval. This work paves the way for the remote sensing, assimilation, and weather forecast applications of WindRAD. WindRAD observation data are received and processed in the FY-3E satellite ground system. The operational data are available to users worldwide and can be obtained from the FENGYUN Satellite Data Center of National Satellite Meteorological Center, China Meteorological Administration (http://satellite.nsmc.org.cn/PortalSite/Data/DataView.aspx).关键词:remote sensing;Wind Radar;scatterometer;instrument performance;in-orbit test;radiometric resolution;data preprocessing;FY-3470|397|0更新时间:2025-04-21 - “中法海洋卫星CFOSAT搭载的海浪波谱仪SWIM对降雨事件存在低估,本研究改进MP算法,提高降雨识别准确度。”
 摘要:Rain flag is necessary for Ku-band altimeters because the presence of rain in the subsatellite track causes backscatter signal attenuation, which can lead to errors in altimeter products. The Surface Wave Investigation and Monitoring (SWIM) instrument payload on the China-France Oceanography Satellite is a Ku-band (13.575 GHz) real-aperture radar that illuminates the surface sequentially at six incidence angles. The nadir beam of SWIM can be used as an altimeter, except for measuring the sea surface height. The rain events identified by the rain flag in SWIM L2 nadir products offered by Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES) are underestimated compared with the rain events from Jason-3. Thus, the rain flag in SWIM L2 nadir products needs to be improved.The dual-frequency rain flag algorithm used in Jason-3 products cannot be applied in SWIM, which only works on the Ku band. To address this issue, this study introduced a rain flag that is based on the matching pursuit (MP) algorithm and modified it to make it applicable to SWIM, which is extremely versatile and can be easily adapted to any type of altimeter data. The along-track waveform of mispointing angles can easily be decomposed by the MP algorithm via wavelet packet decomposition. Then, the intervals where the mispointing angles present short-scale coherent variations are detected. Aside from rain events, σ0 blooms can also cause this kind of variations in the waveform of the mispointing angles. In this study, the along track waveform of σ0 is used to produce the rain flag. The flag produced by the MP algorithm where σ0 is over 15 dB and lasts for 6 s should be removed.The dual-frequency rain flag in Jason-3 products and that in the products of NASA’s Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals for Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) are used to test the performance of the SWIM rain flag presented in this study. The percentage of rain events given by the dual-frequency rain flag in Jason-3 is 3.1%, and that in the SWIM L2 nadir products offered by CNES is 1.03%. When the method presented in this study is used, the difference between the amounts of rain events in Jason-3 and SWIM is only 0.2%. When the rain rate exceeds 3 mm/h, the method performs better than the SWIM L2 nadir product. In addition, the consistency between Jason-3 and SWIM nadir rain flags in the method is good at low latitudes, but it will decrease if latitudes are larger than 40°.The number of rain flags in SWIM L2 nadir products at present is underestimated. This study provides a new SWIM nadir rain flag on the basis of the MP algorithm. Compared with other kinds of rain flag, this new rain flag can be used in altimeter work on a single Ku band without radiometers. The difference is that after the waveform composed of radar mispointing angles is processed by the MP algorithm, the backscatter coefficients is considered, and a sliding window is added to reduce the influence of the σ0 bloom. After collocation with high-resolution observation by GPM, the results show that the rain flag defined by this new method performs well when rain rate is greater than 3 mm/h and consistent with the dual-frequency rain flag. However, when latitudes are larger than 40°, consistency declines, and the reason needs further research.关键词:microwave remote sensing;Ku-band altimeter;CFOSAT;radar waveform;SWIM;MP algorithm;rain flag;σ0-bloom112|277|0更新时间:2025-04-21
摘要:Rain flag is necessary for Ku-band altimeters because the presence of rain in the subsatellite track causes backscatter signal attenuation, which can lead to errors in altimeter products. The Surface Wave Investigation and Monitoring (SWIM) instrument payload on the China-France Oceanography Satellite is a Ku-band (13.575 GHz) real-aperture radar that illuminates the surface sequentially at six incidence angles. The nadir beam of SWIM can be used as an altimeter, except for measuring the sea surface height. The rain events identified by the rain flag in SWIM L2 nadir products offered by Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES) are underestimated compared with the rain events from Jason-3. Thus, the rain flag in SWIM L2 nadir products needs to be improved.The dual-frequency rain flag algorithm used in Jason-3 products cannot be applied in SWIM, which only works on the Ku band. To address this issue, this study introduced a rain flag that is based on the matching pursuit (MP) algorithm and modified it to make it applicable to SWIM, which is extremely versatile and can be easily adapted to any type of altimeter data. The along-track waveform of mispointing angles can easily be decomposed by the MP algorithm via wavelet packet decomposition. Then, the intervals where the mispointing angles present short-scale coherent variations are detected. Aside from rain events, σ0 blooms can also cause this kind of variations in the waveform of the mispointing angles. In this study, the along track waveform of σ0 is used to produce the rain flag. The flag produced by the MP algorithm where σ0 is over 15 dB and lasts for 6 s should be removed.The dual-frequency rain flag in Jason-3 products and that in the products of NASA’s Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals for Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) are used to test the performance of the SWIM rain flag presented in this study. The percentage of rain events given by the dual-frequency rain flag in Jason-3 is 3.1%, and that in the SWIM L2 nadir products offered by CNES is 1.03%. When the method presented in this study is used, the difference between the amounts of rain events in Jason-3 and SWIM is only 0.2%. When the rain rate exceeds 3 mm/h, the method performs better than the SWIM L2 nadir product. In addition, the consistency between Jason-3 and SWIM nadir rain flags in the method is good at low latitudes, but it will decrease if latitudes are larger than 40°.The number of rain flags in SWIM L2 nadir products at present is underestimated. This study provides a new SWIM nadir rain flag on the basis of the MP algorithm. Compared with other kinds of rain flag, this new rain flag can be used in altimeter work on a single Ku band without radiometers. The difference is that after the waveform composed of radar mispointing angles is processed by the MP algorithm, the backscatter coefficients is considered, and a sliding window is added to reduce the influence of the σ0 bloom. After collocation with high-resolution observation by GPM, the results show that the rain flag defined by this new method performs well when rain rate is greater than 3 mm/h and consistent with the dual-frequency rain flag. However, when latitudes are larger than 40°, consistency declines, and the reason needs further research.关键词:microwave remote sensing;Ku-band altimeter;CFOSAT;radar waveform;SWIM;MP algorithm;rain flag;σ0-bloom112|277|0更新时间:2025-04-21 - “最新研究揭示了风云二号卫星降水产品与国际GPM产品在误差特性上的差异,为改进卫星降水反演算法提供重要参考。”
 摘要:Characterizing error components (including systematic and random components) is essential to improve precipitation retrieval algorithms and develop bias adjustment techniques. Benchmarked by the Chinese merged precipitation analysis dataset derived based on automatic weather stations, the errors of satellite precipitation estimates from Fengyun 2 (FY-2F and FY-2G) and the mainstream Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM; IMERG-Final and GSMaP-Gauge) are decomposed into systematic and random components at the hourly scale. The comprehensive performance of the systematic and random errors of the four products are revealed from the perspectives of spatial distribution, temporal pattern, rainfall intensity distribution, and elevation distribution. (1) The systematic errors of FY-2G and FY-2H over Mainland China are close to those of IMERG-Final and GSMaP-Gauge, among which IMERG-Final has the lowest systematic errors. FY-2G and FY-2H adopt only infrared observations as data sources in their precipitation retrieval algorithms, whereas IMERG-Final and GSMaP-Gauge adopt not only infrared data but also high-accuracy microwave data as the data sources. However, the systematic errors of FY-2G and FY-2H reach the level of GPM precipitation products because of the relatively dense gauge networks in the satellite–gauge merging procedure of FY-2G and FY-2H. (2) GSMaP-Gauge has the lowest random errors over Mainland China among the four satellite precipitation estimates. The gap between FY-2G and FY-2H in relation to GPM precipitation products is mainly manifested in the random errors. Particularly, the random errors of IMERG-Final and GSMaP-Gauge over the eastern monsoon and northern arid regions are much lower than those of FY-2G and FY-2H in summer. (3) IMERG-Final has much lower systematic errors at different elevations compared with the three other precipitation products, and GSMaP-Gauge, FY-2G, and FY-2H have close systematic errors at different elevations. The random errors of the four precipitation products vary considerably at different elevations, and GSMaP-Gauge always has the lowest random errors at different elevations. Moreover, IMERG-Final has lower systematic errors than FY-2H and FY-2G only below the altitude of 3,000 m because of the high uncertainty of IMERG-Final over the Tibetan Plateau. IMERG-Final and GSMaP-Gauge perform better than FY-2G and FY-2H over Mainland China, and FY-2-based precipitation estimates still have much room for improvement compared with mainstream GPM-based precipitation estimates.关键词:FY-2;GPM;satellite precipitation estimates;systematic errors;random errors;China117|80|0更新时间:2025-04-21
摘要:Characterizing error components (including systematic and random components) is essential to improve precipitation retrieval algorithms and develop bias adjustment techniques. Benchmarked by the Chinese merged precipitation analysis dataset derived based on automatic weather stations, the errors of satellite precipitation estimates from Fengyun 2 (FY-2F and FY-2G) and the mainstream Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM; IMERG-Final and GSMaP-Gauge) are decomposed into systematic and random components at the hourly scale. The comprehensive performance of the systematic and random errors of the four products are revealed from the perspectives of spatial distribution, temporal pattern, rainfall intensity distribution, and elevation distribution. (1) The systematic errors of FY-2G and FY-2H over Mainland China are close to those of IMERG-Final and GSMaP-Gauge, among which IMERG-Final has the lowest systematic errors. FY-2G and FY-2H adopt only infrared observations as data sources in their precipitation retrieval algorithms, whereas IMERG-Final and GSMaP-Gauge adopt not only infrared data but also high-accuracy microwave data as the data sources. However, the systematic errors of FY-2G and FY-2H reach the level of GPM precipitation products because of the relatively dense gauge networks in the satellite–gauge merging procedure of FY-2G and FY-2H. (2) GSMaP-Gauge has the lowest random errors over Mainland China among the four satellite precipitation estimates. The gap between FY-2G and FY-2H in relation to GPM precipitation products is mainly manifested in the random errors. Particularly, the random errors of IMERG-Final and GSMaP-Gauge over the eastern monsoon and northern arid regions are much lower than those of FY-2G and FY-2H in summer. (3) IMERG-Final has much lower systematic errors at different elevations compared with the three other precipitation products, and GSMaP-Gauge, FY-2G, and FY-2H have close systematic errors at different elevations. The random errors of the four precipitation products vary considerably at different elevations, and GSMaP-Gauge always has the lowest random errors at different elevations. Moreover, IMERG-Final has lower systematic errors than FY-2H and FY-2G only below the altitude of 3,000 m because of the high uncertainty of IMERG-Final over the Tibetan Plateau. IMERG-Final and GSMaP-Gauge perform better than FY-2G and FY-2H over Mainland China, and FY-2-based precipitation estimates still have much room for improvement compared with mainstream GPM-based precipitation estimates.关键词:FY-2;GPM;satellite precipitation estimates;systematic errors;random errors;China117|80|0更新时间:2025-04-21
Atmosphere and Ocean
- “在森林火灾预防领域,专家建立了综合火险评估模型,为准确评估火险情况提供解决方案。”
 摘要:In recent years, the frequent occurrence of forest fires has considerably affected people’s normal work and life and the natural ecosystem. Fire hazard assessment is crucial to the prevention of forest fire and the allocation of fire resources. This study collects historical forest fire events in China from 2002 to 2020. The events are distributed in five climate regions in China, namely, plateau mountain, temperate continental, temperate monsoon, subtropical monsoon, and tropical monsoon climate regions. The meteorological factors, vegetation indices, and topographic factors in the different regions are integrated, and the random forest method is used to establish a comprehensive forest fire hazard assessment model. Fire influencing factors are calculated from different data products, fire events are selected using FIRMS images, meteorological factors are calculated using ERA5-land data, topographic factors are calculated using Shuttle Radar Topography Mission’s digital elevation model products, and vegetation indices are computed using the MODIS reflectance product MCD43A4. The fire hazard assessment model can predict the time series of fire hazards and evaluate the spatial distribution of these hazards. The fire occurrence location revealed by the test data differs from that from the training data. Test case results show that the accuracy of the established fire hazard assessment model is high, and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve reaches 0.84, which produces good results in the time series prediction and spatial distribution assessment of forest fire hazards. Moreover, the predicted fire hazard value is close to the precalibrated fire hazard value. The results of the time series prediction and evaluation of fire hazard spatial distribution are good and close to the values in actual situations. Furthermore, the proposed model ranks the importance of the factors affecting the occurrence of fires. The most important factor is the annual diurnal sequence, which reflects the seasonal factor, followed by moisture and vegetation growth. The importance of topographic factors is low. Importance ranking can help in understanding the driving effects of different factors on the occurrence of fires and identifying which factors exert substantial effects on the occurrence of forest fires. Although the areas of forest fire occurrence and the factors that affect fire occurrence differ, the change rule of the fire hazard value is similar, that is, the fire hazard value is high in the week before the fire and low in other times. The spatial distribution of fire hazards is reasonable, and the fire hazard value in the fire area gradually increases from two months before the fire to the day of the fire. Moreover, the fire hazard value in the same area one year before the fire is much lower than the fire hazard value on the day of the fire, indicating an accurate assessment of the fire hazard situation. The proposed forest fire hazard assessment model involves comprehensive indicators, which can accurately assess fire hazard situations. It can be applied to different regions in China to partially solve the problem of regional restrictions.关键词:forest fire;fire hazard;remote sensing;Random Forest;hazard monitoring995|631|0更新时间:2025-04-21
摘要:In recent years, the frequent occurrence of forest fires has considerably affected people’s normal work and life and the natural ecosystem. Fire hazard assessment is crucial to the prevention of forest fire and the allocation of fire resources. This study collects historical forest fire events in China from 2002 to 2020. The events are distributed in five climate regions in China, namely, plateau mountain, temperate continental, temperate monsoon, subtropical monsoon, and tropical monsoon climate regions. The meteorological factors, vegetation indices, and topographic factors in the different regions are integrated, and the random forest method is used to establish a comprehensive forest fire hazard assessment model. Fire influencing factors are calculated from different data products, fire events are selected using FIRMS images, meteorological factors are calculated using ERA5-land data, topographic factors are calculated using Shuttle Radar Topography Mission’s digital elevation model products, and vegetation indices are computed using the MODIS reflectance product MCD43A4. The fire hazard assessment model can predict the time series of fire hazards and evaluate the spatial distribution of these hazards. The fire occurrence location revealed by the test data differs from that from the training data. Test case results show that the accuracy of the established fire hazard assessment model is high, and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve reaches 0.84, which produces good results in the time series prediction and spatial distribution assessment of forest fire hazards. Moreover, the predicted fire hazard value is close to the precalibrated fire hazard value. The results of the time series prediction and evaluation of fire hazard spatial distribution are good and close to the values in actual situations. Furthermore, the proposed model ranks the importance of the factors affecting the occurrence of fires. The most important factor is the annual diurnal sequence, which reflects the seasonal factor, followed by moisture and vegetation growth. The importance of topographic factors is low. Importance ranking can help in understanding the driving effects of different factors on the occurrence of fires and identifying which factors exert substantial effects on the occurrence of forest fires. Although the areas of forest fire occurrence and the factors that affect fire occurrence differ, the change rule of the fire hazard value is similar, that is, the fire hazard value is high in the week before the fire and low in other times. The spatial distribution of fire hazards is reasonable, and the fire hazard value in the fire area gradually increases from two months before the fire to the day of the fire. Moreover, the fire hazard value in the same area one year before the fire is much lower than the fire hazard value on the day of the fire, indicating an accurate assessment of the fire hazard situation. The proposed forest fire hazard assessment model involves comprehensive indicators, which can accurately assess fire hazard situations. It can be applied to different regions in China to partially solve the problem of regional restrictions.关键词:forest fire;fire hazard;remote sensing;Random Forest;hazard monitoring995|631|0更新时间:2025-04-21 - “最新研究揭示煤层气微渗漏对植被SIF影响,为煤层气遥感判别提供科学依据。”
 摘要:Coalbed methane (CBM) is a self-generated, self-storage, unconventional clean energy source in coal seams and surrounding rock formations. In CBM-enriched areas, hydrocarbon microseepage changes the chemical composition and chemical environment and blocks plant root respiration. As a result, the chloroplast synthesis process is hindered, thus inhibiting photosynthesis and vegetation growth and eventually leading to abnormal changes in vegetation solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF). Therefore, the abnormality of vegetation SIF can be an essential clue for remote sensing surveys of potential CBM-enriched areas.First, this study selects the southern Qinshui Basin (Qinshui County) in Shanxi Province as the research area. Utilizing 0.05° GOSIF satellite Solar-Induced Chlorophyll Fluorescence (SIF) data, we apply a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) downscaling method including three 3×3 convolutional layers and two fully connected layers to derive 1 km resolution SIF data for the region from 2000 to 2020. Second, the vegetation-covered region in the study area is classified into farmland, grassland, and woodland, using the GLC_FCS30-2020 land cover data to enable stratified analysis and control for vegetation-type specific effects. Third, the spatial and temporal variation characteristics of vegetation SIF in the CBM-enriched areas are categorized and discussed. Sen’s slope estimator and Mann-Kendall (MK) tests are employed to analyze spatiotemporal SIF trends. Last, the possible reasons for the abnormal variation in vegetation SIF in the CBM-enriched areas are analyzed through a comparison of the study area and the control area.Results reveal distinct SIF patternsfrom June to September, forestland exhibits the highest mean SIF (0.259—0.290 W/m²·μm·sr), followed by grasslands and farmlands. Almost all vegetation types showed significant SIF increases (p<0.01) from 2000 to 2020. Farmland demonstrates the highest growth rates (4.15% in June) and the highest growth speed (0.0060 W/(m2·μm·sr·a)) followed by grassland and woodland. Notably, woodland SIF in CBM-enriched areas shows a distinct spatial pattern: lower values compared to adjacent control regions in forested zones, whereas higher levels are observed in grassland and farmland ecosystems.The SIF values of woodland in the CBM-enriched area are minimally affected by artificial factors and substantially lower than those in the control area. Results indicate that compared with other influencing factors, hydrocarbon microseepage in CBM-enriched areas is more likely to affect forest land. This study empirically shows that hydrocarbon microseepage in CBM-enriched areas may have a considerable effect on vegetation SIF. Through statistical analysis of multi-year spatiotemporal variations in SIF data and field investigations, this study has preliminarily ruled out the stress effects of sporadic factors such as drought and pests/diseases on woodland. Regarding the consistently lower SIF values observed in coalbed methane-enriched woodland, whether other underlying causes exist requires further in-depth field observations and quantitative analysis in future research.关键词:coalbed methane;solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence;spatiotemporal change;vegetation growth stress;hydrocarbon micro-seepage;downscaling;convolutional neural network;Qinshui basin129|377|0更新时间:2025-04-21
摘要:Coalbed methane (CBM) is a self-generated, self-storage, unconventional clean energy source in coal seams and surrounding rock formations. In CBM-enriched areas, hydrocarbon microseepage changes the chemical composition and chemical environment and blocks plant root respiration. As a result, the chloroplast synthesis process is hindered, thus inhibiting photosynthesis and vegetation growth and eventually leading to abnormal changes in vegetation solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF). Therefore, the abnormality of vegetation SIF can be an essential clue for remote sensing surveys of potential CBM-enriched areas.First, this study selects the southern Qinshui Basin (Qinshui County) in Shanxi Province as the research area. Utilizing 0.05° GOSIF satellite Solar-Induced Chlorophyll Fluorescence (SIF) data, we apply a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) downscaling method including three 3×3 convolutional layers and two fully connected layers to derive 1 km resolution SIF data for the region from 2000 to 2020. Second, the vegetation-covered region in the study area is classified into farmland, grassland, and woodland, using the GLC_FCS30-2020 land cover data to enable stratified analysis and control for vegetation-type specific effects. Third, the spatial and temporal variation characteristics of vegetation SIF in the CBM-enriched areas are categorized and discussed. Sen’s slope estimator and Mann-Kendall (MK) tests are employed to analyze spatiotemporal SIF trends. Last, the possible reasons for the abnormal variation in vegetation SIF in the CBM-enriched areas are analyzed through a comparison of the study area and the control area.Results reveal distinct SIF patternsfrom June to September, forestland exhibits the highest mean SIF (0.259—0.290 W/m²·μm·sr), followed by grasslands and farmlands. Almost all vegetation types showed significant SIF increases (p<0.01) from 2000 to 2020. Farmland demonstrates the highest growth rates (4.15% in June) and the highest growth speed (0.0060 W/(m2·μm·sr·a)) followed by grassland and woodland. Notably, woodland SIF in CBM-enriched areas shows a distinct spatial pattern: lower values compared to adjacent control regions in forested zones, whereas higher levels are observed in grassland and farmland ecosystems.The SIF values of woodland in the CBM-enriched area are minimally affected by artificial factors and substantially lower than those in the control area. Results indicate that compared with other influencing factors, hydrocarbon microseepage in CBM-enriched areas is more likely to affect forest land. This study empirically shows that hydrocarbon microseepage in CBM-enriched areas may have a considerable effect on vegetation SIF. Through statistical analysis of multi-year spatiotemporal variations in SIF data and field investigations, this study has preliminarily ruled out the stress effects of sporadic factors such as drought and pests/diseases on woodland. Regarding the consistently lower SIF values observed in coalbed methane-enriched woodland, whether other underlying causes exist requires further in-depth field observations and quantitative analysis in future research.关键词:coalbed methane;solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence;spatiotemporal change;vegetation growth stress;hydrocarbon micro-seepage;downscaling;convolutional neural network;Qinshui basin129|377|0更新时间:2025-04-21 -
Analysis of groundwater storage anomaly and multisource influencing factors in the North China Plain AI导读
“华北平原地下水储量变化研究揭示了近20年时空趋势及多源影响因素,为水资源管理提供参考。” 摘要:Groundwater is a pivotal source of water supply for agricultural and residential purposes in the North China Plain. However, the excessive exploitation of groundwater in the North China Plain has given rise to numerous ecological and environmental challenges in recent years. Therefore, exploring the shifts in water resources in this region over the past two decades is important for effective water management. Notably, the satellite alternation during 2017—2018 resulted in a notable gap in data, which poses challenges in comprehensively covering this transition period in relevant studies, thus constraining the analysis scope and depth.To address this issue, this study employed the singular spectrum analysis method to interpolate and fill in the missing GRACE Mascon gravity satellite data. Furthermore, GRACE CSR Mascon RL06 gravity satellite data, GLDAS model data, and irrigation water use data were adopted to investigate the spatial and temporal patterns of water storage changes in the North China Plain from 2002 to 2022. By integrating precipitation station data, wheat distribution data, and luminous radiation intensity distribution data, we examined the effects of precipitation, agricultural water use, and domestic water use on the spatiotemporal changes in water storage in the region. This comprehensive approach that considers the main income and expenditure items of groundwater resources offers a robust framework for analyzing the intricate water dynamics in the North China Plain.The study yielded several key findings. (1) Groundwater storage anomaly in the North China Plain exhibited a decreasing trend, with rates of -0.19 and -1.69 cm/a during 2002—2011 and 2012—2019, respectively, followed by an increase of 4.78 cm/a in 2020—2022. (2) Spatially, the northeastern part of the North China Plain presented an upward trend, and the southwestern part exhibited a downward trend between 2002 and 2022, with the north demonstrating a more prominent decrease compared with the south. (3) The average monthly water consumption for farmland irrigation in spring and summer was 2.42 cm/month, peaking at 5 cm/month. (4) The uneven spatial distribution of annual precipitation from 2002 to 2022 led to a pronounced decline in groundwater reserves, particularly in the northern section of the North China Plain. Spatial variations in agricultural and residential water usage considerably influenced the trends of groundwater reserve changes across the region. Notably, these spatial differences were mirrored in the varying degrees of agricultural and residential water consumption. The escalating agricultural and residential water demands exacerbated the already decreasing trend of groundwater storage in the northern part of the North China Plain. (5) The increase in monthly precipitation positively affected groundwater, and the direction of this relationship aligned with the variation in groundwater storage anomaly. These findings provide crucial insights into the complex dynamics of water resources in the North China Plain and can guide the formulation of effective water management strategies.This study examined the spatial and temporal patterns of groundwater storage anomaly in the North China Plain over recent years and revealed the intricate influence of multifaceted factors, including precipitation, agricultural water consumption, and domestic water utilization, on the dynamic anomaly in groundwater storage in this region.关键词:remote sensing;North China Plain;GRACE Mascon;SSA;groundwater storage anomaly;irrigation water use;precipitation;agricultural water use;residential water use;impact analysis412|469|0更新时间:2025-04-21
摘要:Groundwater is a pivotal source of water supply for agricultural and residential purposes in the North China Plain. However, the excessive exploitation of groundwater in the North China Plain has given rise to numerous ecological and environmental challenges in recent years. Therefore, exploring the shifts in water resources in this region over the past two decades is important for effective water management. Notably, the satellite alternation during 2017—2018 resulted in a notable gap in data, which poses challenges in comprehensively covering this transition period in relevant studies, thus constraining the analysis scope and depth.To address this issue, this study employed the singular spectrum analysis method to interpolate and fill in the missing GRACE Mascon gravity satellite data. Furthermore, GRACE CSR Mascon RL06 gravity satellite data, GLDAS model data, and irrigation water use data were adopted to investigate the spatial and temporal patterns of water storage changes in the North China Plain from 2002 to 2022. By integrating precipitation station data, wheat distribution data, and luminous radiation intensity distribution data, we examined the effects of precipitation, agricultural water use, and domestic water use on the spatiotemporal changes in water storage in the region. This comprehensive approach that considers the main income and expenditure items of groundwater resources offers a robust framework for analyzing the intricate water dynamics in the North China Plain.The study yielded several key findings. (1) Groundwater storage anomaly in the North China Plain exhibited a decreasing trend, with rates of -0.19 and -1.69 cm/a during 2002—2011 and 2012—2019, respectively, followed by an increase of 4.78 cm/a in 2020—2022. (2) Spatially, the northeastern part of the North China Plain presented an upward trend, and the southwestern part exhibited a downward trend between 2002 and 2022, with the north demonstrating a more prominent decrease compared with the south. (3) The average monthly water consumption for farmland irrigation in spring and summer was 2.42 cm/month, peaking at 5 cm/month. (4) The uneven spatial distribution of annual precipitation from 2002 to 2022 led to a pronounced decline in groundwater reserves, particularly in the northern section of the North China Plain. Spatial variations in agricultural and residential water usage considerably influenced the trends of groundwater reserve changes across the region. Notably, these spatial differences were mirrored in the varying degrees of agricultural and residential water consumption. The escalating agricultural and residential water demands exacerbated the already decreasing trend of groundwater storage in the northern part of the North China Plain. (5) The increase in monthly precipitation positively affected groundwater, and the direction of this relationship aligned with the variation in groundwater storage anomaly. These findings provide crucial insights into the complex dynamics of water resources in the North China Plain and can guide the formulation of effective water management strategies.This study examined the spatial and temporal patterns of groundwater storage anomaly in the North China Plain over recent years and revealed the intricate influence of multifaceted factors, including precipitation, agricultural water consumption, and domestic water utilization, on the dynamic anomaly in groundwater storage in this region.关键词:remote sensing;North China Plain;GRACE Mascon;SSA;groundwater storage anomaly;irrigation water use;precipitation;agricultural water use;residential water use;impact analysis412|469|0更新时间:2025-04-21 - “在水生态空间健康评价领域,专家构建了北京市水生态空间健康评价指标体系,为保护水生态系统提供解决方案。”
 摘要:Water is the source of life, and its ecological problems elicit extensive concern. The emergence of water ecological problems is related to the water body itself and to the structure and function of the ecosystem. The status of the ecological storeroom of water from the perspective of the whole ecosystem needs to be systematically considered to evaluate and alleviate water ecological problems. Water ecological space comprises various ecological spaces, including water spaces, such as rivers and lakes, shoreline space connecting water and land, and land space closely related to water resource protection. It can reflect the overall situation of the ecosystem related to water. Assessing the health condition of water ecological space is crucial for preserving the core structure and functions of the water ecosystem. However, studies on the comprehensive assessment of water ecological space are lacking, and the related assessment index systems are subject to ground observations and limited indicator categories. The objective of this study is to develop a comprehensive water ecological space health assessment framework on the basis of remote sensing for Beijing.The proposed framework consists of 11 assessment indicators covering the physical structure of ecological space, hydrology and water quality, and vegetation factors on land extracted from remote sensing data with a high spatial resolution. A water ecological space health index (WESHI) is established by integrating the 11 indicators with weights assigned by the combination of the analytical hierarchy process (subjectivity) and entropy weighting method (objectivity). The states of water ecological spaces are divided into four levels (healthy, good, moderate, and poor) on the basis of WESHI. Then, 10 typical water bodies in Beijing, including sources of surface water, landscape lakes, and rivers flowing through suburbs or urban areas, are selected as examples to apply the proposed comprehensive water ecological space health assessment framework.The weights of the assessment indicators demonstrate that hydrology and water quality are the dominant drivers for the health of water ecological space, followed by vegetation factors on land. The physical structure of ecological space has the least effect. The assessment results of the 10 selected water ecological spaces in Beijing reveal several important points. Tang River and Yongding River have the highest and lowest WESHI among all rivers respectively. The WESHI of Kunming Lake is slightly better than that of Yuanmingyuan Lake. Miyun Reservoir has a higher WESHI than Huairou Reservoir. Among the 10 typical water bodies in Beijing, Yongding River and Yuanmingyuan Lake have a good water ecological spaces, and the water ecological spaces of the other water bodies are at the healthy level. These results are consistent with actual situations.The proposed assessment framework can reasonably evaluate the health status of water ecological space in Beijing. Compared with traditional methods that rely on manual investigation, the proposed assessment framework that is based on remote sensing can assess the health status of water ecological space more quickly, comprehensively, and objectively. Moreover, on the basis of the assessment results, targeted ecological restoration is recommended for Yongding River and Yuanmingyuan Lake.关键词:remote sensing;water ecological space;health assessment;assessment framework;index weighting;Beijing;BJ-2 Satellite;comprehensive assessment index construction453|952|0更新时间:2025-04-21
摘要:Water is the source of life, and its ecological problems elicit extensive concern. The emergence of water ecological problems is related to the water body itself and to the structure and function of the ecosystem. The status of the ecological storeroom of water from the perspective of the whole ecosystem needs to be systematically considered to evaluate and alleviate water ecological problems. Water ecological space comprises various ecological spaces, including water spaces, such as rivers and lakes, shoreline space connecting water and land, and land space closely related to water resource protection. It can reflect the overall situation of the ecosystem related to water. Assessing the health condition of water ecological space is crucial for preserving the core structure and functions of the water ecosystem. However, studies on the comprehensive assessment of water ecological space are lacking, and the related assessment index systems are subject to ground observations and limited indicator categories. The objective of this study is to develop a comprehensive water ecological space health assessment framework on the basis of remote sensing for Beijing.The proposed framework consists of 11 assessment indicators covering the physical structure of ecological space, hydrology and water quality, and vegetation factors on land extracted from remote sensing data with a high spatial resolution. A water ecological space health index (WESHI) is established by integrating the 11 indicators with weights assigned by the combination of the analytical hierarchy process (subjectivity) and entropy weighting method (objectivity). The states of water ecological spaces are divided into four levels (healthy, good, moderate, and poor) on the basis of WESHI. Then, 10 typical water bodies in Beijing, including sources of surface water, landscape lakes, and rivers flowing through suburbs or urban areas, are selected as examples to apply the proposed comprehensive water ecological space health assessment framework.The weights of the assessment indicators demonstrate that hydrology and water quality are the dominant drivers for the health of water ecological space, followed by vegetation factors on land. The physical structure of ecological space has the least effect. The assessment results of the 10 selected water ecological spaces in Beijing reveal several important points. Tang River and Yongding River have the highest and lowest WESHI among all rivers respectively. The WESHI of Kunming Lake is slightly better than that of Yuanmingyuan Lake. Miyun Reservoir has a higher WESHI than Huairou Reservoir. Among the 10 typical water bodies in Beijing, Yongding River and Yuanmingyuan Lake have a good water ecological spaces, and the water ecological spaces of the other water bodies are at the healthy level. These results are consistent with actual situations.The proposed assessment framework can reasonably evaluate the health status of water ecological space in Beijing. Compared with traditional methods that rely on manual investigation, the proposed assessment framework that is based on remote sensing can assess the health status of water ecological space more quickly, comprehensively, and objectively. Moreover, on the basis of the assessment results, targeted ecological restoration is recommended for Yongding River and Yuanmingyuan Lake.关键词:remote sensing;water ecological space;health assessment;assessment framework;index weighting;Beijing;BJ-2 Satellite;comprehensive assessment index construction453|952|0更新时间:2025-04-21 - “海南岛SDG 6评估显示,2015至2021年可持续发展水平显著提升,海口市和三亚市得分最高。”
 摘要:The Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6) of water resources is the foundation on which other United Nations goals can be realized. Hainan Island, located in a tropical region, has abundant seawater resources, but its freshwater resource environment is fragile. Based on the United Nations Sustainable Development Assessment System and the actual situation of Hainan Island, this study localized the indicators of SDG 6, collected statistical and remote sensing data at the city and county levels, and adopted the natural water quality footprint indicators in the Co$ting Nature Ecosystem Service Model to construct a complete sustainable development assessment framework. Assessment of SDG 6 for the cities and counties on Hainan Island revealed several crucial points. The results indicate that: First, the SDG index scores (0—100 points) show that the level of sustainable development on Hainan Island has considerably improved, and most of the cities and counties on Hainan Island exhibited a spiral upward trend in their SDG 6 scores from 2015 to 2021. Second, among the 18 cities and counties, Haikou, the provincial capital, and Sanya, a tourist city, had the highest total SDG 6 index scores. Among them, Tunchang County, Wuzhishan City, and Qiongzhong Li and Miao Autonomous County were the top three in terms of growth; their growth rates were 91.4%, 74.2% and 73%, respectively. Third, the overall SDG 6 development level of Hainan Island is unevenly distributed, showing a spatial pattern of high in the central east, stable in the north and south, and low in the west. Based on the above, the ecosystem service indicators proposed in this study and the localized evaluation system for city and county levels of Hainan Island provide decision support for Hainan Province to implement the National Fourteenth Five-Year Plan and achieve the goals of Six Waters Joint Governance.关键词:remote sensing;SDG 6;Natural Footprint on Water Quality (NFWQ);water resource management and assessment;Co$ting nature ecosystem service model;Hainan Island272|443|0更新时间:2025-04-21
摘要:The Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6) of water resources is the foundation on which other United Nations goals can be realized. Hainan Island, located in a tropical region, has abundant seawater resources, but its freshwater resource environment is fragile. Based on the United Nations Sustainable Development Assessment System and the actual situation of Hainan Island, this study localized the indicators of SDG 6, collected statistical and remote sensing data at the city and county levels, and adopted the natural water quality footprint indicators in the Co$ting Nature Ecosystem Service Model to construct a complete sustainable development assessment framework. Assessment of SDG 6 for the cities and counties on Hainan Island revealed several crucial points. The results indicate that: First, the SDG index scores (0—100 points) show that the level of sustainable development on Hainan Island has considerably improved, and most of the cities and counties on Hainan Island exhibited a spiral upward trend in their SDG 6 scores from 2015 to 2021. Second, among the 18 cities and counties, Haikou, the provincial capital, and Sanya, a tourist city, had the highest total SDG 6 index scores. Among them, Tunchang County, Wuzhishan City, and Qiongzhong Li and Miao Autonomous County were the top three in terms of growth; their growth rates were 91.4%, 74.2% and 73%, respectively. Third, the overall SDG 6 development level of Hainan Island is unevenly distributed, showing a spatial pattern of high in the central east, stable in the north and south, and low in the west. Based on the above, the ecosystem service indicators proposed in this study and the localized evaluation system for city and county levels of Hainan Island provide decision support for Hainan Province to implement the National Fourteenth Five-Year Plan and achieve the goals of Six Waters Joint Governance.关键词:remote sensing;SDG 6;Natural Footprint on Water Quality (NFWQ);water resource management and assessment;Co$ting nature ecosystem service model;Hainan Island272|443|0更新时间:2025-04-21
Ecology and Environment
- “在计算机视觉领域,EllipticNet模型通过椭圆方程精确表示遥感有向目标,提升了检测性能和效率。”
 摘要:Remote sensing-oriented object detection is a challenging task in computer vision because traditional horizontal bounding box representations cannot accurately locate remote sensing targets that have various scales, arbitrary orientations, and dense arrangements. The widely used five-parameter oriented bounding box representation increases the complexity of model training because of the periodicity of the orientation angle and the interchangeability of edges. To address these issues, this study proposes an elliptical equation-based remote sensing-oriented object detection network called EllipticNet.EllipticNet decouples the problem of predicting the orientation angle into two subproblems quantitative angle regression and rotation direction classification. The proposed method combines the major and minor axes of the ellipse and its center to describe the remote sensing-oriented target accurately, thereby overcoming the boundary discontinuity problem of five-parameter oriented bounding box representation. Additionally, a novel ellipse-constrained loss function is designed to enhance the intrinsic geometric relationship between ellipse parameters, thus improving the robustness of EllipticNet training. A layer-wise dilated spatial pyramid pooling module is also proposed to substantially enhance EllipticNet’s ability to represent multiscale features.The proposed method is validated on three commonly used public remote sensing datasets, namely, DOTA, HRSC2016, and UCAS_AOD.Results demonstrate that the proposed method is competitive in terms of performance and efficiency and has practical value in remote sensing-oriented object detection.关键词:Oriented object detection;elliptic equation;feature enhancement;high resolution remote sensing image186|427|0更新时间:2025-04-21
摘要:Remote sensing-oriented object detection is a challenging task in computer vision because traditional horizontal bounding box representations cannot accurately locate remote sensing targets that have various scales, arbitrary orientations, and dense arrangements. The widely used five-parameter oriented bounding box representation increases the complexity of model training because of the periodicity of the orientation angle and the interchangeability of edges. To address these issues, this study proposes an elliptical equation-based remote sensing-oriented object detection network called EllipticNet.EllipticNet decouples the problem of predicting the orientation angle into two subproblems quantitative angle regression and rotation direction classification. The proposed method combines the major and minor axes of the ellipse and its center to describe the remote sensing-oriented target accurately, thereby overcoming the boundary discontinuity problem of five-parameter oriented bounding box representation. Additionally, a novel ellipse-constrained loss function is designed to enhance the intrinsic geometric relationship between ellipse parameters, thus improving the robustness of EllipticNet training. A layer-wise dilated spatial pyramid pooling module is also proposed to substantially enhance EllipticNet’s ability to represent multiscale features.The proposed method is validated on three commonly used public remote sensing datasets, namely, DOTA, HRSC2016, and UCAS_AOD.Results demonstrate that the proposed method is competitive in terms of performance and efficiency and has practical value in remote sensing-oriented object detection.关键词:Oriented object detection;elliptic equation;feature enhancement;high resolution remote sensing image186|427|0更新时间:2025-04-21 -
Method of extracting mangrove single-tree growth parameters based on combined airborne-ground LiDAR AI导读
“在红树林生物量估算领域,研究者提出了一种结合空地LiDAR数据的红树林单木生长参数提取方法,有效提升了红树生长参数提取精度,为红树林碳汇能力评估提供技术支撑。” 摘要:Mangrove is a woody plant community growing in tropical and subtropical coastal intertidal zones and an important carbon sink ecosystem. Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) is an important technical means of obtaining 3D structural parameters of forest trees for biomass estimation. Aiming to resolve the difficulty of fully describing the 3D structure of mangroves by using only airborne LiDAR, this research on the method of mangrove single-tree segmentation and parameter extraction based on combined airborne–ground LiDAR helps explore the applicability of LiDAR to the protection of coastal ecosystems and provides technical and data support for mangrove biomass estimation and carbon sink capacity assessment.This study adopts the mangrove nature reserves in Yingluo Port, Zhanjiang, Guangdong, and Maowei Sea in Guangxi as the research areas. A clustering segmentation method constrained by the lower part of the mangrove canopy is developed based on point cloud data obtained from an unmanned aerial vehicle and a handheld LiDAR instrument. The positioning error is eliminated through the registration of two kinds of data. The single-tree-trunk point cloud obtained by the handheld LiDAR instrument is extracted by the threshold method. Point cloud fitting is performed via Hough transformation to extract the relative position information of a single tree. With this information, the crown vertex generated by airborne LiDAR point cloud is constrained, thus improving the segmentation accuracy of single wood. Single-tree segmentation and extraction of tree height and crown width are implemented for different types of mangroves, and the results are compared with those of traditional single-tree segmentation algorithms.With combined airborne—ground LiDAR, the total detection rate for a single tree increases by 13.4%—26.7% compared with the total detection rate of the segmentation method based on the cascaded hierarchical model. The accuracy of single-tree segmentation from the fusion point cloud is high, with an overall detection rate of 62.7%. A total of 47 single trees are correctly detected, and the detection rate for three kinds of mangroves exceeds 50%. The R2 value between the extracted and measured values of mangrove height parameters increases by 1.8%—42.2%, and the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) decreases by 3.4%—55.3%. The segmentation results show that the extracted values of mangrove canopy are generally small. A crown error correction formula is proposed by extracting the point cloud density variable that can represent the density of mangrove canopy overlap and evaluating its linear correlation with the mean absolute error of the extracted values. RMSE after correction is reduced by 45.25%—53.33%.Combined with airborne—ground LiDAR data, the proposed single-tree segmentation algorithm achieves a high single-tree detection rate. The segmentation method can remove point redundancy accurately and effectively improve the accuracy of extracting mangrove tree height, crown width, and other 3D spatial structure parameters. The extracted value of mangrove crown width is generally small, but a fitting analysis of the density variables and errors can effectively correct the mangrove crown width. The combined use of handheld and airborne LiDAR data can provide more accurate and comprehensive structural information, such as tree height and crown width, compared with the use of single-source data and can be effectively applied to the study of mangrove ecosystem 3D structure and biomass parameter acquisition.关键词:remote sensing;mangrove;lidar;Hough transformation;point cloud clustering algorithm;single tree segmentation;3D structure parameter;crown slant226|510|0更新时间:2025-04-21
摘要:Mangrove is a woody plant community growing in tropical and subtropical coastal intertidal zones and an important carbon sink ecosystem. Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) is an important technical means of obtaining 3D structural parameters of forest trees for biomass estimation. Aiming to resolve the difficulty of fully describing the 3D structure of mangroves by using only airborne LiDAR, this research on the method of mangrove single-tree segmentation and parameter extraction based on combined airborne–ground LiDAR helps explore the applicability of LiDAR to the protection of coastal ecosystems and provides technical and data support for mangrove biomass estimation and carbon sink capacity assessment.This study adopts the mangrove nature reserves in Yingluo Port, Zhanjiang, Guangdong, and Maowei Sea in Guangxi as the research areas. A clustering segmentation method constrained by the lower part of the mangrove canopy is developed based on point cloud data obtained from an unmanned aerial vehicle and a handheld LiDAR instrument. The positioning error is eliminated through the registration of two kinds of data. The single-tree-trunk point cloud obtained by the handheld LiDAR instrument is extracted by the threshold method. Point cloud fitting is performed via Hough transformation to extract the relative position information of a single tree. With this information, the crown vertex generated by airborne LiDAR point cloud is constrained, thus improving the segmentation accuracy of single wood. Single-tree segmentation and extraction of tree height and crown width are implemented for different types of mangroves, and the results are compared with those of traditional single-tree segmentation algorithms.With combined airborne—ground LiDAR, the total detection rate for a single tree increases by 13.4%—26.7% compared with the total detection rate of the segmentation method based on the cascaded hierarchical model. The accuracy of single-tree segmentation from the fusion point cloud is high, with an overall detection rate of 62.7%. A total of 47 single trees are correctly detected, and the detection rate for three kinds of mangroves exceeds 50%. The R2 value between the extracted and measured values of mangrove height parameters increases by 1.8%—42.2%, and the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) decreases by 3.4%—55.3%. The segmentation results show that the extracted values of mangrove canopy are generally small. A crown error correction formula is proposed by extracting the point cloud density variable that can represent the density of mangrove canopy overlap and evaluating its linear correlation with the mean absolute error of the extracted values. RMSE after correction is reduced by 45.25%—53.33%.Combined with airborne—ground LiDAR data, the proposed single-tree segmentation algorithm achieves a high single-tree detection rate. The segmentation method can remove point redundancy accurately and effectively improve the accuracy of extracting mangrove tree height, crown width, and other 3D spatial structure parameters. The extracted value of mangrove crown width is generally small, but a fitting analysis of the density variables and errors can effectively correct the mangrove crown width. The combined use of handheld and airborne LiDAR data can provide more accurate and comprehensive structural information, such as tree height and crown width, compared with the use of single-source data and can be effectively applied to the study of mangrove ecosystem 3D structure and biomass parameter acquisition.关键词:remote sensing;mangrove;lidar;Hough transformation;point cloud clustering algorithm;single tree segmentation;3D structure parameter;crown slant226|510|0更新时间:2025-04-21 - “在遥感图像阴影检测领域,研究者提出了融合Transformer与CNN的双分支网络,显著提升了检测准确率,为遥感图像解译和地物要素提取提供新手段。”
 摘要:Shadows in remote sensing imagery play a crucial role in image interpretation and feature extraction but are known to introduce substantial challenges in image analysis. Traditional methods often struggle with complex shadow scenarios, leading to missed or false detections. This study introduces a novel approach that enhances shadow detection accuracy and reliability in high-resolution remote sensing images.The proposed dual-branch network synergistically combines the strengths of Transformer and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) to address the challenges in shadow detection. The network leverages a Transformer branch to capture global contextual relationships and a CNN branch to emphasize local textural details. This architecture is designed to exploit the complementary nature of global and local information, thus providing a comprehensive feature representation. This method also introduces a shadow prediction module that integrates these features for effective shadow segmentation. A joint loss function comprising a primary loss and auxiliary losses is utilized to refine learning and accelerate convergence, thereby enhancing detection accuracy. The proposed method is rigorously tested on the Aerial Imagery Shadow Dataset and demonstrates substantial improvements in shadow detection metrics. It achieves a shadow detection accuracy of 97.112% and substantially reduces the false detection rate, with a balance error rate decrease of 0.389. These results validate the effectiveness of the dual-branch architecture and showcase the advantages of integrating global and local features through our innovative network design. The dual-branch network provides a robust solution to the perennial challenges in shadow detection in remote sensing imagery. By effectively minimizing missed and false detections, the network shows promise for enhancing the interpretability and utility of high-resolution satellite images in various applications, such as urban planning and environmental monitoring. Future work may focus on optimizing the network architecture and exploring its applicability to other complex imaging conditions.关键词:remote sensing image;shadow detection;semantic segmentation;dual-branch network;feature integration;Transformer;CNN;ResNet616|446|0更新时间:2025-04-21
摘要:Shadows in remote sensing imagery play a crucial role in image interpretation and feature extraction but are known to introduce substantial challenges in image analysis. Traditional methods often struggle with complex shadow scenarios, leading to missed or false detections. This study introduces a novel approach that enhances shadow detection accuracy and reliability in high-resolution remote sensing images.The proposed dual-branch network synergistically combines the strengths of Transformer and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) to address the challenges in shadow detection. The network leverages a Transformer branch to capture global contextual relationships and a CNN branch to emphasize local textural details. This architecture is designed to exploit the complementary nature of global and local information, thus providing a comprehensive feature representation. This method also introduces a shadow prediction module that integrates these features for effective shadow segmentation. A joint loss function comprising a primary loss and auxiliary losses is utilized to refine learning and accelerate convergence, thereby enhancing detection accuracy. The proposed method is rigorously tested on the Aerial Imagery Shadow Dataset and demonstrates substantial improvements in shadow detection metrics. It achieves a shadow detection accuracy of 97.112% and substantially reduces the false detection rate, with a balance error rate decrease of 0.389. These results validate the effectiveness of the dual-branch architecture and showcase the advantages of integrating global and local features through our innovative network design. The dual-branch network provides a robust solution to the perennial challenges in shadow detection in remote sensing imagery. By effectively minimizing missed and false detections, the network shows promise for enhancing the interpretability and utility of high-resolution satellite images in various applications, such as urban planning and environmental monitoring. Future work may focus on optimizing the network architecture and exploring its applicability to other complex imaging conditions.关键词:remote sensing image;shadow detection;semantic segmentation;dual-branch network;feature integration;Transformer;CNN;ResNet616|446|0更新时间:2025-04-21 - “在遥感影像去云领域,基于注意力机制的生成对抗网络算法有效保留边缘纹理细节,为云干扰问题提供解决方案。”
 摘要:High-resolution satellite remote sensing images are often compromised by cloud interference because of constraints, such as imaging conditions and sensing equipment. This phenomenon considerably degrades image quality and hinders intelligent interpretation. In recent years, deep learning has been extensively applied to cloud removal in remote sensing images because of its powerful feature learning capabilities. This study presents an attention-based generative adversarial network for cloud removal in remote sensing images. The network aims to address the challenge of preserving textures. Initially, a Fourier residual block is designed to integrate low- and high-frequency cloud images. Subsequently, attention mechanisms are employed for channel and spatial dimensions to capture the spatial distribution information of clouds that guides the network in effectively removing clouds. Then, the model is trained to minimize the joint loss function and ensure the coherence of generated images with real images in terms of content. Experimental results derived from the Remote Sensing Image Cloud Removing (RICE) dataset show that the proposed cloud removal method, which integrates attention mechanisms and generative adversarial networks, can effectively eradicate clouds while preserving textures.The following conclusions are drawn. (1) The proposed Fourier residual block plays a pivotal role in adeptly capturing the details of low- and high-frequency residual information present in cloud images. By merging these diverse features, the block bolsters the network’s ability to extract rich features. (2) The attention mechanisms utilized extract features from spatial and channel dimensions. This extraction enables the model to discern the importance of various features across different dimensions. Moreover, the cloud information obtained through these attention mechanisms allows the model to adaptively reveal cloud changes, thereby enhancing the model’s precision and efficiency in cloud removal. (3) Experimental results from the RICE dataset provide compelling evidence of the proposed method’s effectiveness in terms of cloud removal and texture preservation.关键词:remote sensing imagery cloud removal;Fourier residual block;channel-spatial attention;generative adversarial networks;spatial distribution of clouds816|1453|0更新时间:2025-04-21
摘要:High-resolution satellite remote sensing images are often compromised by cloud interference because of constraints, such as imaging conditions and sensing equipment. This phenomenon considerably degrades image quality and hinders intelligent interpretation. In recent years, deep learning has been extensively applied to cloud removal in remote sensing images because of its powerful feature learning capabilities. This study presents an attention-based generative adversarial network for cloud removal in remote sensing images. The network aims to address the challenge of preserving textures. Initially, a Fourier residual block is designed to integrate low- and high-frequency cloud images. Subsequently, attention mechanisms are employed for channel and spatial dimensions to capture the spatial distribution information of clouds that guides the network in effectively removing clouds. Then, the model is trained to minimize the joint loss function and ensure the coherence of generated images with real images in terms of content. Experimental results derived from the Remote Sensing Image Cloud Removing (RICE) dataset show that the proposed cloud removal method, which integrates attention mechanisms and generative adversarial networks, can effectively eradicate clouds while preserving textures.The following conclusions are drawn. (1) The proposed Fourier residual block plays a pivotal role in adeptly capturing the details of low- and high-frequency residual information present in cloud images. By merging these diverse features, the block bolsters the network’s ability to extract rich features. (2) The attention mechanisms utilized extract features from spatial and channel dimensions. This extraction enables the model to discern the importance of various features across different dimensions. Moreover, the cloud information obtained through these attention mechanisms allows the model to adaptively reveal cloud changes, thereby enhancing the model’s precision and efficiency in cloud removal. (3) Experimental results from the RICE dataset provide compelling evidence of the proposed method’s effectiveness in terms of cloud removal and texture preservation.关键词:remote sensing imagery cloud removal;Fourier residual block;channel-spatial attention;generative adversarial networks;spatial distribution of clouds816|1453|0更新时间:2025-04-21 - “在遥感图像处理领域,专家基于YOLOX-s算法,提出了LAD-YOLOX快速检测算法,有效提升了飞机目标检测性能,满足了在轨实时检测需求。”
 摘要:With the rapid development of space remote sensing technology, the number of high-resolution optical remote sensing images is increasing exponentially. The detection of high-strategic-value targets, such as aircraft, is currently a hot research topic in the field of high-resolution image processing for remote sensing. Traditional remote sensing image object detection algorithms include template matching and traditional machine learning. These algorithms mostly rely on prior knowledge from experts, and the features used are generally primary manual features limited to the pixel level, so they have certain limitations and cannot cope with complex, ever-changing backgrounds and diverse multimodal targets. Remote sensing object detection algorithms for deep learning technology include two- and one-stage methods. Two-stage methods have high accuracy, but they consume abundant resources and have limited processing speeds. YOLO detection algorithms elicit much concern and are applied because of their simple network structure and balanced detection accuracy and speed. However, one-stage models cannot be directly deployed on embedded devices in satellites for real-time detection of aircraft targets because of the limitations in computing power, storage capacity, and model complexity. Therefore, lightweight network models that have reduced demands for computing power and storage need to be developed. These network models with excellent target detection capabilities can then be deployed to aerospace chips with limited resources to complete efficient aircraft target detection tasks.To address the difficulty of deploying current network models with excellent target detection capabilities to aerospace chips with limited computing and storage resources, this study proposes five targeted designs for the benchmark model, which is based on the one-stage YOLOX-s algorithm, and the implementation of the model adopts a lightweight design concept. A fast optical remote sensing aircraft target detection algorithm called lightweight aircraft detection YOLOX (LAD-YOLOX) that is suitable for deployment on embedded platforms is proposed. The effectiveness of the improved strategy and the generalization of the overall model are verified via testing on remote sensing object detection (RSOD) and self-made aircraft datasets, and low-loss model compression is achieved. In addition, algorithm deployment and acceleration are completed using the XILINX EK-U1-ZCU102-G evaluation kit, which can meet the requirements on real-time performance and detection accuracy.First, at the ablation experiment stage, the effectiveness of each improvement module is verified by gradually accumulating the five improvement strategies that are based on the baseline YOLOX-s. Compared with YOLOX-s, LAD-YOLOX achieves low-loss model compression. The parameter number is reduced to 58.83% of the benchmark, and the calculation quantity is reduced to 43.72% of the benchmark. mAP@.5(%) and mAP@.5:.95(%) are only reduced by 0.2%, and the detection speed increases by 24 FPS. Second, the proposed design is applied to the detection of a self-made aircraft dataset. When the depth and width configurations are set to 0.33 and 0.375, respectively, the computational cost is 35.45 GFLOPs, and 54.04% mAP is obtained. FP16 bs=1 is used for inference on RTX4090, and the speed can reach 59.50 FPS, showing the model with the best comprehensive performance in the comparative experiment. Last, via Quantitative Aware Training, the model is deployed and tested on the ZCU102 evaluation kit to obtain the visualization results and detection speeds of aircraft targets. When 6,144 × 6,144 images are used as an input, the average processing speed can reach 26.53 FPS, and the aircraft targets annotated in the self-made aircraft dataset can be accurately identified. Some aircraft targets have overlapping detection frames, misjudgment of difficult cases, and false negatives.To address the imbalanced comprehensive performance of deep learning detection algorithms in real-time processing of remote sensing images in orbit and the difficulty of deployment on embedded devices on satellites, this study proposes a fast aircraft detection algorithm called LAD-YOLOX, which based on optical remote sensing for embedded platforms. First, an ultra-lightweight, high-precision backbone module called ES-Block is designed in a hardware-aware network to reconstruct the original backbone, which based on ShuffleNetv2. Second, GSConv is introduced to construct a lightweight neck called GS-Neck. This design equalizes the parameters between the front and back, thus reducing the computational complexity and precision loss. Third, the lightweight decoupling detection head is designed to further improve the feature coding of classification and location and reduce the parameters to improve detection performance. Last, Varifocal Loss and SIoU Loss are used in the loss function of LAD-YOLOX to improve the convergence speed of model training and the precision of reasoning. Simulation results show that on the RSOD dataset, the proposed algorithm makes detection accuracy lossless, and the calculation amount is compressed to 43.72% of the original YOLOX-s model. The detection speed is increased by 24 FPS. Algorithm deployment and acceleration are completed on the XILINX EK-U1-ZCU102-G evaluation kit. The detection speed on the self-made aircraft dataset can reach 26.53 FPS, which meets the requirements for real-time, accurate detection of aircraft targets in orbit.关键词:remote sensing;In-orbit target detection;lightweight;YOLOX;RSOD dataset;ZCU102255|1353|0更新时间:2025-04-21
摘要:With the rapid development of space remote sensing technology, the number of high-resolution optical remote sensing images is increasing exponentially. The detection of high-strategic-value targets, such as aircraft, is currently a hot research topic in the field of high-resolution image processing for remote sensing. Traditional remote sensing image object detection algorithms include template matching and traditional machine learning. These algorithms mostly rely on prior knowledge from experts, and the features used are generally primary manual features limited to the pixel level, so they have certain limitations and cannot cope with complex, ever-changing backgrounds and diverse multimodal targets. Remote sensing object detection algorithms for deep learning technology include two- and one-stage methods. Two-stage methods have high accuracy, but they consume abundant resources and have limited processing speeds. YOLO detection algorithms elicit much concern and are applied because of their simple network structure and balanced detection accuracy and speed. However, one-stage models cannot be directly deployed on embedded devices in satellites for real-time detection of aircraft targets because of the limitations in computing power, storage capacity, and model complexity. Therefore, lightweight network models that have reduced demands for computing power and storage need to be developed. These network models with excellent target detection capabilities can then be deployed to aerospace chips with limited resources to complete efficient aircraft target detection tasks.To address the difficulty of deploying current network models with excellent target detection capabilities to aerospace chips with limited computing and storage resources, this study proposes five targeted designs for the benchmark model, which is based on the one-stage YOLOX-s algorithm, and the implementation of the model adopts a lightweight design concept. A fast optical remote sensing aircraft target detection algorithm called lightweight aircraft detection YOLOX (LAD-YOLOX) that is suitable for deployment on embedded platforms is proposed. The effectiveness of the improved strategy and the generalization of the overall model are verified via testing on remote sensing object detection (RSOD) and self-made aircraft datasets, and low-loss model compression is achieved. In addition, algorithm deployment and acceleration are completed using the XILINX EK-U1-ZCU102-G evaluation kit, which can meet the requirements on real-time performance and detection accuracy.First, at the ablation experiment stage, the effectiveness of each improvement module is verified by gradually accumulating the five improvement strategies that are based on the baseline YOLOX-s. Compared with YOLOX-s, LAD-YOLOX achieves low-loss model compression. The parameter number is reduced to 58.83% of the benchmark, and the calculation quantity is reduced to 43.72% of the benchmark. mAP@.5(%) and mAP@.5:.95(%) are only reduced by 0.2%, and the detection speed increases by 24 FPS. Second, the proposed design is applied to the detection of a self-made aircraft dataset. When the depth and width configurations are set to 0.33 and 0.375, respectively, the computational cost is 35.45 GFLOPs, and 54.04% mAP is obtained. FP16 bs=1 is used for inference on RTX4090, and the speed can reach 59.50 FPS, showing the model with the best comprehensive performance in the comparative experiment. Last, via Quantitative Aware Training, the model is deployed and tested on the ZCU102 evaluation kit to obtain the visualization results and detection speeds of aircraft targets. When 6,144 × 6,144 images are used as an input, the average processing speed can reach 26.53 FPS, and the aircraft targets annotated in the self-made aircraft dataset can be accurately identified. Some aircraft targets have overlapping detection frames, misjudgment of difficult cases, and false negatives.To address the imbalanced comprehensive performance of deep learning detection algorithms in real-time processing of remote sensing images in orbit and the difficulty of deployment on embedded devices on satellites, this study proposes a fast aircraft detection algorithm called LAD-YOLOX, which based on optical remote sensing for embedded platforms. First, an ultra-lightweight, high-precision backbone module called ES-Block is designed in a hardware-aware network to reconstruct the original backbone, which based on ShuffleNetv2. Second, GSConv is introduced to construct a lightweight neck called GS-Neck. This design equalizes the parameters between the front and back, thus reducing the computational complexity and precision loss. Third, the lightweight decoupling detection head is designed to further improve the feature coding of classification and location and reduce the parameters to improve detection performance. Last, Varifocal Loss and SIoU Loss are used in the loss function of LAD-YOLOX to improve the convergence speed of model training and the precision of reasoning. Simulation results show that on the RSOD dataset, the proposed algorithm makes detection accuracy lossless, and the calculation amount is compressed to 43.72% of the original YOLOX-s model. The detection speed is increased by 24 FPS. Algorithm deployment and acceleration are completed on the XILINX EK-U1-ZCU102-G evaluation kit. The detection speed on the self-made aircraft dataset can reach 26.53 FPS, which meets the requirements for real-time, accurate detection of aircraft targets in orbit.关键词:remote sensing;In-orbit target detection;lightweight;YOLOX;RSOD dataset;ZCU102255|1353|0更新时间:2025-04-21 - “在遥感影像领域,专家提出了基于阴影方向先验的地物阴影检测方法,有效提升了检测精度和边界规整度。”
 摘要:Given the high cost and difficulty of shadow annotation, the shadow detection performance of supervised learning models in high-resolution remote sensing images is severely limited mainly because of the lack of training samples. To solve this problem, this study proposes a shadow detection method that is based on shadow direction prior, which has unique advantages in learning the inherent shadow information contained in unlabeled high-resolution remote sensing images. Through self-supervised learning methods, the advanced semantic information of ground object shadows contained in remote sensing images can be deeply explored, thereby improving the applicability and accuracy of the model. This innovative approach provides a new way to overcome the data limitation problem in shadow detection and offers new possibilities for improving the model’s ability to understand complex high-resolution images.This study proposes an innovative shadow detection method for high-resolution remote sensing images that is based on prior knowledge of the shadow direction and explores the effectiveness of shadow direction prior in representing high-level semantic features of object shadows in remote sensing images. The key task in this method is to construct an auxiliary task through shadow direction prior so that the deep neural network can effectively understand the shadow of objects in remote sensing images. Moreover, to further enhance the deep neural network’s ability to learn the key features of object shadows, this study designs a direction transformation-independent noise processing mechanism and data enhancement strategy for self-supervised shadow detection, both of which improve the generalization ability of the model.The effectiveness of the proposed method is proven through verification on the Aerial Imagery Dataset for Shadow Detection (AISD). Experimental results show that compared with the traditional Unet benchmark model, the proposed method can successfully learn prior knowledge in unlabeled high-resolution remote sensing images. By leveraging this prior knowledge, the developed method improves the accuracy of the Unet model and demonstrates competitive efficiency and performance in small sample cases. The results of this study highlight the superiority of the proposed method in addressing the challenge of shadow identification in high-resolution remote sensing images, especially in the absence of labeled samples. By fully utilizing prior knowledge, the method successfully extends the performance of the Unet model and provides a promising solution for processing unlabeled high-resolution remote sensing images in practical applications.The qualitative and quantitative results consistently show that using a shadow direction prior method can considerably improve the accuracy of shadow detection. The use of the DTICT strategy helps alleviate the interference caused by shadow-free samples and samples containing shadows in special directions during network training. The data enhancement strategy combined with contrast cropping and color transformation provides the network with diverse training samples, thereby enhancing the pre-trained model’s ability to extract object shadow features. The proposed method achieves competitive object shadow detection accuracy by using a small number of labeled samples.关键词:shadow detection;self-supervised learning;data augmentation;shadow direction prior;high-resolution remote sensing imagery228|809|0更新时间:2025-04-21
摘要:Given the high cost and difficulty of shadow annotation, the shadow detection performance of supervised learning models in high-resolution remote sensing images is severely limited mainly because of the lack of training samples. To solve this problem, this study proposes a shadow detection method that is based on shadow direction prior, which has unique advantages in learning the inherent shadow information contained in unlabeled high-resolution remote sensing images. Through self-supervised learning methods, the advanced semantic information of ground object shadows contained in remote sensing images can be deeply explored, thereby improving the applicability and accuracy of the model. This innovative approach provides a new way to overcome the data limitation problem in shadow detection and offers new possibilities for improving the model’s ability to understand complex high-resolution images.This study proposes an innovative shadow detection method for high-resolution remote sensing images that is based on prior knowledge of the shadow direction and explores the effectiveness of shadow direction prior in representing high-level semantic features of object shadows in remote sensing images. The key task in this method is to construct an auxiliary task through shadow direction prior so that the deep neural network can effectively understand the shadow of objects in remote sensing images. Moreover, to further enhance the deep neural network’s ability to learn the key features of object shadows, this study designs a direction transformation-independent noise processing mechanism and data enhancement strategy for self-supervised shadow detection, both of which improve the generalization ability of the model.The effectiveness of the proposed method is proven through verification on the Aerial Imagery Dataset for Shadow Detection (AISD). Experimental results show that compared with the traditional Unet benchmark model, the proposed method can successfully learn prior knowledge in unlabeled high-resolution remote sensing images. By leveraging this prior knowledge, the developed method improves the accuracy of the Unet model and demonstrates competitive efficiency and performance in small sample cases. The results of this study highlight the superiority of the proposed method in addressing the challenge of shadow identification in high-resolution remote sensing images, especially in the absence of labeled samples. By fully utilizing prior knowledge, the method successfully extends the performance of the Unet model and provides a promising solution for processing unlabeled high-resolution remote sensing images in practical applications.The qualitative and quantitative results consistently show that using a shadow direction prior method can considerably improve the accuracy of shadow detection. The use of the DTICT strategy helps alleviate the interference caused by shadow-free samples and samples containing shadows in special directions during network training. The data enhancement strategy combined with contrast cropping and color transformation provides the network with diverse training samples, thereby enhancing the pre-trained model’s ability to extract object shadow features. The proposed method achieves competitive object shadow detection accuracy by using a small number of labeled samples.关键词:shadow detection;self-supervised learning;data augmentation;shadow direction prior;high-resolution remote sensing imagery228|809|0更新时间:2025-04-21 - “在遥感图像场景分类领域,THViT方法通过双阶段高阶Transformer有效提升了分类性能,为解决遥感图像空间特征信息表征问题提供了新方案。”
 摘要:Transformer is widely used in remote sensing image scene classification because of its powerful global feature modeling and long-distance dependency representation capabilities. However, remote sensing scene images encounter challenges, such as complex spatial structures and large changes in the target scale. Directly adopting the fixed-size image block method and deep feature representation of Vision Transformer (ViT) cannot effectively depict the spatial feature information of remote sensing scene images. To alleviate these problems, this study proposes a remote sensing image scene classification method on the basis of two-stage high-order ViT (THViT). The method adopts the LV-ViT-S network, which includes a two-stage dynamic classification of coarse and fine, as the backbone. First, the remote sensing image is segmented into large-scale image blocks for easy classification of remote sensing scene images. Second, on the basis of the class attention mechanism and information region extraction module, the remote sensing scene images are further segmented, and the classification of complex remote sensing scene images is completed. The coarse–fine dynamic classification stage can be adjusted by a threshold. Simultaneously, to improve the discriminability of deep features, THViT introduces Brownian covariance high-order feature representation, which effectively captures the discrimination depth feature representations of remote sensing scene images from a statistical perspective. Moreover, to overcome the limitation that Transformer only utilizes classified tokens as classification features, this study employs classified and high-order feature tokens in the softmax classifier for improving the performance of remote sensing image scene classification. This style verifies the effectiveness of high-order feature tokens for remote sensing image scene classification.Experimental results show that compared with related algorithms, such as CFDNN, GLDBS, GAN, GCN, D-CapsNet, SCCov, ViT, and SCViT, THViT exhibits better performance on NWPU-RESISC45 and Aerial Image Datasets.The research results confirm that the two-stage (coarse to fine), dynamic, high-order features can achieve excellent performance in remote sensing scene classification.关键词:remote sensing images;scene classification;transformer network;feature representation;high-level features391|293|0更新时间:2025-04-21
摘要:Transformer is widely used in remote sensing image scene classification because of its powerful global feature modeling and long-distance dependency representation capabilities. However, remote sensing scene images encounter challenges, such as complex spatial structures and large changes in the target scale. Directly adopting the fixed-size image block method and deep feature representation of Vision Transformer (ViT) cannot effectively depict the spatial feature information of remote sensing scene images. To alleviate these problems, this study proposes a remote sensing image scene classification method on the basis of two-stage high-order ViT (THViT). The method adopts the LV-ViT-S network, which includes a two-stage dynamic classification of coarse and fine, as the backbone. First, the remote sensing image is segmented into large-scale image blocks for easy classification of remote sensing scene images. Second, on the basis of the class attention mechanism and information region extraction module, the remote sensing scene images are further segmented, and the classification of complex remote sensing scene images is completed. The coarse–fine dynamic classification stage can be adjusted by a threshold. Simultaneously, to improve the discriminability of deep features, THViT introduces Brownian covariance high-order feature representation, which effectively captures the discrimination depth feature representations of remote sensing scene images from a statistical perspective. Moreover, to overcome the limitation that Transformer only utilizes classified tokens as classification features, this study employs classified and high-order feature tokens in the softmax classifier for improving the performance of remote sensing image scene classification. This style verifies the effectiveness of high-order feature tokens for remote sensing image scene classification.Experimental results show that compared with related algorithms, such as CFDNN, GLDBS, GAN, GCN, D-CapsNet, SCCov, ViT, and SCViT, THViT exhibits better performance on NWPU-RESISC45 and Aerial Image Datasets.The research results confirm that the two-stage (coarse to fine), dynamic, high-order features can achieve excellent performance in remote sensing scene classification.关键词:remote sensing images;scene classification;transformer network;feature representation;high-level features391|293|0更新时间:2025-04-21 -
Point cloud contour feature point extraction method on the basis of domain feature parameter fusion AI导读
“在目标检测和定位领域,研究者直接利用点云邻域特征提取轮廓特征点,提出基于邻域特征分布的边界点精细提取方法,准确率、召回率及F1分数均高于90%。”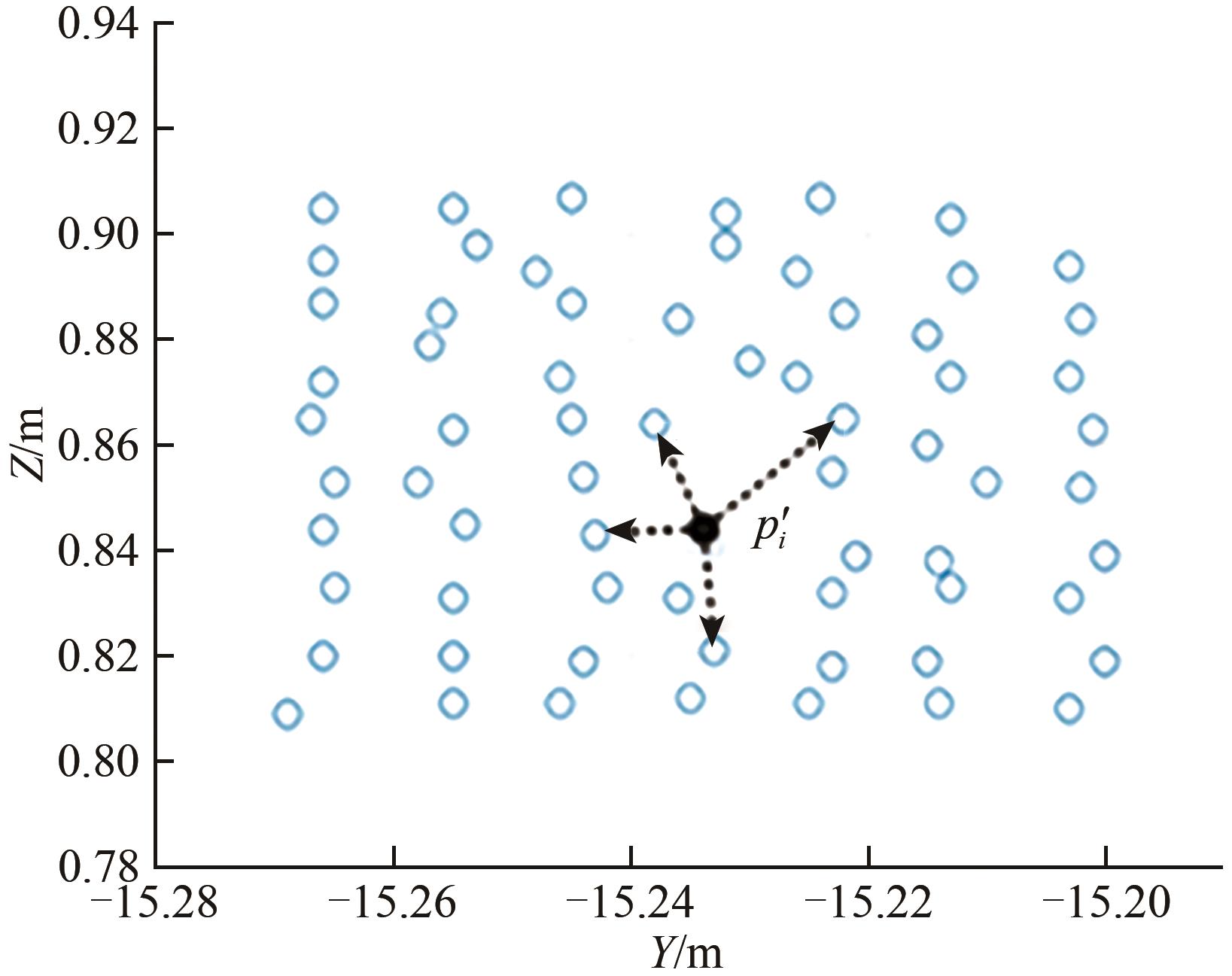 摘要:The feature points of point cloud profiles are the key to determining the geometry of objects and play an important role in target detection and location. The objective of this study is to extract point cloud contour feature points directly by using point cloud neighborhood features. First, Cholesky decomposition is used to determine the main and secondary eigenvectors, and the neighborhood projection plane, with the main and secondary eigenvectors as normal vectors, is constructed. Second, the optimal number of neighboring points is determined by constructing an entropy model of neighborhood dimensional feature information, and the angular distribution characteristics of the vector composed of target and neighborhood points on the projection plane are analyzed. On the basis of the characteristics of the azimuth angle, a fine extraction method of boundary points on the basis of neighborhood feature distribution is proposed. Last, a 2D view formation method of neighborhood points on the projection plane is developed based on the quaternion method, and a multiparameter extraction model is established based on the point-to-line distance and the deviation of points on both sides of the line. Experimental results show that the proposed method is superior to ordered-point Hough transform, patch segmentation, and binary image methods. In terms of noise immunity, the proposed method can extract contour feature points under different noises, and its robustness is better than that of the binary image method, region-clustering curvature method, and regional growth method. In addition, the accuracy rate, recall rate, and F1 score of the developed method are higher than 90%. The F1 score of the proposed method is 4.2% higher than that of the region-clustering curvature method and 32.4% higher than that of the Hough transform method. The proposed method is suitable for regular planar building shapes and can be used to extract the contour feature points of irregularly curved building shapes.关键词:remote sensing;point cloud;Outline points;Feature points;Boundary points;Fold points;Neighborhood feature;Projection plane;feature extraction1118|498|0更新时间:2025-04-21
摘要:The feature points of point cloud profiles are the key to determining the geometry of objects and play an important role in target detection and location. The objective of this study is to extract point cloud contour feature points directly by using point cloud neighborhood features. First, Cholesky decomposition is used to determine the main and secondary eigenvectors, and the neighborhood projection plane, with the main and secondary eigenvectors as normal vectors, is constructed. Second, the optimal number of neighboring points is determined by constructing an entropy model of neighborhood dimensional feature information, and the angular distribution characteristics of the vector composed of target and neighborhood points on the projection plane are analyzed. On the basis of the characteristics of the azimuth angle, a fine extraction method of boundary points on the basis of neighborhood feature distribution is proposed. Last, a 2D view formation method of neighborhood points on the projection plane is developed based on the quaternion method, and a multiparameter extraction model is established based on the point-to-line distance and the deviation of points on both sides of the line. Experimental results show that the proposed method is superior to ordered-point Hough transform, patch segmentation, and binary image methods. In terms of noise immunity, the proposed method can extract contour feature points under different noises, and its robustness is better than that of the binary image method, region-clustering curvature method, and regional growth method. In addition, the accuracy rate, recall rate, and F1 score of the developed method are higher than 90%. The F1 score of the proposed method is 4.2% higher than that of the region-clustering curvature method and 32.4% higher than that of the Hough transform method. The proposed method is suitable for regular planar building shapes and can be used to extract the contour feature points of irregularly curved building shapes.关键词:remote sensing;point cloud;Outline points;Feature points;Boundary points;Fold points;Neighborhood feature;Projection plane;feature extraction1118|498|0更新时间:2025-04-21
Models and Methods
0

