
最新刊期
卷 29 , 期 7 , 2025
-
Research on the remote sensing large model for large-scale calculation of land spatial parameters AI导读
“在地理空间智能领域,专家提出土地空间对象化建模框架,为土地空间参数精准解算提供新思路。”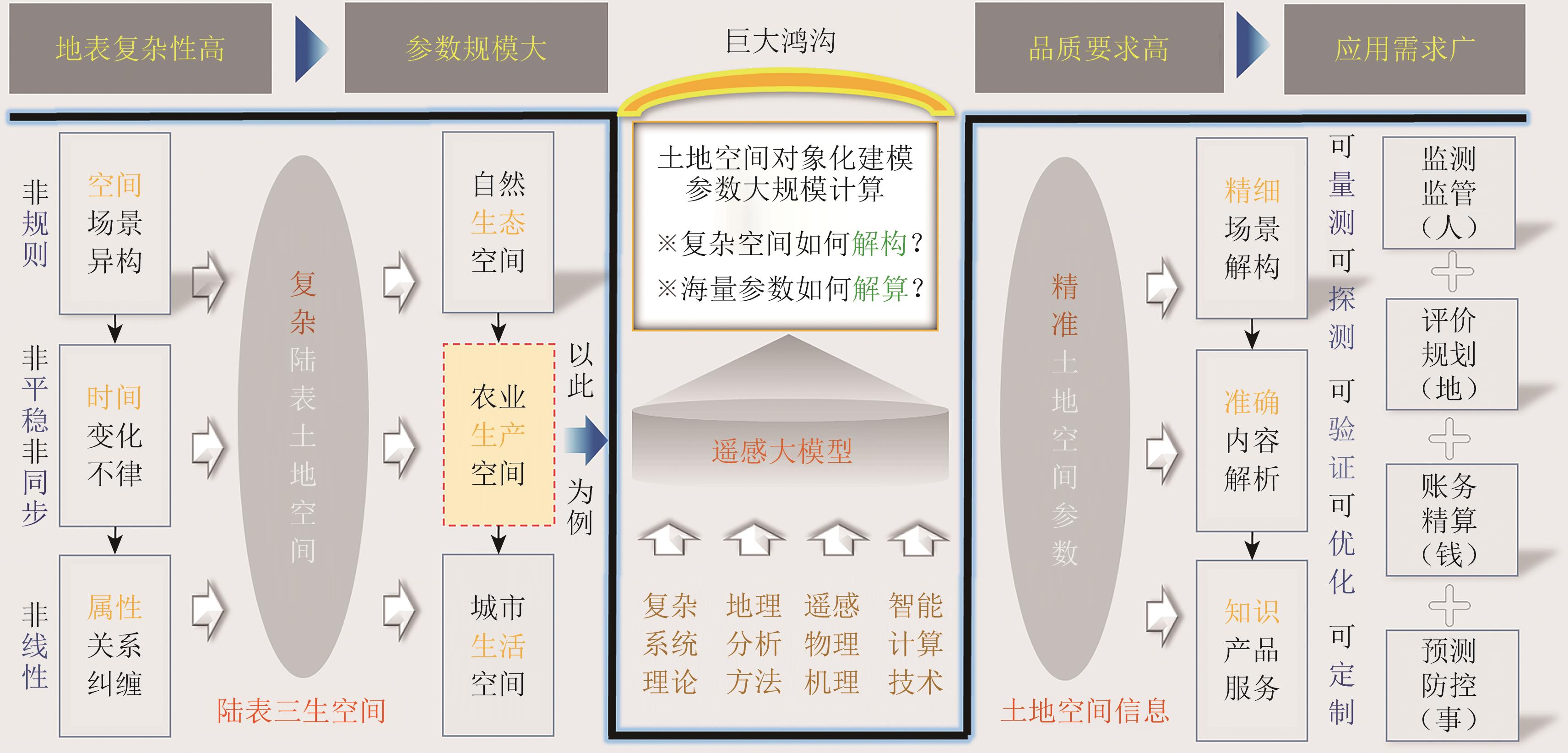 摘要:With the rapid development of the social economy, digitization, informatization, and intelligence have become important trends in promoting national construction. In the era of big data, the essence of intelligent applications in various industries is to correlate ubiquitous information and solve required parameters in their respective spaces. How to intelligently analyze large-scale spatial parameters on the complex land surface, which is dependent on natural resources, has become an important proposition for digital driven high-quality development in the new era. As a new trend in the development of Artificial Intelligence (AI), the revolutionary influence of Large Models (LMs) on scientific research paradigms, production methods, and industrial models cannot be underestimated. Investing in LM research is an inevitable choice. In the field of geographic AI, a significant gap remains between the scientific design and practical application of LMs. This article adheres to the principle of deconstructing complex land surface systems and solving precise land parameters. It proposes to conduct land spatial object-oriented modeling supported by multisource and multimodal observation data. The article proposes an object-oriented modeling approach for land surface space, integrating basic geographic data to build an object-oriented base, and transmitting remote sensing data to collaborators’ knowledge in a signal manner to systematically analyze complex land spaces. On this basis, a land spatial parameter system and a solution framework are outlined via the integration of five land parameters from land use, land cover change, land soil, land resource, and land type/application. Furthermore, an intelligent computing remote sensing LM is designed for large-scale parameter solving via integrating three core systems, namely, symbol, perception, and control systems. This model deploys heterogeneous deep learning algorithms to break through the bottlenecks in mapping, transforming, and transmitting relationships on key nodes. It is worth emphasizing that in deep learning algorithms, we introduce attention and external incremental information to solve the ordered decomposition and step-by-step simplification of complex problems, thereby achieving large-scale, accurate, and fast solution of land parameters. A preliminary experiment is conducted using the solution of land use parameters in agricultural production spaces as an application case. Results show that the proposed framework has great potential in improving the accuracy of large-scale parameter calculation in land space. The experiment has shown that the remote sensing model constructed in this article has good performance, revealing that the land spatial information generated by this research model has five advantages of measurability, detectability, verifiability, optimizability, and customizability, and has broad application potential in the comprehensive service of human, land, money, and matter. The proposed model helps serve the intelligent customization of refined land information products and deepen the understanding of land space. Finally, prospects for LM research on land spatial parameter calculation are presented from the perspectives of model adaptability/robustness and interpretability/credibility of results. This study is based on the existing research of the authors’ team and presents the spiral evolution from remote sensing regression to geography, from big data to big model research in recent years. It is another milestone in theoretical development and practical application. It should be noted that the LM framework established in this article is more of an intelligent computing strategy proposed for solving large-scale land parameter problems in complex geographic systems, and there is still room for optimization and adjustment in specific implementation stages.关键词:large model;geospatial artificial intelligence (GeoAI);land spatial object-oriented modeling;land parameter solving;attention mechanism;deep learning network;agricultural production space743|2367|0更新时间:2025-11-03
摘要:With the rapid development of the social economy, digitization, informatization, and intelligence have become important trends in promoting national construction. In the era of big data, the essence of intelligent applications in various industries is to correlate ubiquitous information and solve required parameters in their respective spaces. How to intelligently analyze large-scale spatial parameters on the complex land surface, which is dependent on natural resources, has become an important proposition for digital driven high-quality development in the new era. As a new trend in the development of Artificial Intelligence (AI), the revolutionary influence of Large Models (LMs) on scientific research paradigms, production methods, and industrial models cannot be underestimated. Investing in LM research is an inevitable choice. In the field of geographic AI, a significant gap remains between the scientific design and practical application of LMs. This article adheres to the principle of deconstructing complex land surface systems and solving precise land parameters. It proposes to conduct land spatial object-oriented modeling supported by multisource and multimodal observation data. The article proposes an object-oriented modeling approach for land surface space, integrating basic geographic data to build an object-oriented base, and transmitting remote sensing data to collaborators’ knowledge in a signal manner to systematically analyze complex land spaces. On this basis, a land spatial parameter system and a solution framework are outlined via the integration of five land parameters from land use, land cover change, land soil, land resource, and land type/application. Furthermore, an intelligent computing remote sensing LM is designed for large-scale parameter solving via integrating three core systems, namely, symbol, perception, and control systems. This model deploys heterogeneous deep learning algorithms to break through the bottlenecks in mapping, transforming, and transmitting relationships on key nodes. It is worth emphasizing that in deep learning algorithms, we introduce attention and external incremental information to solve the ordered decomposition and step-by-step simplification of complex problems, thereby achieving large-scale, accurate, and fast solution of land parameters. A preliminary experiment is conducted using the solution of land use parameters in agricultural production spaces as an application case. Results show that the proposed framework has great potential in improving the accuracy of large-scale parameter calculation in land space. The experiment has shown that the remote sensing model constructed in this article has good performance, revealing that the land spatial information generated by this research model has five advantages of measurability, detectability, verifiability, optimizability, and customizability, and has broad application potential in the comprehensive service of human, land, money, and matter. The proposed model helps serve the intelligent customization of refined land information products and deepen the understanding of land space. Finally, prospects for LM research on land spatial parameter calculation are presented from the perspectives of model adaptability/robustness and interpretability/credibility of results. This study is based on the existing research of the authors’ team and presents the spiral evolution from remote sensing regression to geography, from big data to big model research in recent years. It is another milestone in theoretical development and practical application. It should be noted that the LM framework established in this article is more of an intelligent computing strategy proposed for solving large-scale land parameter problems in complex geographic systems, and there is still room for optimization and adjustment in specific implementation stages.关键词:large model;geospatial artificial intelligence (GeoAI);land spatial object-oriented modeling;land parameter solving;attention mechanism;deep learning network;agricultural production space743|2367|0更新时间:2025-11-03 - “遥感地表温度研究快速增长,中美贡献突出,研究热点转向机器学习等新领域。”
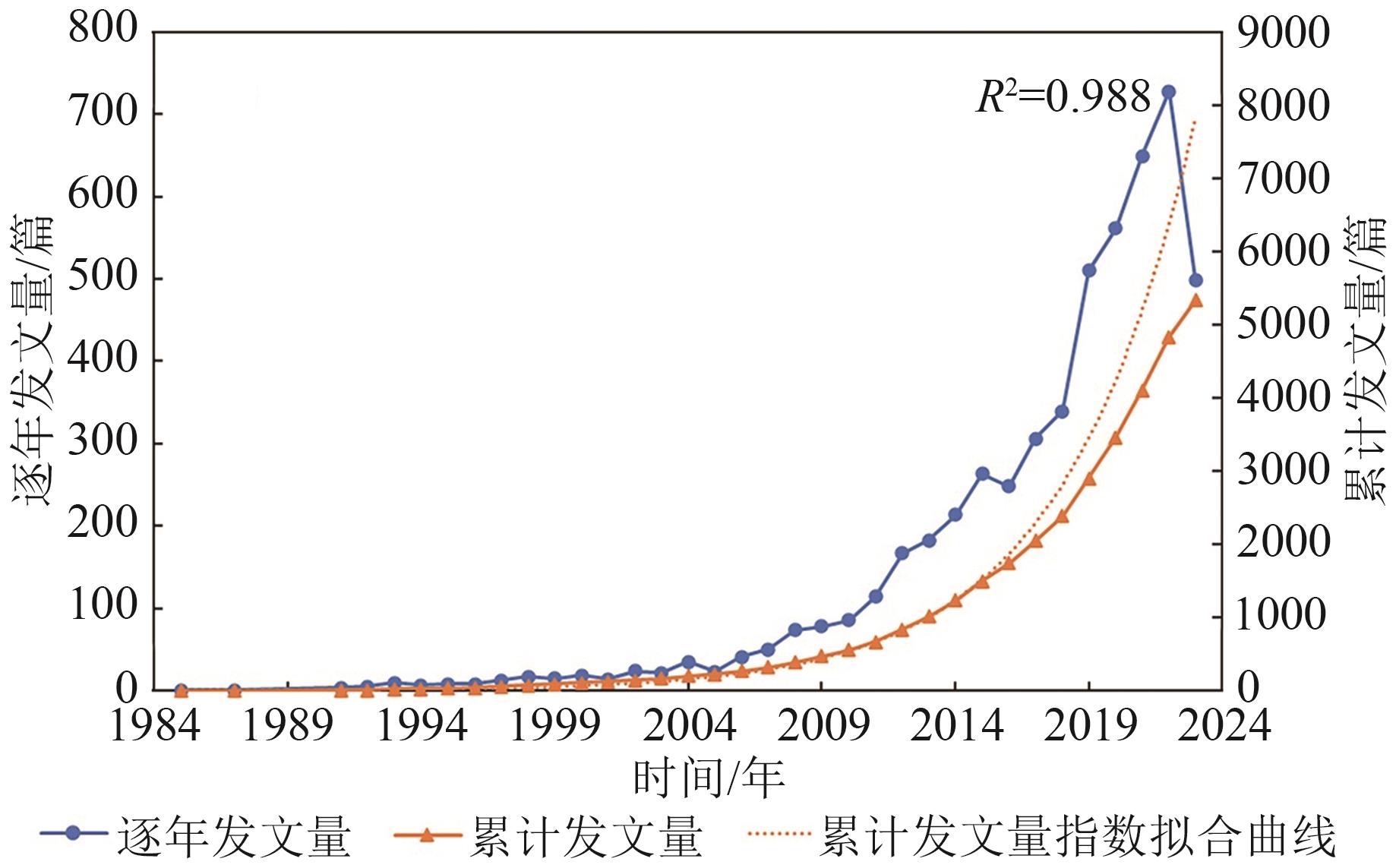 摘要:Land Surface Temperature (LST), which determines the radiation and energy exchange at the surface, is one of the key parameters in the physical processes of the ground surface. It has been widely used in numerical forecasting, agricultural situation estimation, disaster monitoring, ecological environment assessment, and many other aspects. With the development of remote sensing technology, the study of LST based on remote sensing has received extensive attention from scholars at home and abroad.In this paper, based on the core database of Web of Science, we used VOSviewer and CiteSpace software to conduct a bibliometric study on 5336 papers on remote sensing-derived LST from 1985 to 2023. We analyzed the number of papers, research institutions, countries, authors, issuing journals, and keywords and looked forward to the future trend by combining with the hot spots of current research.Results show that (1) the field of remote sensing-derived LST has experienced rapid growth, especially after 2012, showing exponential expansion. China and the United States have made particularly outstanding contributions to this field, with 2169 and 1422 papers respectively. Chinese scholars have played a pivotal role in the field of remote sensing-derived LST, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences has achieved remarkable results. The organizations have shown a close cooperation between institutions, presenting an internationalized research pattern that promotes the sharing of scientific research resources and dissemination of knowledge worldwide. (2) Over time, the research center in the field of remote sensing-derived LST still focuses on the basic disciplines and gradually shifts to the applied disciplines. In terms of journals, Remote Sensing has become the main journal in the field of remote sensing-derived LST with its all-open-source feature, and Remote Sensing of Environment leads in popularity with a high citation count of 38884, underscoring its academic influence. (3) By clustering the keywords, four mainstream clusters are identified. LST data from sources like AVHRR, MODIS, and Landsat are extensively utilized, marking a shift in research focus from traditional topics like vegetation index and soil to emerging domains such as machine learning and local climate zones. This evolution is characterized by ongoing innovation and development in technological methods and research content. In the past decade, in addition to the traditional research directions of inversion, validation, and normalization of remotely sensed surface temperature, reconstruction, downscaling, and spatiotemporal fusion have become emerging research hotspots in the field.关键词:remote sensing;land surface temperature;bibliometrics;research hotspots;Development trends;fields of application;satellite data1778|988|0更新时间:2025-11-03
摘要:Land Surface Temperature (LST), which determines the radiation and energy exchange at the surface, is one of the key parameters in the physical processes of the ground surface. It has been widely used in numerical forecasting, agricultural situation estimation, disaster monitoring, ecological environment assessment, and many other aspects. With the development of remote sensing technology, the study of LST based on remote sensing has received extensive attention from scholars at home and abroad.In this paper, based on the core database of Web of Science, we used VOSviewer and CiteSpace software to conduct a bibliometric study on 5336 papers on remote sensing-derived LST from 1985 to 2023. We analyzed the number of papers, research institutions, countries, authors, issuing journals, and keywords and looked forward to the future trend by combining with the hot spots of current research.Results show that (1) the field of remote sensing-derived LST has experienced rapid growth, especially after 2012, showing exponential expansion. China and the United States have made particularly outstanding contributions to this field, with 2169 and 1422 papers respectively. Chinese scholars have played a pivotal role in the field of remote sensing-derived LST, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences has achieved remarkable results. The organizations have shown a close cooperation between institutions, presenting an internationalized research pattern that promotes the sharing of scientific research resources and dissemination of knowledge worldwide. (2) Over time, the research center in the field of remote sensing-derived LST still focuses on the basic disciplines and gradually shifts to the applied disciplines. In terms of journals, Remote Sensing has become the main journal in the field of remote sensing-derived LST with its all-open-source feature, and Remote Sensing of Environment leads in popularity with a high citation count of 38884, underscoring its academic influence. (3) By clustering the keywords, four mainstream clusters are identified. LST data from sources like AVHRR, MODIS, and Landsat are extensively utilized, marking a shift in research focus from traditional topics like vegetation index and soil to emerging domains such as machine learning and local climate zones. This evolution is characterized by ongoing innovation and development in technological methods and research content. In the past decade, in addition to the traditional research directions of inversion, validation, and normalization of remotely sensed surface temperature, reconstruction, downscaling, and spatiotemporal fusion have become emerging research hotspots in the field.关键词:remote sensing;land surface temperature;bibliometrics;research hotspots;Development trends;fields of application;satellite data1778|988|0更新时间:2025-11-03
Research Progress
-
Radiometric calibration method for deep convective clouds in the reflective bands of FY-4A/AGRI AI导读
“风云四号A星AGRI辐射性能退化,采用DCC方法评估,为定标系数更新提供依据。”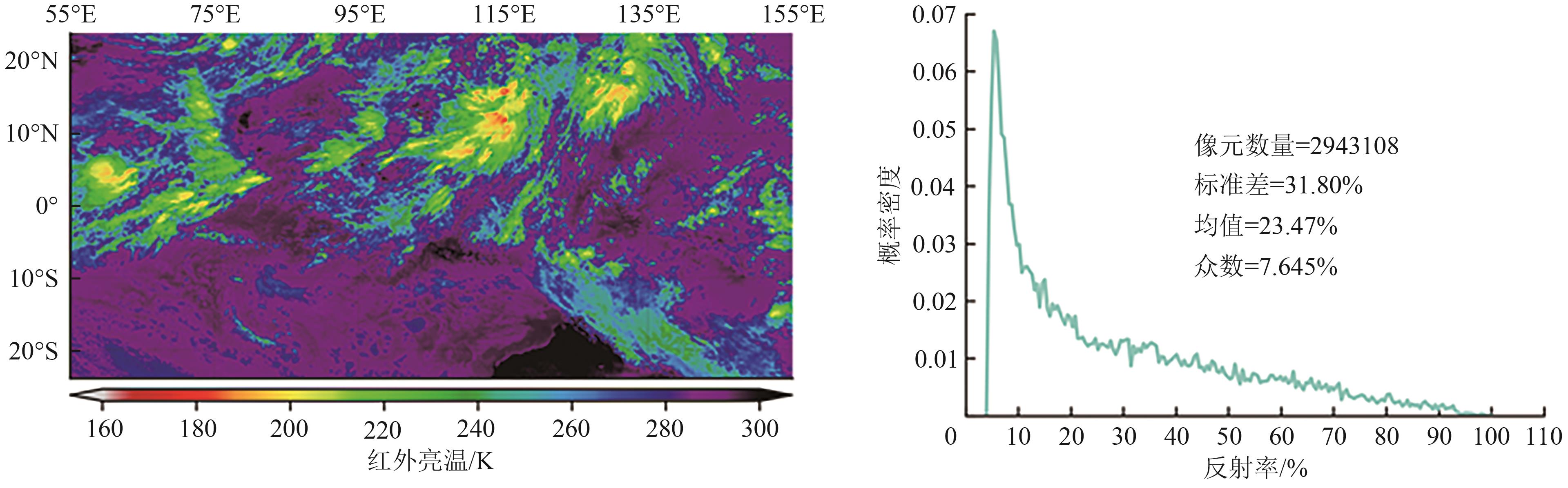 摘要:The advanced geostationary orbit radiometer (AGRI) of FY-4A satellite has been on orbit for 6 years, and the radiation performance of some reflective channels have significantly degraded, affecting the accuracy of quantitative remote sensing product applications. On-orbit vicarious calibration methods based on Deep Convective Cloud (DCC) targets can track and correct the radiometric response of spaceborne optical sensors for attenuation. This method relies on large-sample statistical analysis, and conducting sensitivity studies on factors influencing the calibration accuracy and stability in this method and developing optimal solutions holds significant importance.The procedure of the fundamental DCC calibration and tracking method is outlined as follows. Initially, DCC target pixels were extracted from FY-4A/AGRI L1 level data, the reflectance of the target pixels was calculated, and anisotropic correction was executed using the DCC Angle Distribution Model (ADM). Subsequently, daily or monthly Probability Density Functions (PDFs) of DCC reflectance were constructed, and the trend in peak reflectance (also known as mode) or reflectance mean was tracked to monitor and evaluate the radiometric performance of the FY-4A/AGRI instrument. To improve the calibration accuracy and stability, the sensitivity research scheme for infrared brightness temperature threshold, pixel uniformity conditions, and DCC ADM was proposed. Lastly, the DCC model was corrected, and an optimal solution was established according to the sensitivity analysis results.Results indicate that for the infrared brightness temperature threshold, the sensitivity of DCC mean reflectance is lower than that of PDF peak reflectance in the visible light channel, and in the short-wave infrared channel, the sensitivity of DCC PDF peak reflectance is slightly lower than that of reflectance mean. In the visible-near-infrared band, the CERES ADM can better correct the effect of DCC reflectance anisotropy and is significantly better than the Hu model. However, neither of the two ADMs has obvious correction effect in the short-wave infrared band. Based on the above sensitivity studies, the threshold selection and ADM correction strategy in the DCC method are determined. The radiation response of FY-4A/AGRI reflected bands from March 2017 to April 2023 is tracked and evaluated. Results show that the radiation response of 0.47, 0.65, and 2.25 μm channels degrades significantly, with total attenuation rates of 45.55%, 26.22%, and 6.362%, respectively. This result provides a reference for updating the AGRI operation calibration coefficient.A sensitivity analysis on the key factors in the radiometric calibration tracking method was conducted based on DCC for satellite optical sensors, enhancing calibration accuracy and stability through the establishment of an optimal solution. By utilizing optimization methods, the variations in the radiometric response performance in the reflectance band of the FY-4A/AGRI were quantitatively evaluated, providing valuable reference for updating the operational calibration coefficients of this instrument.关键词:remote sensing and sensors;radiometric calibration;Deep convective cloud;advanced geostationary radiation imager;angular distribution model;top of atmosphere reflectance;reflective solar bands670|715|0更新时间:2025-11-03
摘要:The advanced geostationary orbit radiometer (AGRI) of FY-4A satellite has been on orbit for 6 years, and the radiation performance of some reflective channels have significantly degraded, affecting the accuracy of quantitative remote sensing product applications. On-orbit vicarious calibration methods based on Deep Convective Cloud (DCC) targets can track and correct the radiometric response of spaceborne optical sensors for attenuation. This method relies on large-sample statistical analysis, and conducting sensitivity studies on factors influencing the calibration accuracy and stability in this method and developing optimal solutions holds significant importance.The procedure of the fundamental DCC calibration and tracking method is outlined as follows. Initially, DCC target pixels were extracted from FY-4A/AGRI L1 level data, the reflectance of the target pixels was calculated, and anisotropic correction was executed using the DCC Angle Distribution Model (ADM). Subsequently, daily or monthly Probability Density Functions (PDFs) of DCC reflectance were constructed, and the trend in peak reflectance (also known as mode) or reflectance mean was tracked to monitor and evaluate the radiometric performance of the FY-4A/AGRI instrument. To improve the calibration accuracy and stability, the sensitivity research scheme for infrared brightness temperature threshold, pixel uniformity conditions, and DCC ADM was proposed. Lastly, the DCC model was corrected, and an optimal solution was established according to the sensitivity analysis results.Results indicate that for the infrared brightness temperature threshold, the sensitivity of DCC mean reflectance is lower than that of PDF peak reflectance in the visible light channel, and in the short-wave infrared channel, the sensitivity of DCC PDF peak reflectance is slightly lower than that of reflectance mean. In the visible-near-infrared band, the CERES ADM can better correct the effect of DCC reflectance anisotropy and is significantly better than the Hu model. However, neither of the two ADMs has obvious correction effect in the short-wave infrared band. Based on the above sensitivity studies, the threshold selection and ADM correction strategy in the DCC method are determined. The radiation response of FY-4A/AGRI reflected bands from March 2017 to April 2023 is tracked and evaluated. Results show that the radiation response of 0.47, 0.65, and 2.25 μm channels degrades significantly, with total attenuation rates of 45.55%, 26.22%, and 6.362%, respectively. This result provides a reference for updating the AGRI operation calibration coefficient.A sensitivity analysis on the key factors in the radiometric calibration tracking method was conducted based on DCC for satellite optical sensors, enhancing calibration accuracy and stability through the establishment of an optimal solution. By utilizing optimization methods, the variations in the radiometric response performance in the reflectance band of the FY-4A/AGRI were quantitatively evaluated, providing valuable reference for updating the operational calibration coefficients of this instrument.关键词:remote sensing and sensors;radiometric calibration;Deep convective cloud;advanced geostationary radiation imager;angular distribution model;top of atmosphere reflectance;reflective solar bands670|715|0更新时间:2025-11-03 - “风云四号B星快速扫描成像仪晴空图像合成算法,提升了植被、水体监测等生态遥感业务水平。”
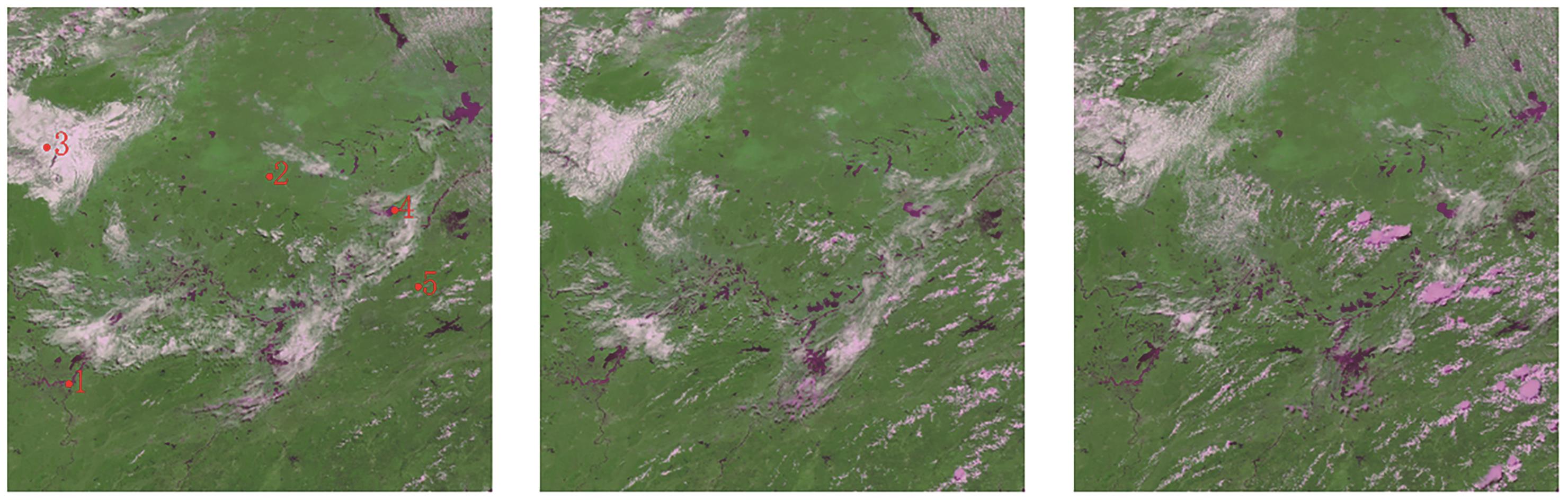 摘要:The clear-sky image synthesis in a single day is of great significance for daily water body recognition and other business applications. This paper proposes a clear-sky image synthesis algorithm based on a binary Gaussian mixture model for a 1-minute continuous imaging sequence data of the Geostationary High-speed Imager (GHI) of the FY-4B satellite. The GHI is the world’s first quantitative remote sensing instrument capable of high-frequency imaging of geostationary orbit during day and night. It is designed to meet short-term forecasting needs, with a total of seven visible and infrared channels, providing continuous observation of multiple spectral bands at 1-minute intervals in a 2000 × 2000 km area.Generally, except for ice and snow, the reflectivity of clouds is higher than that of the underlying surface. For the same location, the change in reflectivity is relatively small, whereas the change in reflectivity of passing clouds is significant. That is, the distribution of surface reflectance shows low mean and small variance (with relatively concentrated samples), whereas the distribution of cloud reflectance passing through shows high mean and large variance (with scattered samples). Therefore, the algorithm in this article assumes that the reflectance sequence samples of a single pixel within a single day are composed of clear-sky reflectance samples and cloud reflectance samples, which satisfy Gaussian distributions. The problem of synthesizing clear-sky images is transformed into estimating the distribution parameters of clear-sky reflectance samples. The algorithm is divided into three main steps: initial guess value (Step I), pixel classification (Step C), and parameter update (Step U). In the initial parameter estimation, a simple threshold method is used to initialize the clear-sky binary Gaussian distribution parameters. For the sequential processing of time-series images, Gaussian distribution function is used to identify the clear-sky type to which new image pixels belong. The average, standard deviation, and other parameters of the two types of clear sky at the location are updated based on the new identification results. Finally, when the sequential processing of all intraday image data are completed, the average reflectance of the clear-sky type is used as the estimated reflectance of the clear-sky composite result for that location.The method has linear time and memory space complexity, and the effective clear-sky pixel ratio and image information entropy of the clear-sky composite image gradually increase. Compared with typical clear sky algorithms, it has higher robustness in distinguishing clear sky and filtering ability for cloud edge shadows.High-frequency single-day clear-sky composite images can be applied in ecological remote sensing applications such as vegetation, water environment, and water monitoring.关键词:Clear Sky Synthesis Image;FY-4B;GHI;Gaussian model;Water Body Identification;multi-temporal remote sensing data182|1251|0更新时间:2025-11-03
摘要:The clear-sky image synthesis in a single day is of great significance for daily water body recognition and other business applications. This paper proposes a clear-sky image synthesis algorithm based on a binary Gaussian mixture model for a 1-minute continuous imaging sequence data of the Geostationary High-speed Imager (GHI) of the FY-4B satellite. The GHI is the world’s first quantitative remote sensing instrument capable of high-frequency imaging of geostationary orbit during day and night. It is designed to meet short-term forecasting needs, with a total of seven visible and infrared channels, providing continuous observation of multiple spectral bands at 1-minute intervals in a 2000 × 2000 km area.Generally, except for ice and snow, the reflectivity of clouds is higher than that of the underlying surface. For the same location, the change in reflectivity is relatively small, whereas the change in reflectivity of passing clouds is significant. That is, the distribution of surface reflectance shows low mean and small variance (with relatively concentrated samples), whereas the distribution of cloud reflectance passing through shows high mean and large variance (with scattered samples). Therefore, the algorithm in this article assumes that the reflectance sequence samples of a single pixel within a single day are composed of clear-sky reflectance samples and cloud reflectance samples, which satisfy Gaussian distributions. The problem of synthesizing clear-sky images is transformed into estimating the distribution parameters of clear-sky reflectance samples. The algorithm is divided into three main steps: initial guess value (Step I), pixel classification (Step C), and parameter update (Step U). In the initial parameter estimation, a simple threshold method is used to initialize the clear-sky binary Gaussian distribution parameters. For the sequential processing of time-series images, Gaussian distribution function is used to identify the clear-sky type to which new image pixels belong. The average, standard deviation, and other parameters of the two types of clear sky at the location are updated based on the new identification results. Finally, when the sequential processing of all intraday image data are completed, the average reflectance of the clear-sky type is used as the estimated reflectance of the clear-sky composite result for that location.The method has linear time and memory space complexity, and the effective clear-sky pixel ratio and image information entropy of the clear-sky composite image gradually increase. Compared with typical clear sky algorithms, it has higher robustness in distinguishing clear sky and filtering ability for cloud edge shadows.High-frequency single-day clear-sky composite images can be applied in ecological remote sensing applications such as vegetation, water environment, and water monitoring.关键词:Clear Sky Synthesis Image;FY-4B;GHI;Gaussian model;Water Body Identification;multi-temporal remote sensing data182|1251|0更新时间:2025-11-03 - “在星载GNSS-R海面高度反演误差研究领域,专家提出了基于神经网络与注意力机制结合训练的误差补偿模型,有效修正了反演误差,为提高反演精度提供了解决方案。”
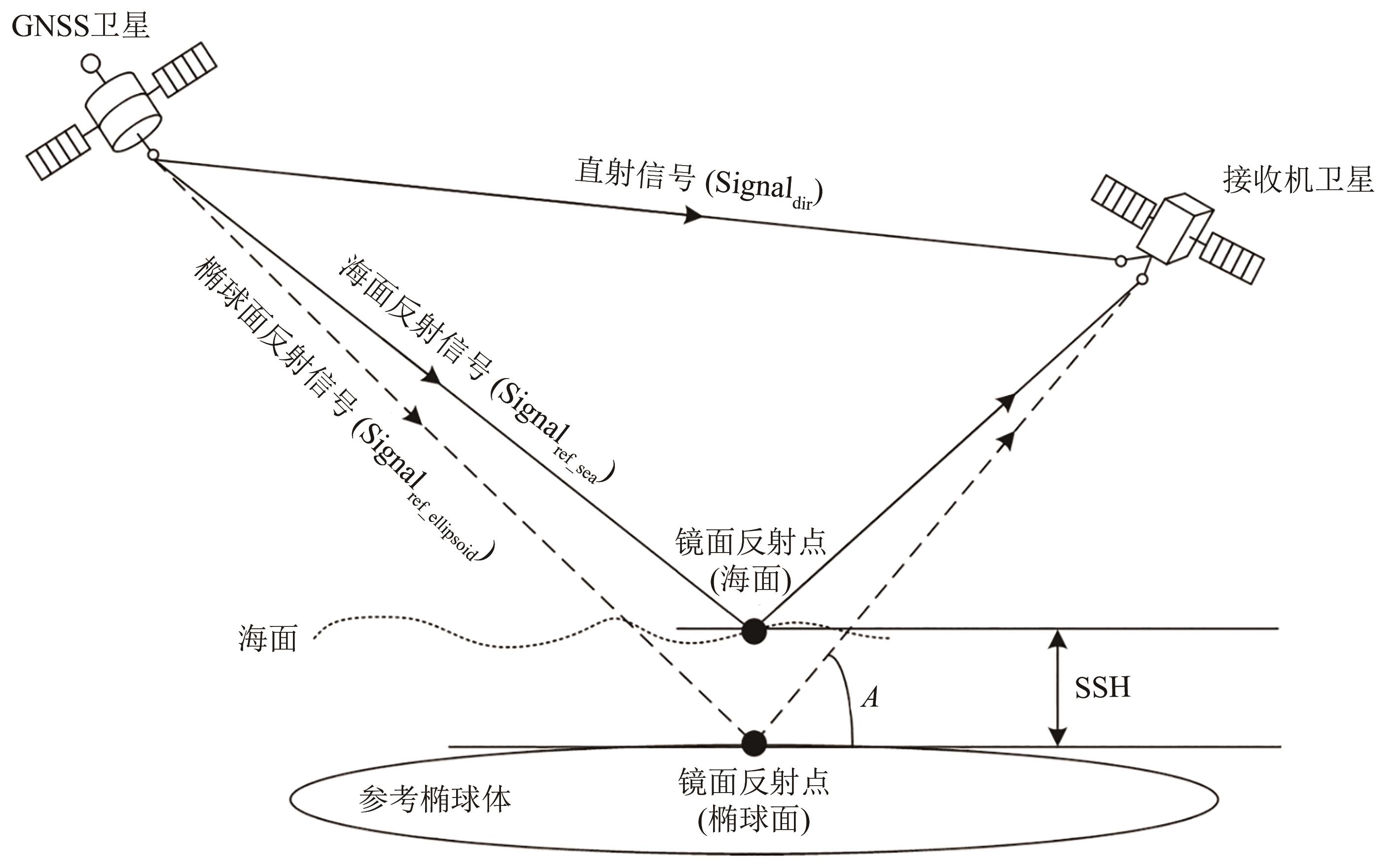 摘要:In the current research on sea surface height inversion from satellite-borne GNSS reflected signals, classical algorithms are usually used to invert sea surface height. However, due to the existence of multiple complex errors, such as inaccurate receiver orbit, system error, ionosphere error, and troposphere error, the results inverted using classical algorithms are mostly of low accuracy. Therefore, an error model is needed to correct the inversion results. Classic error models generally improve the accuracy of sea surface height inversion by correcting common errors, such as tropospheric error, ionosphere error, and antenna baseline attitude error, but there remain large errors that cannot be corrected. To address this problem, this paper proposes an error compensation model based on the combined training of neural networks and Attention Mechanisms (AMs) to correct the sea surface height inversion results.This paper proposes a training method that combines a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model with an AM to accurately train the error of sea surface height inversion from satellite-borne GNSS reflection signals. An error compensation model is generated to replace the classical error model, thereby improving the accuracy of sea surface height inversion.The proposed model was compared with the classic error model, CNN model, and random forest model and tested on about 2 million delay Doppler mapping data of the FY-3E dataset. The evaluation indicators used Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE). For the Global Positioning System reflected signal data corrected using the error compensation model, the MAE was 1.74 m, and the RMSE was 2.25 m. For the Beidou Navigation Satellite System reflected signal data, the MAE was 0.97 m, and the RMSE was 2.16 m. Compared with the classic error model, the correction accuracy was improved by about 80%. Compared with the random forest model and CNN model, the accuracy was also slightly improved.This paper proposes an error compensation model based on the training of CNN and AM to correct the sea surface height inversion results. Experiments show that the proposed error compensation model effectively corrects the sea surface height inversion error of space-borne GNSS-R.关键词:GNSS-R;neural network;satellite-based;FY-3E;sea surface height inversion;Error;DDM;Beidou329|1612|0更新时间:2025-11-03
摘要:In the current research on sea surface height inversion from satellite-borne GNSS reflected signals, classical algorithms are usually used to invert sea surface height. However, due to the existence of multiple complex errors, such as inaccurate receiver orbit, system error, ionosphere error, and troposphere error, the results inverted using classical algorithms are mostly of low accuracy. Therefore, an error model is needed to correct the inversion results. Classic error models generally improve the accuracy of sea surface height inversion by correcting common errors, such as tropospheric error, ionosphere error, and antenna baseline attitude error, but there remain large errors that cannot be corrected. To address this problem, this paper proposes an error compensation model based on the combined training of neural networks and Attention Mechanisms (AMs) to correct the sea surface height inversion results.This paper proposes a training method that combines a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model with an AM to accurately train the error of sea surface height inversion from satellite-borne GNSS reflection signals. An error compensation model is generated to replace the classical error model, thereby improving the accuracy of sea surface height inversion.The proposed model was compared with the classic error model, CNN model, and random forest model and tested on about 2 million delay Doppler mapping data of the FY-3E dataset. The evaluation indicators used Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE). For the Global Positioning System reflected signal data corrected using the error compensation model, the MAE was 1.74 m, and the RMSE was 2.25 m. For the Beidou Navigation Satellite System reflected signal data, the MAE was 0.97 m, and the RMSE was 2.16 m. Compared with the classic error model, the correction accuracy was improved by about 80%. Compared with the random forest model and CNN model, the accuracy was also slightly improved.This paper proposes an error compensation model based on the training of CNN and AM to correct the sea surface height inversion results. Experiments show that the proposed error compensation model effectively corrects the sea surface height inversion error of space-borne GNSS-R.关键词:GNSS-R;neural network;satellite-based;FY-3E;sea surface height inversion;Error;DDM;Beidou329|1612|0更新时间:2025-11-03 - “最新研究利用I-DINCAE模型和DNN技术,成功重构南海海表温度数据,揭示其时空变化特征。”
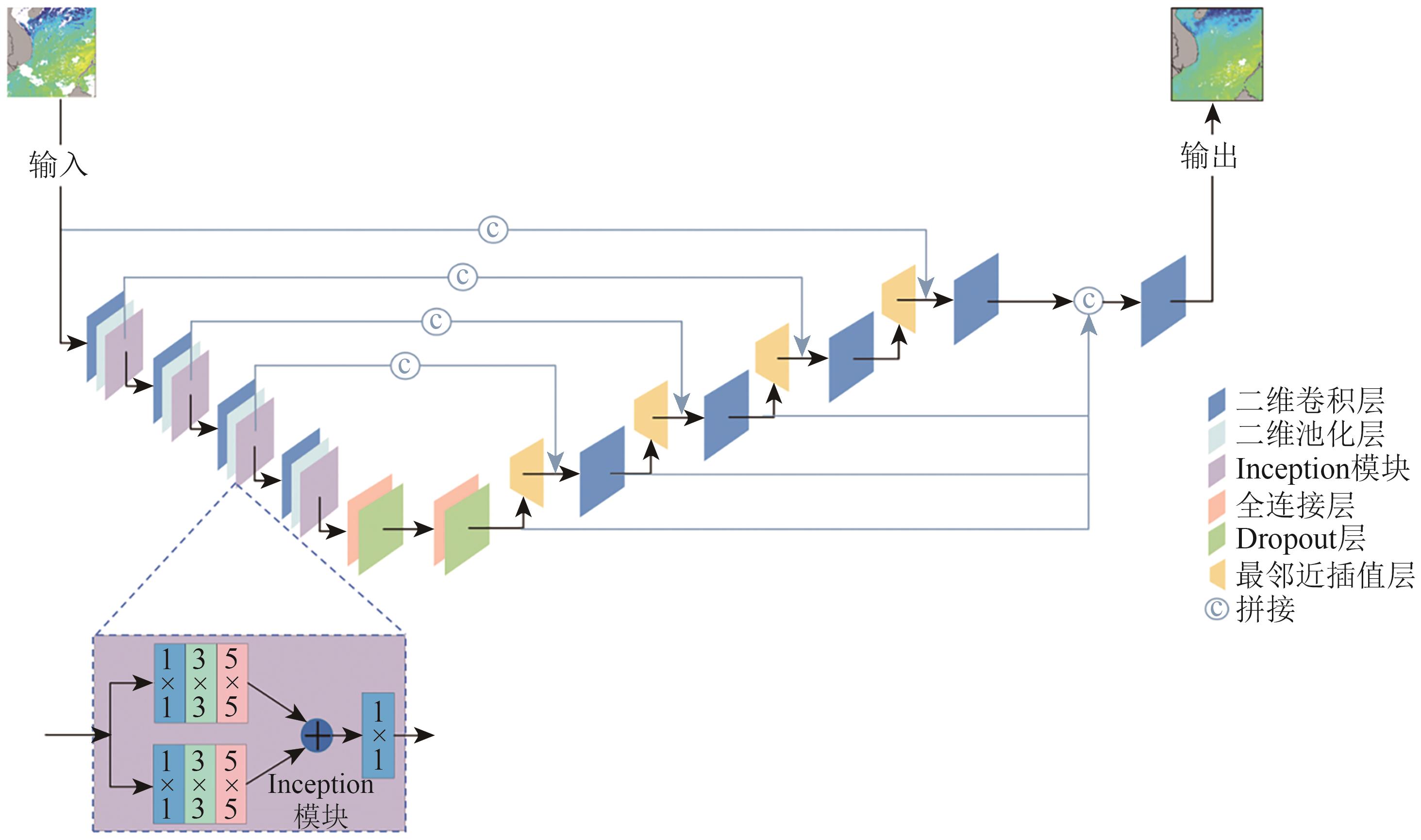 摘要:The Sea Surface Temperature (SST) is an important indicator for studying ocean dynamics, ocean-atmosphere interaction, and climate change, which is closely related to multiple marine environmental factors, such as ocean currents, salinity, and nutrient distribution, collectively affecting the balance and evolution of marine ecosystems. Although the traditional SST acquisition methods are precise, they are limited by the number and coverage of sampling points, making it difficult to meet the requirements of large-scale and high-resolution ocean research. Satellite remote sensing data can cover global waters with high update frequency and is widely used in ocean research. However, during the collection process of satellite remote sensing data, SST data are often missing due to factors such as weather conditions, satellite scanning orbit range, and satellite sensor operation failures, which limits the use of data to some extent. Therefore, precise reconstruction of missing data in satellite remote sensing SST data to obtain high-quality and fully covered SST datasets is of great significance for ocean research. This study incorporates an Inception module into a deep interpolation convolutional autoencoder (DINCAE) and proposes the improved DINCAE (I-DINCAE) model used for data reconstruction of SST products with the FY-3C satellite in the South China Sea. The I-DINCAE is used to reconstruct the missing SST data in the South China Sea from 2014 to 2020, and the reconstruction accuracy of the DINCAE and I-DINCAE models is compared and analyzed. To further improve the accuracy of SST data, deep neural networks (DNNs) are used to calibrate satellite data in combination with the measured data, thereby optimizing the quality of the SST dataset. Finally, based on the corrected SST data, spatiotemporal variation analysis is conducted to reveal the characteristics of SST changes. At the same time, combined with many years of measured data, DNN model is used to calibrate the reconstructed temperature data of the new model. A dataset of 11,993 independent measured data points is used for testing. Results show that the RMSE, MAE, and R² of the reconstructed SST and measured SST are 1.27 ℃, 0.96 ℃, and 0.84, which decreased to 0.57 ℃, 0.43 ℃, and 0.92 after the DNN model correction, respectively. Based on the corrected SST data, the spatiotemporal distribution and variation characteristics of SST in the South China Sea at monthly and quarterly scales are analyzed from two dimensions of time and space. Results show that on the seasonal scale, the SST of the South China Sea has obvious variation characteristics. This shows that the SST reaches the highest value in the summer, and the SST decreases to the lowest value in the winter. On the monthly scale, the SST variation in the South China Sea presents a sine (cosine) wave form, with SST usually reaching a maximum value in June and a minimum value in January. This study not only reveals the uniqueness of the marine environment in the South China Sea but also provides an important basis for understanding the marine ecosystem and climate change in the South China Sea.关键词:sea surface temperature;data reconstruction;deep learning;FY-3C;spatio-temporal variation263|1542|0更新时间:2025-11-03
摘要:The Sea Surface Temperature (SST) is an important indicator for studying ocean dynamics, ocean-atmosphere interaction, and climate change, which is closely related to multiple marine environmental factors, such as ocean currents, salinity, and nutrient distribution, collectively affecting the balance and evolution of marine ecosystems. Although the traditional SST acquisition methods are precise, they are limited by the number and coverage of sampling points, making it difficult to meet the requirements of large-scale and high-resolution ocean research. Satellite remote sensing data can cover global waters with high update frequency and is widely used in ocean research. However, during the collection process of satellite remote sensing data, SST data are often missing due to factors such as weather conditions, satellite scanning orbit range, and satellite sensor operation failures, which limits the use of data to some extent. Therefore, precise reconstruction of missing data in satellite remote sensing SST data to obtain high-quality and fully covered SST datasets is of great significance for ocean research. This study incorporates an Inception module into a deep interpolation convolutional autoencoder (DINCAE) and proposes the improved DINCAE (I-DINCAE) model used for data reconstruction of SST products with the FY-3C satellite in the South China Sea. The I-DINCAE is used to reconstruct the missing SST data in the South China Sea from 2014 to 2020, and the reconstruction accuracy of the DINCAE and I-DINCAE models is compared and analyzed. To further improve the accuracy of SST data, deep neural networks (DNNs) are used to calibrate satellite data in combination with the measured data, thereby optimizing the quality of the SST dataset. Finally, based on the corrected SST data, spatiotemporal variation analysis is conducted to reveal the characteristics of SST changes. At the same time, combined with many years of measured data, DNN model is used to calibrate the reconstructed temperature data of the new model. A dataset of 11,993 independent measured data points is used for testing. Results show that the RMSE, MAE, and R² of the reconstructed SST and measured SST are 1.27 ℃, 0.96 ℃, and 0.84, which decreased to 0.57 ℃, 0.43 ℃, and 0.92 after the DNN model correction, respectively. Based on the corrected SST data, the spatiotemporal distribution and variation characteristics of SST in the South China Sea at monthly and quarterly scales are analyzed from two dimensions of time and space. Results show that on the seasonal scale, the SST of the South China Sea has obvious variation characteristics. This shows that the SST reaches the highest value in the summer, and the SST decreases to the lowest value in the winter. On the monthly scale, the SST variation in the South China Sea presents a sine (cosine) wave form, with SST usually reaching a maximum value in June and a minimum value in January. This study not only reveals the uniqueness of the marine environment in the South China Sea but also provides an important basis for understanding the marine ecosystem and climate change in the South China Sea.关键词:sea surface temperature;data reconstruction;deep learning;FY-3C;spatio-temporal variation263|1542|0更新时间:2025-11-03 - “国家卫星气象中心发布风云三号D星雪深产品,验证显示精度提升,为林区雪深反演算法改进提供参考。”
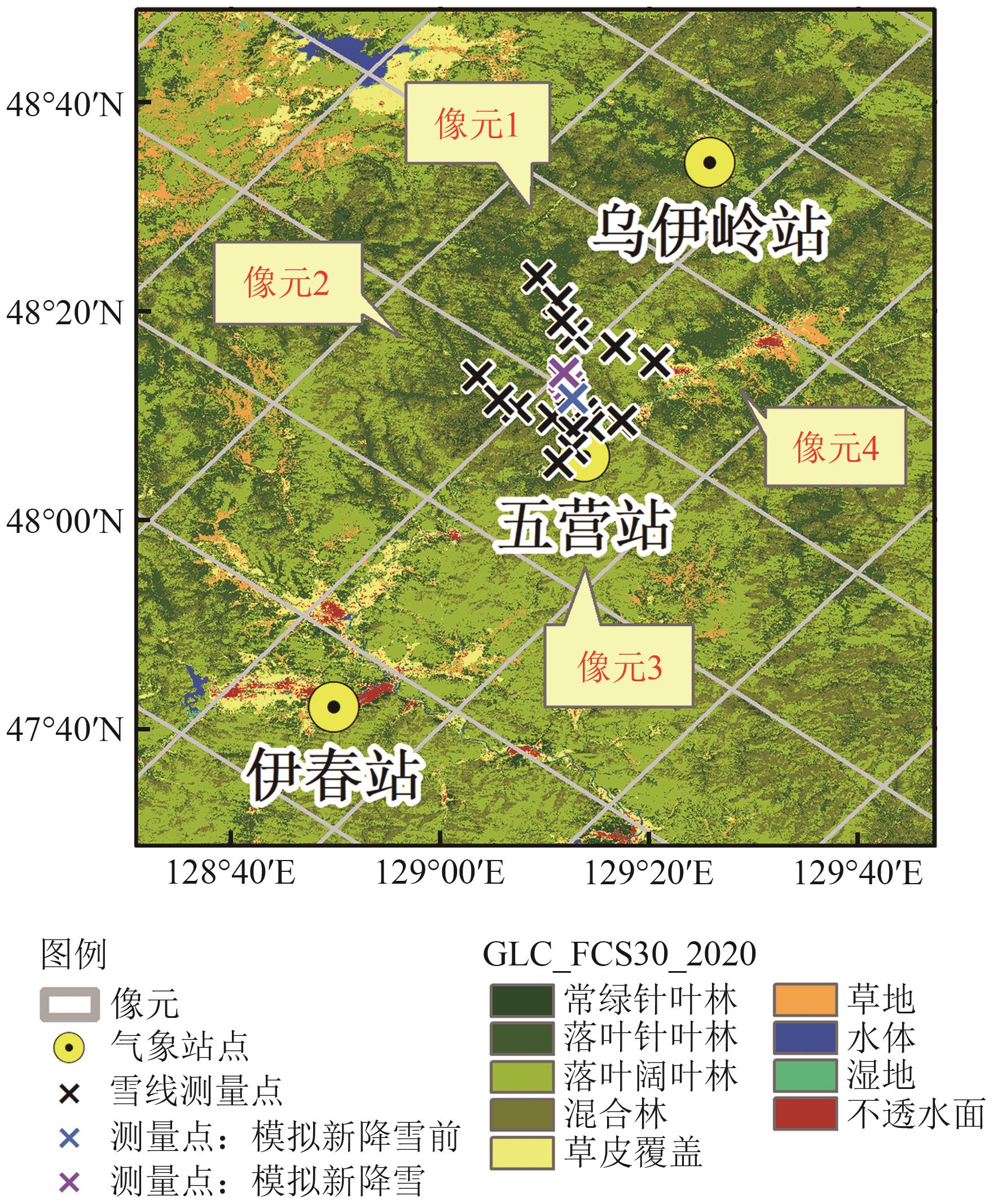 摘要:Snow Depth (SD) and Snow Water Equivalent (SWE) are crucial parameters for describing snow cover information. High-precision SD and SWE data are critical in investigating weather forecast, hydrology, surface processes, and other applications. Passive microwave remote sensing is an effective means of observing SD and SWE. Since April 2019, the National Satellite Meteorological Center has released passive microwave global SD and SWE products of microwave radiation imager aboard the Fengyun-3D Satellite (FY-3D). Compared with the FY-3B SD retrieval algorithm, the operational algorithm of the FY-3D introduces fractional forest cover for performing empirical correction on forest influence in Northeast China. This study investigates the performance of the improved FY-3D SD and SWE operational algorithms and verify the accuracy of the corresponding products in the forest area in Northeast China.This article obtains the situation of SD in the study area over the years through observation data from meteorological stations in Yichun, Heilongjiang Province. The FY-3D SD and SWE operational products are validated through measured snow course and SD data observed by meteorological stations in the forest areas. Moreover, the uncertainty of FY-3D SD products and the representativeness of meteorological stations are analyzed.Results indicate a strong temporal heterogeneity in SD distribution in the Yichun Region. The verification results indicate that the FY-3D SD product exhibits an overall underestimation, and the RMSE is 5 cm and 13.2 cm when compared with the measurements of snow course and the observations of meteorological station, respectively. Conversely, the RMSE between the FY-3D SWE product and the snow course data is 2.1 mm. The FY-3D SD operational algorithm, as a semi-empirical algorithm, cannot eliminate the influence of forests on microwave radiation brightness temperature. Although forest radiometric correction can enhance the correlation between brightness temperature gradient and SD, the empirical nature of forest radiometric correction also increases the uncertainty of SD inversion results.Analysis shows that the FY-3D algorithm has a lag in response to sudden snow drops due to its lack of response to new snow with an exponential correlation length of 0.11 mm. At the beginning of the snow season, when the SD remains below 5 cm, the change in brightness temperature gradient caused by soil freezing can be misjudged by the inversion algorithm, leading to overestimation of SD during this period. In the preliminary exploration of site representativeness, the analysis of the differences between point and surface combined with field observations show that snow in forest areas is deeply influenced by various factors, leading to strong local spatial heterogeneity. This work can provide reference for improving the SD inversion algorithm in forest regions based on domestic FY-3D brightness temperature data in the future.关键词:FY-3D/MWRI;snow depth;snow water equivalent;product validation;forest region299|796|0更新时间:2025-11-03
摘要:Snow Depth (SD) and Snow Water Equivalent (SWE) are crucial parameters for describing snow cover information. High-precision SD and SWE data are critical in investigating weather forecast, hydrology, surface processes, and other applications. Passive microwave remote sensing is an effective means of observing SD and SWE. Since April 2019, the National Satellite Meteorological Center has released passive microwave global SD and SWE products of microwave radiation imager aboard the Fengyun-3D Satellite (FY-3D). Compared with the FY-3B SD retrieval algorithm, the operational algorithm of the FY-3D introduces fractional forest cover for performing empirical correction on forest influence in Northeast China. This study investigates the performance of the improved FY-3D SD and SWE operational algorithms and verify the accuracy of the corresponding products in the forest area in Northeast China.This article obtains the situation of SD in the study area over the years through observation data from meteorological stations in Yichun, Heilongjiang Province. The FY-3D SD and SWE operational products are validated through measured snow course and SD data observed by meteorological stations in the forest areas. Moreover, the uncertainty of FY-3D SD products and the representativeness of meteorological stations are analyzed.Results indicate a strong temporal heterogeneity in SD distribution in the Yichun Region. The verification results indicate that the FY-3D SD product exhibits an overall underestimation, and the RMSE is 5 cm and 13.2 cm when compared with the measurements of snow course and the observations of meteorological station, respectively. Conversely, the RMSE between the FY-3D SWE product and the snow course data is 2.1 mm. The FY-3D SD operational algorithm, as a semi-empirical algorithm, cannot eliminate the influence of forests on microwave radiation brightness temperature. Although forest radiometric correction can enhance the correlation between brightness temperature gradient and SD, the empirical nature of forest radiometric correction also increases the uncertainty of SD inversion results.Analysis shows that the FY-3D algorithm has a lag in response to sudden snow drops due to its lack of response to new snow with an exponential correlation length of 0.11 mm. At the beginning of the snow season, when the SD remains below 5 cm, the change in brightness temperature gradient caused by soil freezing can be misjudged by the inversion algorithm, leading to overestimation of SD during this period. In the preliminary exploration of site representativeness, the analysis of the differences between point and surface combined with field observations show that snow in forest areas is deeply influenced by various factors, leading to strong local spatial heterogeneity. This work can provide reference for improving the SD inversion algorithm in forest regions based on domestic FY-3D brightness temperature data in the future.关键词:FY-3D/MWRI;snow depth;snow water equivalent;product validation;forest region299|796|0更新时间:2025-11-03
Chinese Satellites
- “白鹤滩水电站库岸潜在失稳边坡监测研究取得进展,提出了改进的时序InSAR库岸区形变估计方法,为长期变形监测预警提供参考。”
 摘要:The Baihetan Hydropower Station is the world’s second-largest hydropower station. Long-term and effective deformation monitoring for this area is of great significance. In this paper, InSAR technology was applied to monitor the temporal deformation of a potential unstable slope of a reservoir bank of the Baihetan Hydropower Station to explore its spatiotemporal deformation discipline under the combined effect of water level and precipitation changes. To address the limitation that the effects of climate and environment are often ignored in traditional InSAR linear deformation models, an improved time-series InSAR method was proposed in this paper. This method is based on a periodic model incorporated with the precipitation parameters in the deformation modeling process, with consideration of the effects of water level and precipitation changes in the reservoir bank area; during the deformation estimation process, parameters of deformation rate, elevation corrections, and precipitation factors were calculated based on the functional systems of temporal phase observations, generating the final temporal deformation results for the potential unstable slopes. The Dawanzi-Qiluogou section of the Baihetan Hydropower Station’s reservoir was selected as the study area in the experiment, and a period of 31-month deformation time series was obtained. Findings indicated that the temporal deformation characteristic was dominated by a linear trend with periodical variations following the water levels and a two-month lag effect referencing to the dry-rainy alternate month. In addition, the slope deformation in the near river area of the Dawanzi-Qiluogou section was greater than that in the far river area, with the maximum cumulative deformation of -155 mm from January 2010 to July 2022. The maximum deformation difference for the pixels on the exit and central sections was estimated as 98 mm, which is the main cause of cracks in the tunnel wall of the downstream exit section of the Dawanzi Tunnel. The residual high-pass deformation was utilized to evaluate the modeling accuracy of the proposed model, which was estimated as an accuracy increasement of 12.5% compared to the traditional model. In-situ GNSS monitoring results were used to evaluate the external accuracy of the obtained deformation, which was estimated as ±2.9 mm. Research results can provide reference for the long-term deformation monitoring and landslide hazard identification for the unstable slopes on the reservoir bank of the Baihetan Hydropower Station.关键词:InSAR;deformation monitoring;Bank Slopes;Unstable;Time series modeling104|236|0更新时间:2025-11-03
摘要:The Baihetan Hydropower Station is the world’s second-largest hydropower station. Long-term and effective deformation monitoring for this area is of great significance. In this paper, InSAR technology was applied to monitor the temporal deformation of a potential unstable slope of a reservoir bank of the Baihetan Hydropower Station to explore its spatiotemporal deformation discipline under the combined effect of water level and precipitation changes. To address the limitation that the effects of climate and environment are often ignored in traditional InSAR linear deformation models, an improved time-series InSAR method was proposed in this paper. This method is based on a periodic model incorporated with the precipitation parameters in the deformation modeling process, with consideration of the effects of water level and precipitation changes in the reservoir bank area; during the deformation estimation process, parameters of deformation rate, elevation corrections, and precipitation factors were calculated based on the functional systems of temporal phase observations, generating the final temporal deformation results for the potential unstable slopes. The Dawanzi-Qiluogou section of the Baihetan Hydropower Station’s reservoir was selected as the study area in the experiment, and a period of 31-month deformation time series was obtained. Findings indicated that the temporal deformation characteristic was dominated by a linear trend with periodical variations following the water levels and a two-month lag effect referencing to the dry-rainy alternate month. In addition, the slope deformation in the near river area of the Dawanzi-Qiluogou section was greater than that in the far river area, with the maximum cumulative deformation of -155 mm from January 2010 to July 2022. The maximum deformation difference for the pixels on the exit and central sections was estimated as 98 mm, which is the main cause of cracks in the tunnel wall of the downstream exit section of the Dawanzi Tunnel. The residual high-pass deformation was utilized to evaluate the modeling accuracy of the proposed model, which was estimated as an accuracy increasement of 12.5% compared to the traditional model. In-situ GNSS monitoring results were used to evaluate the external accuracy of the obtained deformation, which was estimated as ±2.9 mm. Research results can provide reference for the long-term deformation monitoring and landslide hazard identification for the unstable slopes on the reservoir bank of the Baihetan Hydropower Station.关键词:InSAR;deformation monitoring;Bank Slopes;Unstable;Time series modeling104|236|0更新时间:2025-11-03 - “广州市地表形变监测研究取得新进展,揭示了地表形变时空分异特征,证实地铁运营时间与沿线沉降呈显著负相关,并提出基于1000米缓冲区的监测评估指标,为城市地质安全防控提供科学依据。”
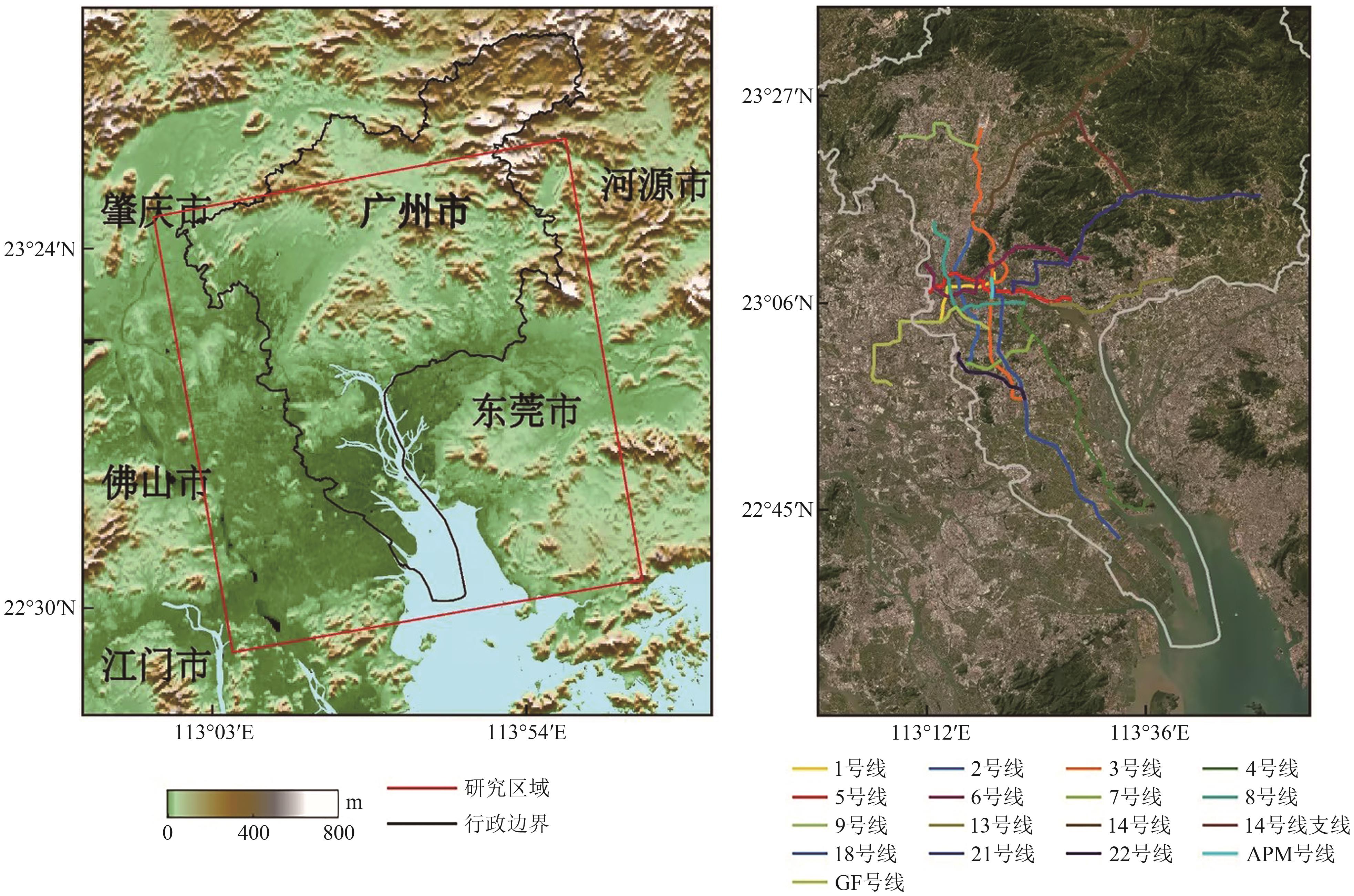 摘要:As one of the core cities of the Pearl River Delta, Guangzhou plays an important role in economic development and transportation. However, with the advancement of large-scale engineering construction and the increase in human activities, geologic hazards have become more prominent. Therefore, high-precision deformation monitoring and cause analysis are essential to safeguard the city’s socioeconomic development and public safety. Although attribution analyses of surface deformation along metro lines are executed based on a buffer zone, few studies have addressed the sensitivity of buffer size selection to the influence factors of subsidence. Clear attribution analysis can provide guidance for the prevention and control of geological disasters along the subway.From May 2017 to May 2020, a total of 85 scenes of Sentinel-1A data covering Guangzhou were collected. IPTA time-series InSAR technology is then used to obtain the surface deformation time series of the city. By combining GIS spatial analysis techniques and Pearson correlation statistics, the influencing factors behind the deformation were quantitatively analyzed. In addition, field survey data were introduced to examine the effect of buffer zone distance selection along subway lines on the correlation between various influencing factors and surface deformation. Results show that surface deformation within Guangzhou exhibits a decentralized distribution, characterized by localized deformation along metro lines and residential areas, large-scale deformation in landfill sites, and widespread deformation in farmland areas. The largest deformation is observed at LiKeng landfill, with a deformation rate of -54.5 mm/a. Specific to the subsidence along metro lines, obvious deformations (≤20 mm/a) are primarily concentrated on Lines 4, 9, 14, 6, and 18, with a pixel percentage of 0.14%, 0.08%, 0.07%, 0.05%, and 0.04%, respectively. The largest deformation rate was recorded at KeMuLang station on Line 6, reaching -39.5 mm/yr. Moreover, attribution analysis was conducted between surface deformation, operation time, subway distance, road network density, and building load. Settlement along the metro line demonstrates a moderate negative correlation with operation time (r=-0.53), suggesting that as metro lines operate for longer durations, settlement magnitudes decrease. For subway distance, a negative correlation between settlement and distance was observed; the likelihood of settlement increases as proximity to the subway decreases. A positive correlation exists between settlement and road network density and between settlement and building loads; the correlation coefficient of each line is mostly less than 0.2. Moreover, three buffer zones were selected (i.e., 800, 1000, and 1500 m) to analyze their sensitivity to the abovementioned factors. Results show that only subway distance is sensitive to the buffer zone size, whereas the remaining factors (road network density and building load) are not sensitive to buffer changes. Moreover, 58 field samples were collected to select the appropriate buffer zone for the attribution analysis of deformation along Guangzhou’s metro lines, and the result is 1000 m. The influence factors studied in this paper are relatively limited. Future work should concentrate on building construction, groundwater level, excavation depths, geological conditions, and other factors. Furthermore, quantitative analysis based on machine learning should be explored.关键词:Guangzhou Metro;InSAR;deformation monitoring;Attribution analysis;land subsidence476|742|0更新时间:2025-11-03
摘要:As one of the core cities of the Pearl River Delta, Guangzhou plays an important role in economic development and transportation. However, with the advancement of large-scale engineering construction and the increase in human activities, geologic hazards have become more prominent. Therefore, high-precision deformation monitoring and cause analysis are essential to safeguard the city’s socioeconomic development and public safety. Although attribution analyses of surface deformation along metro lines are executed based on a buffer zone, few studies have addressed the sensitivity of buffer size selection to the influence factors of subsidence. Clear attribution analysis can provide guidance for the prevention and control of geological disasters along the subway.From May 2017 to May 2020, a total of 85 scenes of Sentinel-1A data covering Guangzhou were collected. IPTA time-series InSAR technology is then used to obtain the surface deformation time series of the city. By combining GIS spatial analysis techniques and Pearson correlation statistics, the influencing factors behind the deformation were quantitatively analyzed. In addition, field survey data were introduced to examine the effect of buffer zone distance selection along subway lines on the correlation between various influencing factors and surface deformation. Results show that surface deformation within Guangzhou exhibits a decentralized distribution, characterized by localized deformation along metro lines and residential areas, large-scale deformation in landfill sites, and widespread deformation in farmland areas. The largest deformation is observed at LiKeng landfill, with a deformation rate of -54.5 mm/a. Specific to the subsidence along metro lines, obvious deformations (≤20 mm/a) are primarily concentrated on Lines 4, 9, 14, 6, and 18, with a pixel percentage of 0.14%, 0.08%, 0.07%, 0.05%, and 0.04%, respectively. The largest deformation rate was recorded at KeMuLang station on Line 6, reaching -39.5 mm/yr. Moreover, attribution analysis was conducted between surface deformation, operation time, subway distance, road network density, and building load. Settlement along the metro line demonstrates a moderate negative correlation with operation time (r=-0.53), suggesting that as metro lines operate for longer durations, settlement magnitudes decrease. For subway distance, a negative correlation between settlement and distance was observed; the likelihood of settlement increases as proximity to the subway decreases. A positive correlation exists between settlement and road network density and between settlement and building loads; the correlation coefficient of each line is mostly less than 0.2. Moreover, three buffer zones were selected (i.e., 800, 1000, and 1500 m) to analyze their sensitivity to the abovementioned factors. Results show that only subway distance is sensitive to the buffer zone size, whereas the remaining factors (road network density and building load) are not sensitive to buffer changes. Moreover, 58 field samples were collected to select the appropriate buffer zone for the attribution analysis of deformation along Guangzhou’s metro lines, and the result is 1000 m. The influence factors studied in this paper are relatively limited. Future work should concentrate on building construction, groundwater level, excavation depths, geological conditions, and other factors. Furthermore, quantitative analysis based on machine learning should be explored.关键词:Guangzhou Metro;InSAR;deformation monitoring;Attribution analysis;land subsidence476|742|0更新时间:2025-11-03 - “最新研究突破:基于自监督对比学习的InSAR时序形变深度聚类方法,有效提升形变信息解译准确性。”
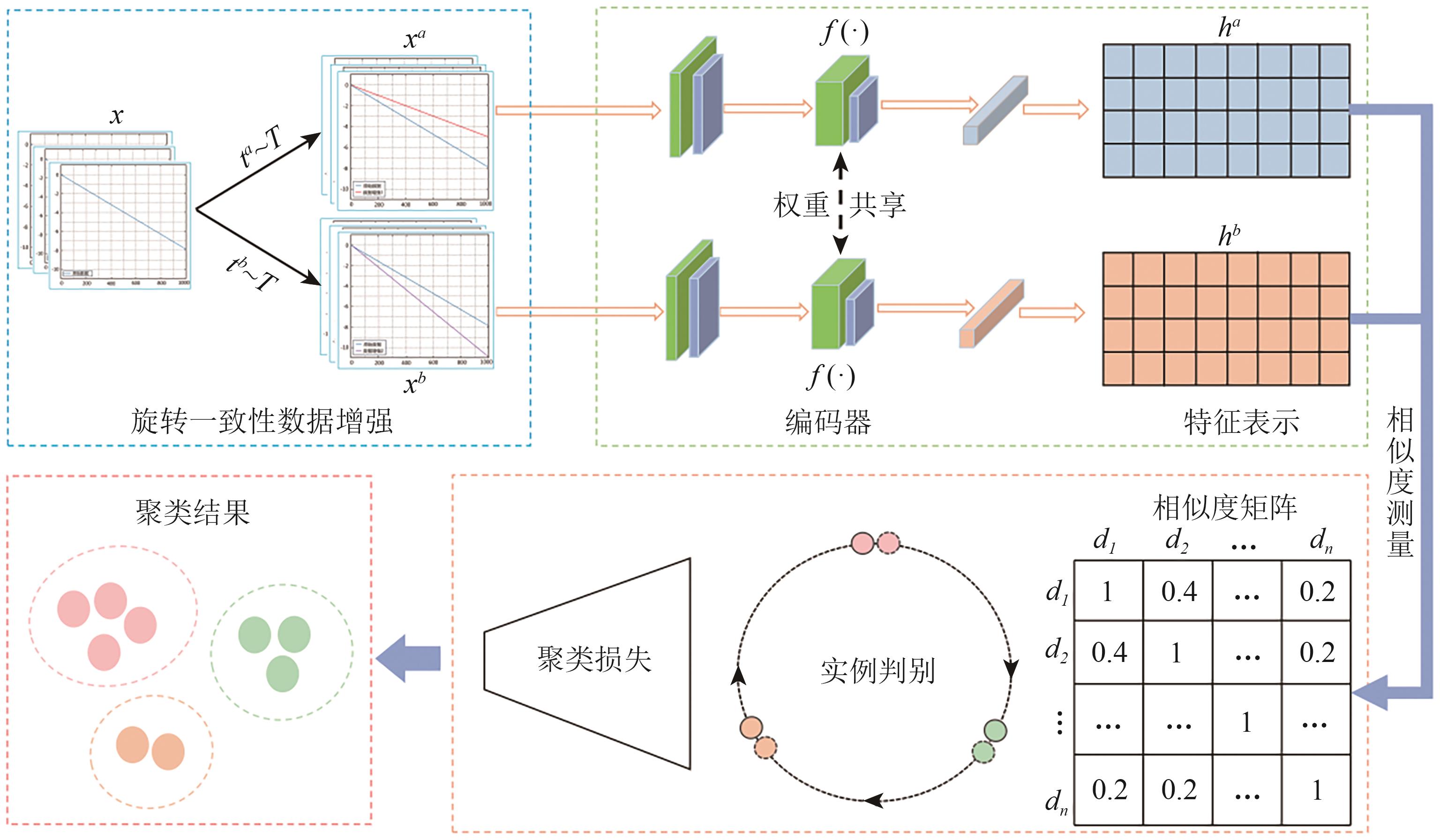 摘要:The time-series Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) technique is widely recognized for its capability to monitor large-scale deformations, making it instrumental in applications such as geologic disaster monitoring, urban infrastructure safety assessment, and mining slope evaluation. This study aims to address the challenges in deciphering large-scale deformation time-series data obtained through InSAR. By leveraging self-supervised contrastive learning, we enhance the classification and clustering capabilities of InSAR time-series deformation data, which is critical for identifying geohazard signals and supporting infrastructure safety evaluation.We propose a novel deep clustering framework based on self-supervised contrastive learning to enhance clustering performance on unlabeled deformation time-series data. To overcome the limitations of traditional time-series data augmentation techniques, a rotational consistency-based data augmentation strategy is introduced. This strategy maintains morphological similarity by rotating the original time series at different angles, enabling the model to better capture invariance in time-series transformations. The method’s clustering performance is evaluated against traditional K-means clustering, with key metrics such as clustering accuracy and normalized mutual information (NMI) used for comparison. The framework is further validated using deformation data extracted from the Sentinel-1 ascending orbit dataset, covering the Kafang tailings pond in Gejiu City, Yunnan Province from January 2020 to October 2022.The proposed method outperformed traditional K-means clustering, achieving a 25.8% improvement in clustering accuracy and a 16.3% increase in NMI. Compared with the K-shape method, the proposed method shows better accuracy in capturing time-series features and similarity measurement. The clustering analysis performed on the Sentinel-1 dataset successfully classified deformation time series into meaningful groups, revealing distinct deformation patterns and effectively identifying potential danger signals.The integration of self-supervised contrastive learning with InSAR time-series analysis enhances the interpretability and classification of deformation patterns. The proposed method provides a robust and efficient tool for geohazard monitoring, urban infrastructure evaluation, and mining slope safety assessment. This approach has potential for broader applications in large-scale remote sensing data analysis.关键词:self-supervised contrastive learning;Data enhancement;time series analysis;deformation clustering;time-series InSAR354|874|0更新时间:2025-11-03
摘要:The time-series Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) technique is widely recognized for its capability to monitor large-scale deformations, making it instrumental in applications such as geologic disaster monitoring, urban infrastructure safety assessment, and mining slope evaluation. This study aims to address the challenges in deciphering large-scale deformation time-series data obtained through InSAR. By leveraging self-supervised contrastive learning, we enhance the classification and clustering capabilities of InSAR time-series deformation data, which is critical for identifying geohazard signals and supporting infrastructure safety evaluation.We propose a novel deep clustering framework based on self-supervised contrastive learning to enhance clustering performance on unlabeled deformation time-series data. To overcome the limitations of traditional time-series data augmentation techniques, a rotational consistency-based data augmentation strategy is introduced. This strategy maintains morphological similarity by rotating the original time series at different angles, enabling the model to better capture invariance in time-series transformations. The method’s clustering performance is evaluated against traditional K-means clustering, with key metrics such as clustering accuracy and normalized mutual information (NMI) used for comparison. The framework is further validated using deformation data extracted from the Sentinel-1 ascending orbit dataset, covering the Kafang tailings pond in Gejiu City, Yunnan Province from January 2020 to October 2022.The proposed method outperformed traditional K-means clustering, achieving a 25.8% improvement in clustering accuracy and a 16.3% increase in NMI. Compared with the K-shape method, the proposed method shows better accuracy in capturing time-series features and similarity measurement. The clustering analysis performed on the Sentinel-1 dataset successfully classified deformation time series into meaningful groups, revealing distinct deformation patterns and effectively identifying potential danger signals.The integration of self-supervised contrastive learning with InSAR time-series analysis enhances the interpretability and classification of deformation patterns. The proposed method provides a robust and efficient tool for geohazard monitoring, urban infrastructure evaluation, and mining slope safety assessment. This approach has potential for broader applications in large-scale remote sensing data analysis.关键词:self-supervised contrastive learning;Data enhancement;time series analysis;deformation clustering;time-series InSAR354|874|0更新时间:2025-11-03
InSAR Deformation Monitoring
-
Study on the summer surface thermal environment of Nanjing urban area based on local climate zone AI导读
“南京市主城区夏季热环境研究揭示了建筑密度与地表温度的关系,为缓解城市热岛效应提供科学依据。”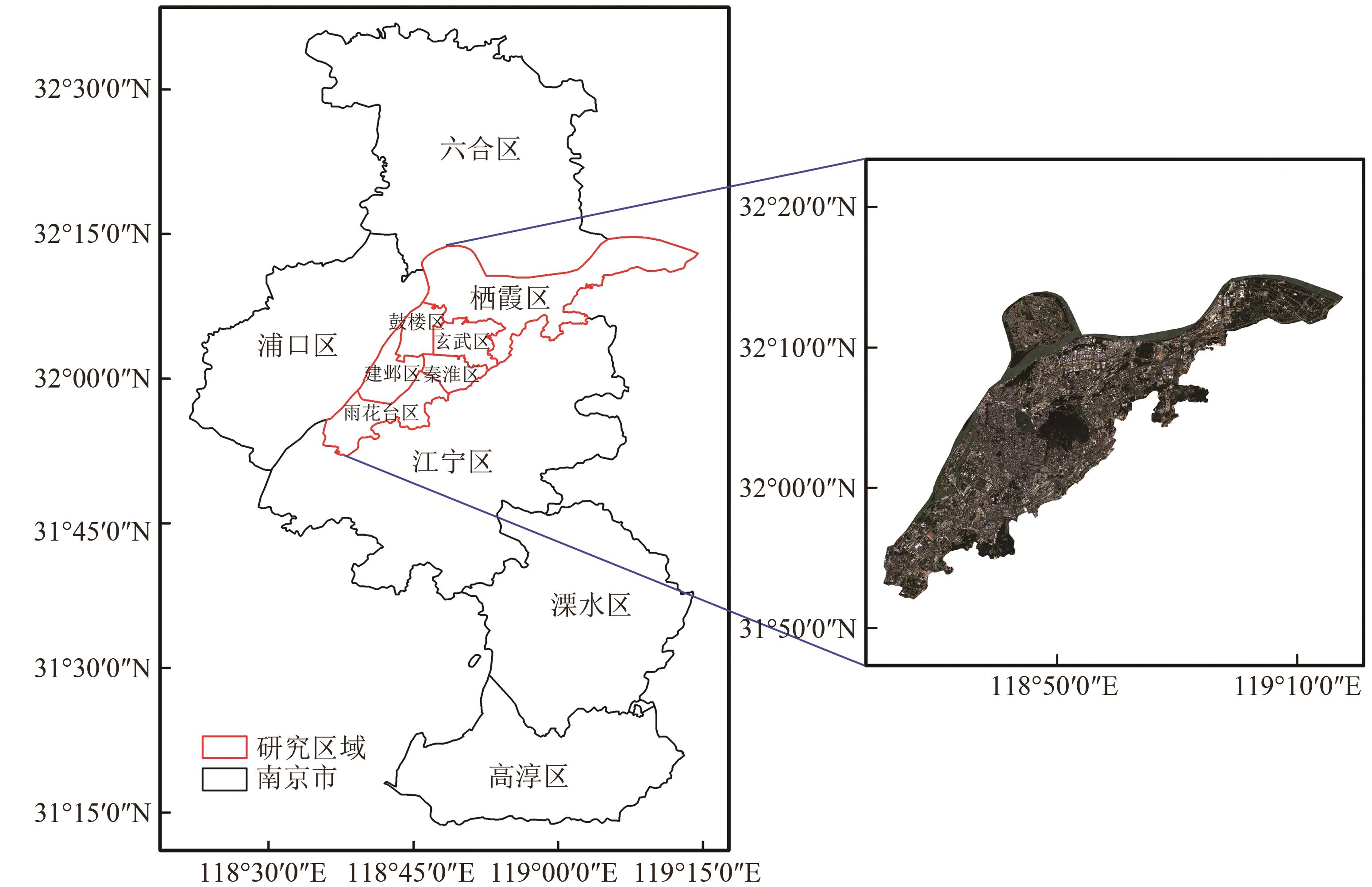 摘要:The issue of global warming has become increasingly prevalent in recent years. Concurrently, there exists a considerable prevalence of extreme meteorological occurrences in urban environment, exemplified by the intense heat that characterizes the summer season. The urban heat environment has become a research focus under the background of global warming and rapid urbanization. At present, Local Climate Zone (LCZ) represents the principal method of classification employed in the field of urban thermal environment research. In comparison with the traditional urban–rural dichotomy, this approach entails a further subdivision of the city on the basis of the physical characteristics of the buildings and the natural ground cover features. Based on the LCZ system, this paper investigated the summer thermal environment characteristics of the main urban area of Nanjing from two perspectives: interclass and intraclass, using Landsat image inversion of surface temperature. The classification of LCZs divided the study area into 12 categories, of which 8 were designated for building types and 4 were designated for surface cover types. The proportion of building types within the study area was greater than that of ground cover types. The building types exhibited a high proportion of open high-rise (LCZ 4) and dense mid-rise (LCZ 2), which were predominantly concentrated in the central urban areas. The largest surface cover type was bare soil and sand (LCZ F). Results indicated that the thermal environments among LCZ classes showed large differences. Higher building densities had higher mean LSTs. The mean LSTs tended to rise gradually as building height decreased. The time-series trend of the mean temperature for the various LCZ types was highly consistent with the overall mean temperature trend observed in the study area. Large low-rise (LCZ 8) consistently presented high average surface temperatures during the summer months, reaching a maximum of 53.2 ℃. Moreover, the average surface temperature for each building type was higher than the average surface temperature for the study area as a whole, and the average surface temperature for each natural ground cover type except bare soil or sand was lower than the average surface temperature for the study area as a whole. The mean surface temperature of compact mid-rise (LCZ 2), compact low-rise (LCZ 3), large low-rise (LCZ 8), and heavy industry (LCZ 10) were higher than the overall mean temperature of the study area. Furthermore, this study presented intraclass analysis of different LCZ types using relative rates of change in LST. An increased sensitivity to temperature fluctuations may have adverse effects on human well-being and economic productivity. Another important finding was that the intra-LCZ thermal environment analyses indicated a heightened sensitivity to temperature fluctuations in the following categories: compact mid-rise (LCZ 2), compact low-rise (LCZ 3), heavy industry (LCZ 10), and bare soil and sand (LCZ F). The findings of this study can serve as a valuable reference point and provide insights for further research in the fields of urban planning, the mitigation of the urban heat island effect, and the enhancement of the urban heat environment.关键词:Urban heat environment;Local Climate Zone;Nanjing city;land surface temperature;Inter-LCZ difference;Intra-LCZ difference336|1253|0更新时间:2025-11-03
摘要:The issue of global warming has become increasingly prevalent in recent years. Concurrently, there exists a considerable prevalence of extreme meteorological occurrences in urban environment, exemplified by the intense heat that characterizes the summer season. The urban heat environment has become a research focus under the background of global warming and rapid urbanization. At present, Local Climate Zone (LCZ) represents the principal method of classification employed in the field of urban thermal environment research. In comparison with the traditional urban–rural dichotomy, this approach entails a further subdivision of the city on the basis of the physical characteristics of the buildings and the natural ground cover features. Based on the LCZ system, this paper investigated the summer thermal environment characteristics of the main urban area of Nanjing from two perspectives: interclass and intraclass, using Landsat image inversion of surface temperature. The classification of LCZs divided the study area into 12 categories, of which 8 were designated for building types and 4 were designated for surface cover types. The proportion of building types within the study area was greater than that of ground cover types. The building types exhibited a high proportion of open high-rise (LCZ 4) and dense mid-rise (LCZ 2), which were predominantly concentrated in the central urban areas. The largest surface cover type was bare soil and sand (LCZ F). Results indicated that the thermal environments among LCZ classes showed large differences. Higher building densities had higher mean LSTs. The mean LSTs tended to rise gradually as building height decreased. The time-series trend of the mean temperature for the various LCZ types was highly consistent with the overall mean temperature trend observed in the study area. Large low-rise (LCZ 8) consistently presented high average surface temperatures during the summer months, reaching a maximum of 53.2 ℃. Moreover, the average surface temperature for each building type was higher than the average surface temperature for the study area as a whole, and the average surface temperature for each natural ground cover type except bare soil or sand was lower than the average surface temperature for the study area as a whole. The mean surface temperature of compact mid-rise (LCZ 2), compact low-rise (LCZ 3), large low-rise (LCZ 8), and heavy industry (LCZ 10) were higher than the overall mean temperature of the study area. Furthermore, this study presented intraclass analysis of different LCZ types using relative rates of change in LST. An increased sensitivity to temperature fluctuations may have adverse effects on human well-being and economic productivity. Another important finding was that the intra-LCZ thermal environment analyses indicated a heightened sensitivity to temperature fluctuations in the following categories: compact mid-rise (LCZ 2), compact low-rise (LCZ 3), heavy industry (LCZ 10), and bare soil and sand (LCZ F). The findings of this study can serve as a valuable reference point and provide insights for further research in the fields of urban planning, the mitigation of the urban heat island effect, and the enhancement of the urban heat environment.关键词:Urban heat environment;Local Climate Zone;Nanjing city;land surface temperature;Inter-LCZ difference;Intra-LCZ difference336|1253|0更新时间:2025-11-03 - “据最新研究,利用高分六号卫星数据,对海南省城市绿度空间热环境效益进行综合评价,为城市绿色发展提供方法范式。”
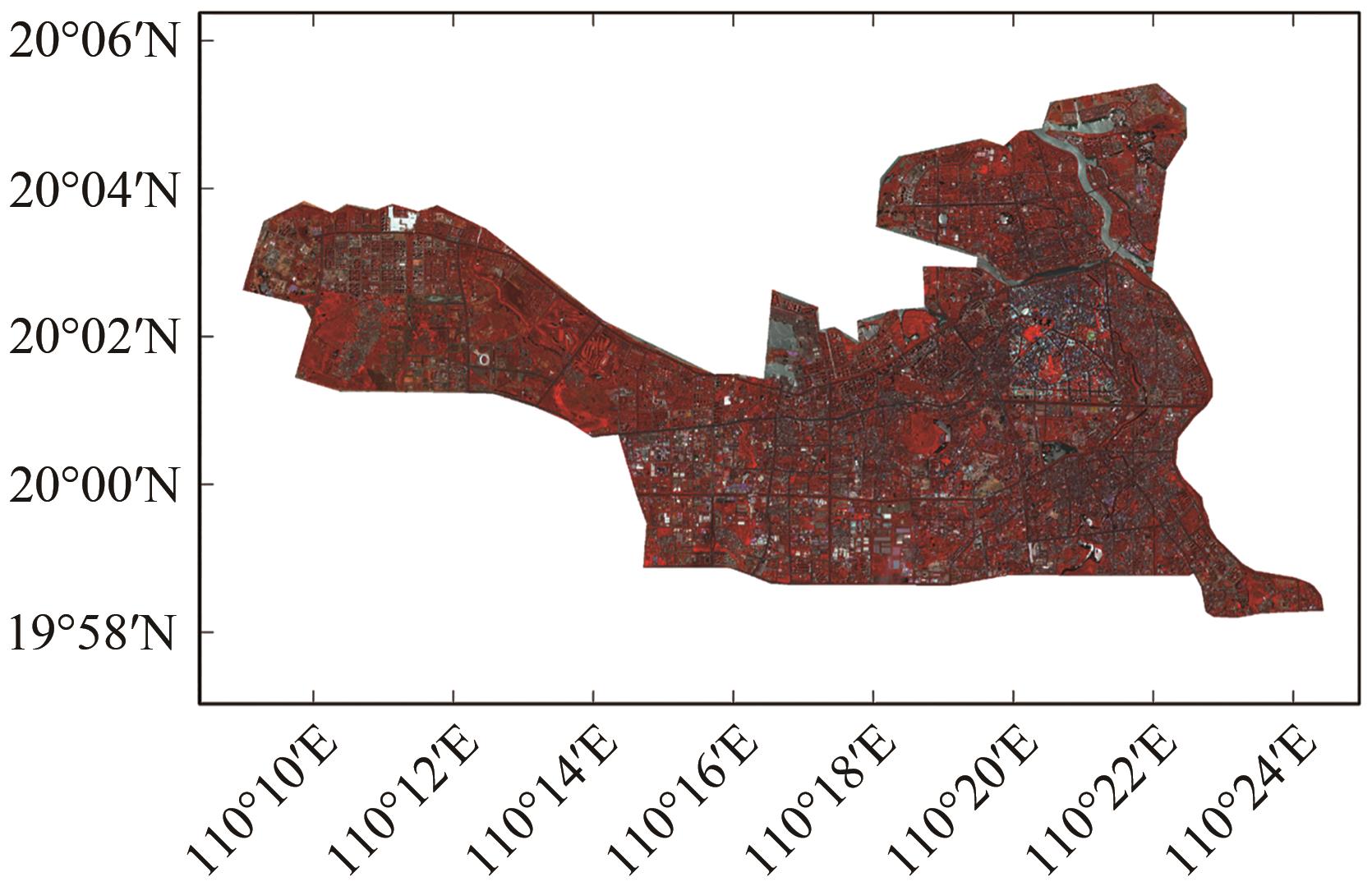 摘要:As the primary region for ecological civilization construction, urban areas have seen an increasing focus on improving their ecological environment. Green space, as a crucial component of urban ecosystems, holds significant importance in enhancing urban environmental quality, promoting biodiversity, and improving the overall well-being of urban residents. Conducting evaluations of the environmental benefits of green spaces can provide valuable insights for fine-grained urban environmental management. Under the rapid urbanization in China, this study conducts a comprehensive assessment of the thermal environmental benefits produced by typical urban green spaces in Hainan Province using advanced remote sensing techniques based on Gaofen-6 and Landsat satellite data. First, vegetation in the study area is extracted and classified into three main types—trees, shrubs, and grasslands—using multiscale segmentation and random forest algorithms. Various landscape pattern indices are computed, and multiregional surface temperatures are inverted to analyze the effect of urban green landscapes on the urban heat environment. By employing Pearson correlation analysis and geographical detector methods, the study investigates the characteristics of the drivers linking green landscape patterns with surface temperatures. Finally, utilizing a hierarchical analysis method based on selected factor indicators, a Green Space Environmental Benefit Index (GEBI) is established to quantitatively assess the thermal environmental benefits generated by green spaces in Haikou and Sanya Cities. Research findings reveal distinctive features of green spaces in Haikou and Sanya. (1) Haikou City is predominantly characterized by shrub vegetation, whereas Sanya City is dominated by grassland and shrub vegetation. (2) The cooling effect of green spaces is correlated with factors such as green area size and diversity, as well as landscape patch shape and density. Green spaces exhibit poorer cooling effects when fragmented and irregularly shaped. (3) The GEBI distributions in the study areas show alternating high- and low-value regions. The GEBI hotspots and cold spots in Haikou City are concentrated in the north, whereas in Sanya City, hotspots are mainly located in the west and southeast, with a smaller cold spot range. Overall, the quality of green spaces in both cities is relatively good, but an uneven distribution of green spaces persists in some older residential areas and large commercial districts. This study identifies areas of vulnerability and strengths in green environmental spaces, offering a paradigm for promoting green city development. It represents an advancement in the study of urban green space environmental benefits, providing insights for urban ecological planning, construction, and fine-grained environmental management, thereby facilitating sustainable urban development.关键词:urban remote sensing;urban green space;Surface temperature;environmental benefits;geographical detector;machine learning;GF-6 satellite250|1317|0更新时间:2025-11-03
摘要:As the primary region for ecological civilization construction, urban areas have seen an increasing focus on improving their ecological environment. Green space, as a crucial component of urban ecosystems, holds significant importance in enhancing urban environmental quality, promoting biodiversity, and improving the overall well-being of urban residents. Conducting evaluations of the environmental benefits of green spaces can provide valuable insights for fine-grained urban environmental management. Under the rapid urbanization in China, this study conducts a comprehensive assessment of the thermal environmental benefits produced by typical urban green spaces in Hainan Province using advanced remote sensing techniques based on Gaofen-6 and Landsat satellite data. First, vegetation in the study area is extracted and classified into three main types—trees, shrubs, and grasslands—using multiscale segmentation and random forest algorithms. Various landscape pattern indices are computed, and multiregional surface temperatures are inverted to analyze the effect of urban green landscapes on the urban heat environment. By employing Pearson correlation analysis and geographical detector methods, the study investigates the characteristics of the drivers linking green landscape patterns with surface temperatures. Finally, utilizing a hierarchical analysis method based on selected factor indicators, a Green Space Environmental Benefit Index (GEBI) is established to quantitatively assess the thermal environmental benefits generated by green spaces in Haikou and Sanya Cities. Research findings reveal distinctive features of green spaces in Haikou and Sanya. (1) Haikou City is predominantly characterized by shrub vegetation, whereas Sanya City is dominated by grassland and shrub vegetation. (2) The cooling effect of green spaces is correlated with factors such as green area size and diversity, as well as landscape patch shape and density. Green spaces exhibit poorer cooling effects when fragmented and irregularly shaped. (3) The GEBI distributions in the study areas show alternating high- and low-value regions. The GEBI hotspots and cold spots in Haikou City are concentrated in the north, whereas in Sanya City, hotspots are mainly located in the west and southeast, with a smaller cold spot range. Overall, the quality of green spaces in both cities is relatively good, but an uneven distribution of green spaces persists in some older residential areas and large commercial districts. This study identifies areas of vulnerability and strengths in green environmental spaces, offering a paradigm for promoting green city development. It represents an advancement in the study of urban green space environmental benefits, providing insights for urban ecological planning, construction, and fine-grained environmental management, thereby facilitating sustainable urban development.关键词:urban remote sensing;urban green space;Surface temperature;environmental benefits;geographical detector;machine learning;GF-6 satellite250|1317|0更新时间:2025-11-03
Models and Methods
0

