
最新刊期
卷 30 , 期 1 , 2026
- “水色遥感历经六十余年发展,已从光学遥感知识积累阶段,逐步跃迁至智能驱动的机理建模新阶段。中国湖泊水色遥感技术正经历从经验建模、机理建模到人工智能驱动的范式革新,逐步构建起“基础光学建模—国产卫星研发—智能算法创新—行业业务应用”的技术体系,分析了其面临的挑战与机遇,为智能水色遥感的未来发展提出了若干思考。”
 摘要:Lake water color remote sensing has undergone a significant transformation over the past six decades, evolving from an initial phase of knowledge discovery and accumulation in optical remote sensing into a new, intelligently driven era focused on mechanistic modeling. The development in China began in the 1980s, with its industrialization marked by the launch of the HY-1A satellite in 2002. Since the 1990s, extensive national efforts in lake environmental restoration and management have provided continuous impetus for its advancement. The period after 2020 witnessed the large-scale integration of artificial intelligence (AI), propelling the field into an intelligent epoch characterized by dramatically enhanced automation and intelligence, thereby enabling comprehensive, large-scale regional monitoring applications.Remote sensing technology is currently undergoing a paradigm shift from empirical and mechanistic modeling toward AI-driven approaches, progressively establishing a technical framework integrating “basic optical modeling–domestic satellite development–intelligent algorithm innovation–operational industry application.” The theoretical cornerstone remains the water radiative transfer theory, which quantitatively links the apparent and inherent optical properties of water bodies with the concentrations of optically active constituents. However, lake water color remote sensing faces unique complexities not encountered in traditional marine applications. These complexities include challenges stemming from the generally small size and rapid dynamic changes of lakes, which demand high spatial and temporal resolution from sensors. Furthermore, atmospheric correction is particularly difficult because of the prevalence of absorbing aerosols near human settlements, often rendering marine algorithms ineffective. Other complications involve discriminating between algal blooms and aquatic vegetation with similar spectral features, correcting for significant land adjacency effects in enclosed basins, and developing universally applicable inversion algorithms owing to the high spatial and temporal heterogeneity of inland waters.The rise of intelligent water color remote sensing represents a pivotal breakthrough. Machine and deep learning techniques are now being deployed to tackle the persistent challenge of atmospheric correction over diverse lakes and to achieve the simultaneous retrieval of multiple water quality parameters. These data-driven methods overcome the limitations of region-specific empirical algorithms and the sensitivity of semianalytical models to parameterization, offering a promising path toward robust, generalizable models. This intelligent approach signifies a profound paradigm shift from retrieving single elements to constructing integrated, AI-powered systems. Future trajectories point toward the deep integration of physics and AI, such as embedding differentiable radiative transfer equations into neural networks with physical constraints. The development of a dual-stage framework involving a “global foundational model” trained on multisource satellite data and “regional adaptation modules” fine-tuned with local measurements is envisioned. Ultimately, the integration of remote sensing with hydrodynamic models to create lake ecological digital twins will enable probabilistic forecasting of events like algal blooms and provide powerful decision-support capabilities for sustainable water management.In conclusion, lake water color remote sensing has firmly entered an intelligent era defined by substantially improved automation, scalability, efficiency, and accuracy. This evolution, from empirical to physical to AI-driven modeling paradigms, provides a solid technical foundation for advancing water environment monitoring, management, and ecological restoration on a global scale.关键词:lake;water color remote sensing;remote sensing algorithm;artificial intelligence;paradigm shift0|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30
摘要:Lake water color remote sensing has undergone a significant transformation over the past six decades, evolving from an initial phase of knowledge discovery and accumulation in optical remote sensing into a new, intelligently driven era focused on mechanistic modeling. The development in China began in the 1980s, with its industrialization marked by the launch of the HY-1A satellite in 2002. Since the 1990s, extensive national efforts in lake environmental restoration and management have provided continuous impetus for its advancement. The period after 2020 witnessed the large-scale integration of artificial intelligence (AI), propelling the field into an intelligent epoch characterized by dramatically enhanced automation and intelligence, thereby enabling comprehensive, large-scale regional monitoring applications.Remote sensing technology is currently undergoing a paradigm shift from empirical and mechanistic modeling toward AI-driven approaches, progressively establishing a technical framework integrating “basic optical modeling–domestic satellite development–intelligent algorithm innovation–operational industry application.” The theoretical cornerstone remains the water radiative transfer theory, which quantitatively links the apparent and inherent optical properties of water bodies with the concentrations of optically active constituents. However, lake water color remote sensing faces unique complexities not encountered in traditional marine applications. These complexities include challenges stemming from the generally small size and rapid dynamic changes of lakes, which demand high spatial and temporal resolution from sensors. Furthermore, atmospheric correction is particularly difficult because of the prevalence of absorbing aerosols near human settlements, often rendering marine algorithms ineffective. Other complications involve discriminating between algal blooms and aquatic vegetation with similar spectral features, correcting for significant land adjacency effects in enclosed basins, and developing universally applicable inversion algorithms owing to the high spatial and temporal heterogeneity of inland waters.The rise of intelligent water color remote sensing represents a pivotal breakthrough. Machine and deep learning techniques are now being deployed to tackle the persistent challenge of atmospheric correction over diverse lakes and to achieve the simultaneous retrieval of multiple water quality parameters. These data-driven methods overcome the limitations of region-specific empirical algorithms and the sensitivity of semianalytical models to parameterization, offering a promising path toward robust, generalizable models. This intelligent approach signifies a profound paradigm shift from retrieving single elements to constructing integrated, AI-powered systems. Future trajectories point toward the deep integration of physics and AI, such as embedding differentiable radiative transfer equations into neural networks with physical constraints. The development of a dual-stage framework involving a “global foundational model” trained on multisource satellite data and “regional adaptation modules” fine-tuned with local measurements is envisioned. Ultimately, the integration of remote sensing with hydrodynamic models to create lake ecological digital twins will enable probabilistic forecasting of events like algal blooms and provide powerful decision-support capabilities for sustainable water management.In conclusion, lake water color remote sensing has firmly entered an intelligent era defined by substantially improved automation, scalability, efficiency, and accuracy. This evolution, from empirical to physical to AI-driven modeling paradigms, provides a solid technical foundation for advancing water environment monitoring, management, and ecological restoration on a global scale.关键词:lake;water color remote sensing;remote sensing algorithm;artificial intelligence;paradigm shift0|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30
Scholar's View Point
- “遥感变化检测在城市规划等领域应用广泛,SAR技术克服了光学检测受天气和光照影响的问题,具有独特优势。专家构建了双时相变化检测一般流程,梳理了主流数据和方法,为后续研究提供重要参考。”
 摘要:Remote sensing Change Detection (CD), as a crucial monitoring technique, has been widely applied in fields such as urban planning, disaster assessment, and resource management. Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) possesses all-weather, all-time imaging capabilities, effectively overcoming the limitations of optical CD that are influenced by weather conditions and illumination variations. Its microwave penetration ability, polarization characteristics, and coherent imaging mechanism provide unique advantages in monitoring subsurface and occluded changes, object structure and physical property variations, and subtle changes. Currently, most existing reviews on bi-temporal CD focus on optical imagery and deep learning algorithms, lacking a systematic and targeted summary of SAR-based CD. Furthermore, with the advancement of deep learning and multisource data fusion, homogeneous and heterogeneous CD based on SAR imagery have emerged as prominent research frontiers.On the basis of the challenges outlined above, this article draws upon classical and recent literature to first explore the diverse application scenarios and domains of CD under varying imaging conditions. SAR imaging modes mainly include Stripmap, ScanSAR, and Spotlight, each of which has distinct advantages in resolution and coverage, catering to diverse CD tasks. Polarization modes, such as single, dual, and full polarization, affect the change type and richness of information extracted from SAR data. Different frequency bands, such as L-band, C-band, and X-band, exhibit varying penetration capabilities and sensitivities. With the increasing availability of multitemporal SAR and multisource data, the applications of SAR-based CD are expanding. Multitemporal SAR leverages time-series information to enhance the detection of periodic changes, while the fusion of SAR and optical data overcomes single-sensor limitations, thereby advancing multimodal CD methods.Then, a comprehensive SAR CD framework is constructed, which includes data acquisition, image preprocessing, change identification, and post-processing. During data acquisition, factors such as satellite coverage, imaging mode, and band selection must be considered. Image preprocessing primarily involves image co-registration, radiometric correction, geometric correction, and noise reduction. In the change identification phase, traditional homogeneous CD methods primarily depend on the generation of difference images followed by detailed difference analysis. Conventional heterogeneous CD approaches typically employ post-classification, similarity measurement, and feature space transformation to establish cross-modal correspondences. By contrast, deep learning-based methods utilize neural networks to automatically extract homogeneous or heterogeneous features and identify changes. Finally, the post-processing focuses on accuracy assessment and validation of the detection results.Moreover, the article systematically reviews the mainstream datasets and methods for SAR-based homogeneous and heterogeneous CD. Homogeneous datasets consist of bi-temporal SAR images from the same sensor, while heterogeneous datasets typically include SAR and optical image pairs. These datasets offer preprocessed imagery and accurate binary change labels to support learning and evaluation. The reviewed methods encompass both traditional and deep learning-based approaches tailored for these two scenarios. Traditional methods offer computational efficiency but rely heavily on manually designed features. Deep learning methods, with their powerful learning capabilities, modality adaptability, and end-to-end modeling advantages, can effectively extract both unimodal and multimodal features. Additionally, curated links to datasets and model codes are provided to support future research in this field.Finally, the main challenges in the field are summarized from the perspectives of data, algorithms, and applications, including issues such as data quality and availability, model representational capacity and computational complexity, and the limited scope of current CD applications. In response to these challenges, future research directions are proposed, focusing on multimodal data fusion, intelligent and lightweight model design, and diversified CD applications.关键词:bi-temporal remote sensing change detection;SAR imagery;traditional methods;deep learning;homogeneous and heterogeneous5|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30
摘要:Remote sensing Change Detection (CD), as a crucial monitoring technique, has been widely applied in fields such as urban planning, disaster assessment, and resource management. Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) possesses all-weather, all-time imaging capabilities, effectively overcoming the limitations of optical CD that are influenced by weather conditions and illumination variations. Its microwave penetration ability, polarization characteristics, and coherent imaging mechanism provide unique advantages in monitoring subsurface and occluded changes, object structure and physical property variations, and subtle changes. Currently, most existing reviews on bi-temporal CD focus on optical imagery and deep learning algorithms, lacking a systematic and targeted summary of SAR-based CD. Furthermore, with the advancement of deep learning and multisource data fusion, homogeneous and heterogeneous CD based on SAR imagery have emerged as prominent research frontiers.On the basis of the challenges outlined above, this article draws upon classical and recent literature to first explore the diverse application scenarios and domains of CD under varying imaging conditions. SAR imaging modes mainly include Stripmap, ScanSAR, and Spotlight, each of which has distinct advantages in resolution and coverage, catering to diverse CD tasks. Polarization modes, such as single, dual, and full polarization, affect the change type and richness of information extracted from SAR data. Different frequency bands, such as L-band, C-band, and X-band, exhibit varying penetration capabilities and sensitivities. With the increasing availability of multitemporal SAR and multisource data, the applications of SAR-based CD are expanding. Multitemporal SAR leverages time-series information to enhance the detection of periodic changes, while the fusion of SAR and optical data overcomes single-sensor limitations, thereby advancing multimodal CD methods.Then, a comprehensive SAR CD framework is constructed, which includes data acquisition, image preprocessing, change identification, and post-processing. During data acquisition, factors such as satellite coverage, imaging mode, and band selection must be considered. Image preprocessing primarily involves image co-registration, radiometric correction, geometric correction, and noise reduction. In the change identification phase, traditional homogeneous CD methods primarily depend on the generation of difference images followed by detailed difference analysis. Conventional heterogeneous CD approaches typically employ post-classification, similarity measurement, and feature space transformation to establish cross-modal correspondences. By contrast, deep learning-based methods utilize neural networks to automatically extract homogeneous or heterogeneous features and identify changes. Finally, the post-processing focuses on accuracy assessment and validation of the detection results.Moreover, the article systematically reviews the mainstream datasets and methods for SAR-based homogeneous and heterogeneous CD. Homogeneous datasets consist of bi-temporal SAR images from the same sensor, while heterogeneous datasets typically include SAR and optical image pairs. These datasets offer preprocessed imagery and accurate binary change labels to support learning and evaluation. The reviewed methods encompass both traditional and deep learning-based approaches tailored for these two scenarios. Traditional methods offer computational efficiency but rely heavily on manually designed features. Deep learning methods, with their powerful learning capabilities, modality adaptability, and end-to-end modeling advantages, can effectively extract both unimodal and multimodal features. Additionally, curated links to datasets and model codes are provided to support future research in this field.Finally, the main challenges in the field are summarized from the perspectives of data, algorithms, and applications, including issues such as data quality and availability, model representational capacity and computational complexity, and the limited scope of current CD applications. In response to these challenges, future research directions are proposed, focusing on multimodal data fusion, intelligent and lightweight model design, and diversified CD applications.关键词:bi-temporal remote sensing change detection;SAR imagery;traditional methods;deep learning;homogeneous and heterogeneous5|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30
Review
- “介绍了其在山地植被冠层二向反射特性机理模型领域的研究进展,专家们从单一坡面和复合坡面两种尺度综述了当前机理模型的主要进展,为山区定量遥感反演和监测应用提供理论支撑。”
 摘要:The Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function (BRDF) is an essential function that characterizes the bidirectional reflectance properties of vegetation canopies. Mountains account for approximately 24% of the Earth’s land surface and 67% of China’s land area. Complex terrain alters the geometric configuration among the sun, surface, and sensor, as well as the canopy structure and radiative transfer processes, thereby distorting the shape and magnitude of the BRDF and introducing significant uncertainties in land surface parameter retrievals. Therefore, quantifying the radiative transfer process in complex terrain from a mechanistic perspective and constructing a mountainous canopy BRDF model are crucial for accurately describing the bidirectional reflectance characteristics of mountainous surfaces. These tasks are fundamental for understanding the mechanisms by which topography influences reflectance features and serve as essential prerequisites for retrieving key land surface parameters in mountainous regions. Various models have been developed to simulate the BRDF of vegetation canopies over flat surfaces, establishing quantitative relationships between canopy parameters and reflectance. However, given the extensive distribution of mountainous areas in China, extending the mechanistic modeling of canopy bidirectional reflectance from flat and homogeneous surfaces to complex mountainous terrains is urgently required.Modeling canopy BRDFs is central to comprehensively understanding the bidirectional reflectance characteristics of complex surfaces in mountainous areas. This paper first provides a brief introduction to the theoretical background of BRDF definitions over flat and complex terrains, followed by a review of the development in canopy BRDF models over flat surfaces. Subsequently, it focuses on two typical complex terrains—single- and composite-slope surfaces—to analyze the current development trends and characteristics of mechanistic canopy BRDF models over complex terrain. Finally, we present a vision and concept for future canopy BRDF models over complex terrain.In accordance with the spatial scale relationship between the Digital Elevation Model (DEM) and the resolution of remote sensing pixels, complex terrain modeling can be classified into single-slope modeling, where each pixel contains a unique slope and aspect, and composite-slope modeling, where each pixel encompasses multiple slopes and aspects. The former mainly optimizes the modeling process through three approaches: (1) correcting the geometry between the sun, terrain, and sensor; (2) correcting the geometry between the sun, canopy, and sensor; and (3) refining the radiative transfer process on sloped surfaces. Unlike single-slope modeling, composite-slope modeling targets larger-scale scenarios and requires consideration of subpixel topographic effects. Current composite-slope models can be categorized into three types on the basis of terrain representation methods: (1) specific-shape models; (2) models based on mean-slope approximation; (3) DEM-based BRDF models.Perspectives on the future development of vegetation canopy bidirectional reflectance models over complex terrain are presented as follows(1) mountain bidirectional reflectance modeling considering mixed land-cover types—how to extend current single land-cover BRDF modeling to account for within-scene heterogeneity and multiple scattering among different land-cover types, thereby constructing a multiscale, all-terrain, multitype physical model, which remains a significant challenge; (2) the urgent need to develop multiscale radiative transfer models coupling mountainous surfaces and the atmosphere; (3) advancing mountain 3D remote sensing observation techniques and validation methods for complex terrain BRDF models—because multiangular field observations in mountainous regions are difficult, ground-based multiangular datasets are generally lacking; and (4) promoting the operational application of complex terrain BRDF models. The progressive refinement of mountainous vegetation canopy bidirectional reflectance models has significantly enhanced their application potential, providing essential modeling support for simulating land surface parameters in mountainous regions across different scales. These advancements hold great significance for vegetation parameter retrieval, energy balance estimation, and climate change assessment in mountainous environments.关键词:anisotropic reflectance;BRDF;complex terrain;single slope;composite slope5|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30
摘要:The Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function (BRDF) is an essential function that characterizes the bidirectional reflectance properties of vegetation canopies. Mountains account for approximately 24% of the Earth’s land surface and 67% of China’s land area. Complex terrain alters the geometric configuration among the sun, surface, and sensor, as well as the canopy structure and radiative transfer processes, thereby distorting the shape and magnitude of the BRDF and introducing significant uncertainties in land surface parameter retrievals. Therefore, quantifying the radiative transfer process in complex terrain from a mechanistic perspective and constructing a mountainous canopy BRDF model are crucial for accurately describing the bidirectional reflectance characteristics of mountainous surfaces. These tasks are fundamental for understanding the mechanisms by which topography influences reflectance features and serve as essential prerequisites for retrieving key land surface parameters in mountainous regions. Various models have been developed to simulate the BRDF of vegetation canopies over flat surfaces, establishing quantitative relationships between canopy parameters and reflectance. However, given the extensive distribution of mountainous areas in China, extending the mechanistic modeling of canopy bidirectional reflectance from flat and homogeneous surfaces to complex mountainous terrains is urgently required.Modeling canopy BRDFs is central to comprehensively understanding the bidirectional reflectance characteristics of complex surfaces in mountainous areas. This paper first provides a brief introduction to the theoretical background of BRDF definitions over flat and complex terrains, followed by a review of the development in canopy BRDF models over flat surfaces. Subsequently, it focuses on two typical complex terrains—single- and composite-slope surfaces—to analyze the current development trends and characteristics of mechanistic canopy BRDF models over complex terrain. Finally, we present a vision and concept for future canopy BRDF models over complex terrain.In accordance with the spatial scale relationship between the Digital Elevation Model (DEM) and the resolution of remote sensing pixels, complex terrain modeling can be classified into single-slope modeling, where each pixel contains a unique slope and aspect, and composite-slope modeling, where each pixel encompasses multiple slopes and aspects. The former mainly optimizes the modeling process through three approaches: (1) correcting the geometry between the sun, terrain, and sensor; (2) correcting the geometry between the sun, canopy, and sensor; and (3) refining the radiative transfer process on sloped surfaces. Unlike single-slope modeling, composite-slope modeling targets larger-scale scenarios and requires consideration of subpixel topographic effects. Current composite-slope models can be categorized into three types on the basis of terrain representation methods: (1) specific-shape models; (2) models based on mean-slope approximation; (3) DEM-based BRDF models.Perspectives on the future development of vegetation canopy bidirectional reflectance models over complex terrain are presented as follows(1) mountain bidirectional reflectance modeling considering mixed land-cover types—how to extend current single land-cover BRDF modeling to account for within-scene heterogeneity and multiple scattering among different land-cover types, thereby constructing a multiscale, all-terrain, multitype physical model, which remains a significant challenge; (2) the urgent need to develop multiscale radiative transfer models coupling mountainous surfaces and the atmosphere; (3) advancing mountain 3D remote sensing observation techniques and validation methods for complex terrain BRDF models—because multiangular field observations in mountainous regions are difficult, ground-based multiangular datasets are generally lacking; and (4) promoting the operational application of complex terrain BRDF models. The progressive refinement of mountainous vegetation canopy bidirectional reflectance models has significantly enhanced their application potential, providing essential modeling support for simulating land surface parameters in mountainous regions across different scales. These advancements hold great significance for vegetation parameter retrieval, energy balance estimation, and climate change assessment in mountainous environments.关键词:anisotropic reflectance;BRDF;complex terrain;single slope;composite slope5|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30
Research Progress
- “基于长时序夜间灯光遥感数据,专家定量分析了近30年来中国城市发展的梯度特征及时空分异规律,为城镇化优化发展提供科学依据。”
 摘要:Urbanization is one of the key indicators of socioeconomic development, representing the transition from a rural to an urban society. It involves profound transformations in population distribution, economic structure, social organization, and land use patterns. A quantitative analysis of the spatiotemporal differentiation of urbanization can provide a scientific basis for optimizing its development. With advances in remote sensing technology, nighttime light data has emerged as an innovative research tool, offering a precise means of monitoring spatial disparities and the agglomeration patterns of economic activities during urbanization.This paper utilizes long-term nighttime light remote sensing data, employing the total nighttime light value and the nighttime light growth difference index as proxy variables to assess urbanization levels. By integrating methods such as center-of-gravity migration, the standard deviation ellipse, the global Moran’s I index, and local spatial autocorrelation, the study quantitatively analyzes the gradient characteristics and spatiotemporal differentiation of urban development across provincial capitals, prefecture-level, county-level, and township-level areas in China over the past 30 years, focusing on contribution rate, growth rate, and center-of-gravity distribution.Results indicate the following (1) Contribution rate: Between 1992 and 2022, the nationwide total nighttime light value maintained steady growth. In the early 1990s, prefecture-level cities exhibited the highest contribution rate, with provincial capitals and townships contributing equally, while county-level cities contributed the least. After 2000, township-level cities surpassed provincial capitals and outperformed prefecture-level cities around 2004, becoming the highest-contributing region. In 2007, county-level cities overtook provincial capitals, and by 2022, their contribution was comparable to that of prefecture-level cities; meanwhile, provincial capitals became the lowest-contributing tier after 2010. (2) Growth rate: From 1992 to 2000, provincial capitals and some prefecture-level cities led other urban tiers, with the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei, Yangtze River Delta, and Pearl River Delta regions being particularly prominent. Between 2000 and 2010, provincial capitals began to approach saturation, while prefecture-level and some county-level cities gradually emerged as the core; these areas in north, east, central, and south China exhibited medium or higher growth rates. However, in the northwest, southwest, and northeast—where development levels were lower—provincial capitals remained the fastest growing among the four tiers. From 2010 to 2022, township-level cities became predominant, while provincial capitals experienced predominantly “slow-to-low” growth, indicating a gradual shift in the center of urbanization toward townships. (3) Center-of-gravity distribution: From 1992 to 2022, China’s urbanization underwent significant changes. The center of urban development exhibited a gradient downward shift, progressively transferring from provincial capitals to prefecture-level, county-level, and finally township-level cities. This migration trajectory is highly consistent with the “core–periphery” theory, and the expanding area of the urbanization ellipse demonstrates a clear expansion effect. In terms of spatial correlation, “high–high” clusters have shown a trend of shifting from the eastern coastal areas toward the northwestern inland. The urbanization growth levels across different tiers exhibit a significantly positive spatial correlation, with Moran’s I values generally above zero but on a declining trend. From 1992 to 2000, “H-H” clusters were primarily concentrated in provincial capitals and coastal prefecture-level cities; from 2000 to 2010, county-level cities accounted for a larger share of the high-value clusters; and from 2010 to 2022, township areas emerged as new growth poles, while some provincial capitals formed “L-L” clusters with internal urbanization nearing saturation. These findings mark the entry of China’s urbanization into a new phase characterized by a multicentric and networked development pattern.关键词:Urbanization;nighttime light remote sensing;Spatiotemporal Differentiation;Gradient Characteristics1|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30
摘要:Urbanization is one of the key indicators of socioeconomic development, representing the transition from a rural to an urban society. It involves profound transformations in population distribution, economic structure, social organization, and land use patterns. A quantitative analysis of the spatiotemporal differentiation of urbanization can provide a scientific basis for optimizing its development. With advances in remote sensing technology, nighttime light data has emerged as an innovative research tool, offering a precise means of monitoring spatial disparities and the agglomeration patterns of economic activities during urbanization.This paper utilizes long-term nighttime light remote sensing data, employing the total nighttime light value and the nighttime light growth difference index as proxy variables to assess urbanization levels. By integrating methods such as center-of-gravity migration, the standard deviation ellipse, the global Moran’s I index, and local spatial autocorrelation, the study quantitatively analyzes the gradient characteristics and spatiotemporal differentiation of urban development across provincial capitals, prefecture-level, county-level, and township-level areas in China over the past 30 years, focusing on contribution rate, growth rate, and center-of-gravity distribution.Results indicate the following (1) Contribution rate: Between 1992 and 2022, the nationwide total nighttime light value maintained steady growth. In the early 1990s, prefecture-level cities exhibited the highest contribution rate, with provincial capitals and townships contributing equally, while county-level cities contributed the least. After 2000, township-level cities surpassed provincial capitals and outperformed prefecture-level cities around 2004, becoming the highest-contributing region. In 2007, county-level cities overtook provincial capitals, and by 2022, their contribution was comparable to that of prefecture-level cities; meanwhile, provincial capitals became the lowest-contributing tier after 2010. (2) Growth rate: From 1992 to 2000, provincial capitals and some prefecture-level cities led other urban tiers, with the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei, Yangtze River Delta, and Pearl River Delta regions being particularly prominent. Between 2000 and 2010, provincial capitals began to approach saturation, while prefecture-level and some county-level cities gradually emerged as the core; these areas in north, east, central, and south China exhibited medium or higher growth rates. However, in the northwest, southwest, and northeast—where development levels were lower—provincial capitals remained the fastest growing among the four tiers. From 2010 to 2022, township-level cities became predominant, while provincial capitals experienced predominantly “slow-to-low” growth, indicating a gradual shift in the center of urbanization toward townships. (3) Center-of-gravity distribution: From 1992 to 2022, China’s urbanization underwent significant changes. The center of urban development exhibited a gradient downward shift, progressively transferring from provincial capitals to prefecture-level, county-level, and finally township-level cities. This migration trajectory is highly consistent with the “core–periphery” theory, and the expanding area of the urbanization ellipse demonstrates a clear expansion effect. In terms of spatial correlation, “high–high” clusters have shown a trend of shifting from the eastern coastal areas toward the northwestern inland. The urbanization growth levels across different tiers exhibit a significantly positive spatial correlation, with Moran’s I values generally above zero but on a declining trend. From 1992 to 2000, “H-H” clusters were primarily concentrated in provincial capitals and coastal prefecture-level cities; from 2000 to 2010, county-level cities accounted for a larger share of the high-value clusters; and from 2010 to 2022, township areas emerged as new growth poles, while some provincial capitals formed “L-L” clusters with internal urbanization nearing saturation. These findings mark the entry of China’s urbanization into a new phase characterized by a multicentric and networked development pattern.关键词:Urbanization;nighttime light remote sensing;Spatiotemporal Differentiation;Gradient Characteristics1|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30 - “夜光遥感在城市环境等领域应用广泛,但城市水体环境评估相对匮乏。专家探索了适用于不同形态内陆水体区域的夜光影像最佳空间降尺度方法,为城市湖泊光污染评估及滨湖环境社会人文环境分析提供方法和数据支撑。”
 摘要:Remote sensing images of nighttime lights (NTL) have been widely used in environmental protection, socioeconomic assessment, and armed conflicts in urban areas. However, NTL pollution in urban water lakes is seldom studied due to the coarse spatial resolution of existing NTL images, such as those from the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program and the Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership (Suomi-NPP) Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS). Spatial downscaling techniques are needed to support NTL pollution studies for urban lakes. Urban lakes of provincial capitals in Yangtze River Basin are selected as our study area, which had been polluted by NTL because of rapid urbanization. This study aims to develop optimal spatial downscaling methods for NPP-VIIRS NTL images of urban lakes, using NPP-VIIRS NTL, LJ-1 01 NTL, and Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS images, to overcome the absence of remote sensing images of NTL in the study of inland water environment.Lake brightness temperature (LBT), floating algae index (FAI), and Forel-Ule index (FUI) are selected as interpretive factors of urban lakes. These interpretive factors have four combinations: LBT(T), LBT and FAI(TA), LBT and FUI(TU), LBT, FAI and FUI(TAU). Three downscaling models, namely, disaggregation procedure for radiometric surface temperature (DisTrad), geographically weighted regression (GWR), and random forest (RF), are used with these combinations. A total of 11 object-oriented downscaling methods are employed for every urban lake. These methods are evaluated using the coefficient of determination (R²) and root mean square error (RMSE) to identify the most effective approach for different types of urban lakes. Finally, this study employed the area and perimeter area ratio, average brightness of NTL (ANTL) and brightness threshold (RNTL), and lakeside greenness to explore the impact factors on the applicability of NTL spatial downscaling methods.The downscaling NPP NTL images are significantly correlated with LJ-1 01 NTL images for most of the urban lakes, except South Lake of Wuhan and Yao Lake of Nanchang. The RMSE between downscaling NPP images and LJ-1 01 images are less than 3 nW/(cm²∙sr) for urban lakes except for highly influenced urban lakes, such as East Lake, Huangjia Lake, South Lake, and Qingshan Lake. Among object-oriented DisTrad (OD), object-oriented GWR (OGWR), and object-oriented random forest (ORF) models, OD is robust, while ORF is unstable, the performance of OGWR is relatively moderate. The optimal combination of interpretive factors is different for the three spatial downscaling models. LBT and FUI (-TU) is the best combination for the OGWR model, while LBT and FAI (-TA) is the optimal combination for the OD model. No stable and ideal interpretive factor combination is available for the ORF model. The morphology of urban lakes and the intensity of human activities affect the applicability of NTL downscaling methods considerably. Meanwhile, the weather conditions of Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS acquisition dates may affect the performance of each model in different urban lakes.OD-TA is the most robust, while OGWR-TU is most suitable for lakes with large areas (>10 km2) and high PARA (>65). OD-TA is mainly applicable to urban lakes with area <30 km2, PARA>50, and greenness between 30—50. OGWR-TU is most suitable for Dianchi Lake and Chaohu Lake. The study underscores the importance of spatial morphology and built-up area attributes in the downscaling method’s performance, providing a methodological foundation for urban lake NTL pollution assessment and environmental analysis.关键词:Nighttime light (NTL);brightness temperature;spatial downscaling;NPP-VIIRS;urban lake1|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30
摘要:Remote sensing images of nighttime lights (NTL) have been widely used in environmental protection, socioeconomic assessment, and armed conflicts in urban areas. However, NTL pollution in urban water lakes is seldom studied due to the coarse spatial resolution of existing NTL images, such as those from the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program and the Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership (Suomi-NPP) Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS). Spatial downscaling techniques are needed to support NTL pollution studies for urban lakes. Urban lakes of provincial capitals in Yangtze River Basin are selected as our study area, which had been polluted by NTL because of rapid urbanization. This study aims to develop optimal spatial downscaling methods for NPP-VIIRS NTL images of urban lakes, using NPP-VIIRS NTL, LJ-1 01 NTL, and Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS images, to overcome the absence of remote sensing images of NTL in the study of inland water environment.Lake brightness temperature (LBT), floating algae index (FAI), and Forel-Ule index (FUI) are selected as interpretive factors of urban lakes. These interpretive factors have four combinations: LBT(T), LBT and FAI(TA), LBT and FUI(TU), LBT, FAI and FUI(TAU). Three downscaling models, namely, disaggregation procedure for radiometric surface temperature (DisTrad), geographically weighted regression (GWR), and random forest (RF), are used with these combinations. A total of 11 object-oriented downscaling methods are employed for every urban lake. These methods are evaluated using the coefficient of determination (R²) and root mean square error (RMSE) to identify the most effective approach for different types of urban lakes. Finally, this study employed the area and perimeter area ratio, average brightness of NTL (ANTL) and brightness threshold (RNTL), and lakeside greenness to explore the impact factors on the applicability of NTL spatial downscaling methods.The downscaling NPP NTL images are significantly correlated with LJ-1 01 NTL images for most of the urban lakes, except South Lake of Wuhan and Yao Lake of Nanchang. The RMSE between downscaling NPP images and LJ-1 01 images are less than 3 nW/(cm²∙sr) for urban lakes except for highly influenced urban lakes, such as East Lake, Huangjia Lake, South Lake, and Qingshan Lake. Among object-oriented DisTrad (OD), object-oriented GWR (OGWR), and object-oriented random forest (ORF) models, OD is robust, while ORF is unstable, the performance of OGWR is relatively moderate. The optimal combination of interpretive factors is different for the three spatial downscaling models. LBT and FUI (-TU) is the best combination for the OGWR model, while LBT and FAI (-TA) is the optimal combination for the OD model. No stable and ideal interpretive factor combination is available for the ORF model. The morphology of urban lakes and the intensity of human activities affect the applicability of NTL downscaling methods considerably. Meanwhile, the weather conditions of Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS acquisition dates may affect the performance of each model in different urban lakes.OD-TA is the most robust, while OGWR-TU is most suitable for lakes with large areas (>10 km2) and high PARA (>65). OD-TA is mainly applicable to urban lakes with area <30 km2, PARA>50, and greenness between 30—50. OGWR-TU is most suitable for Dianchi Lake and Chaohu Lake. The study underscores the importance of spatial morphology and built-up area attributes in the downscaling method’s performance, providing a methodological foundation for urban lake NTL pollution assessment and environmental analysis.关键词:Nighttime light (NTL);brightness temperature;spatial downscaling;NPP-VIIRS;urban lake1|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30 - “介绍了其在冻土参量遥感反演领域的研究进展,相关专家通过实验分析了黑土在冻结过程中的微波辐射响应深度变化,为冻土参量遥感反演提供了重要参考。”
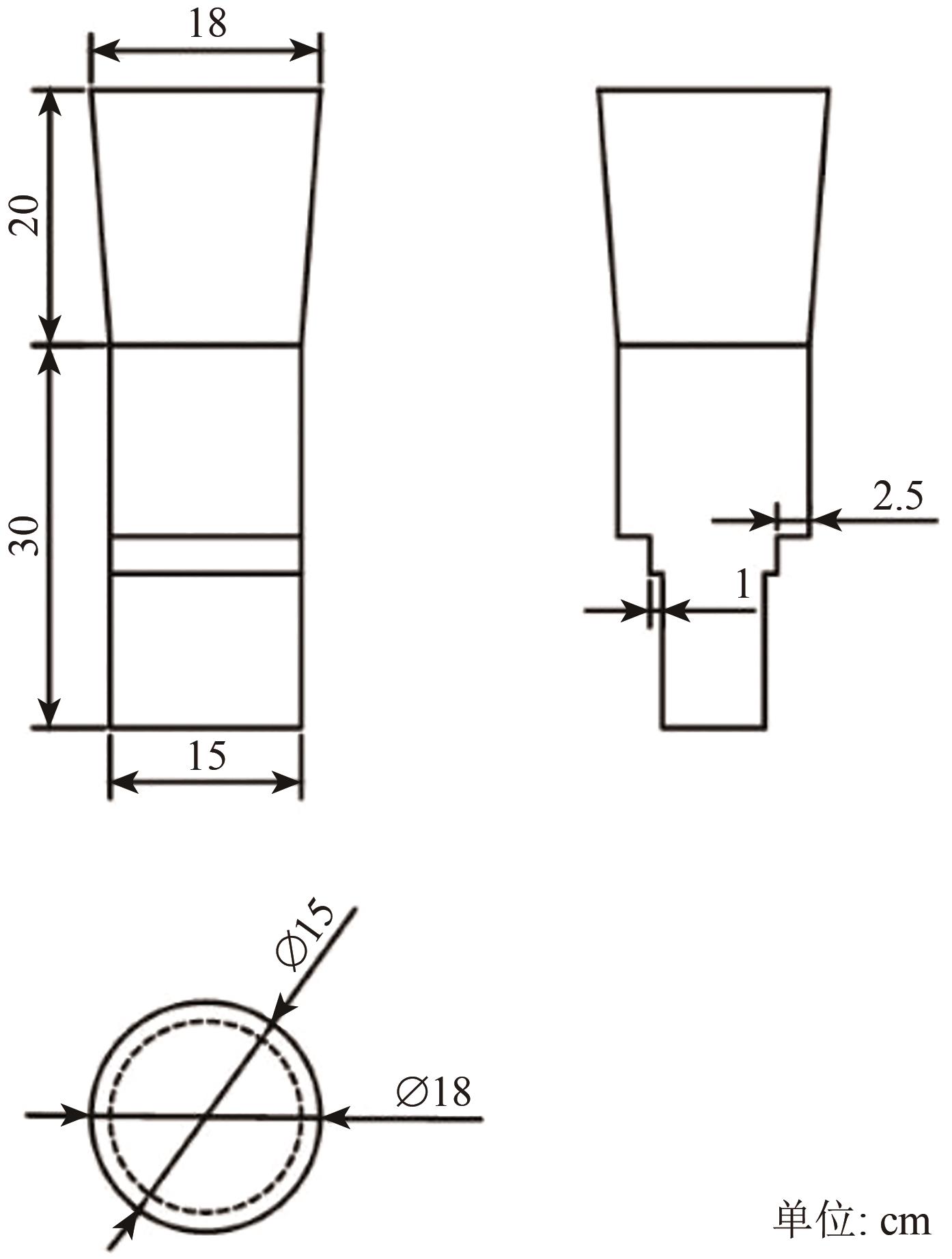 摘要:In the detection of frozen soil parameters, the L-band offers stronger penetration capability than other microwave bands do, making it more advantageous for studying soil properties in frozen conditions. However, limited research has been conducted on the microwave radiation response depth of the L-band in such environments. Additionally, the microwave radiation response characteristics of soil under freezing conditions are not fully understood. This study aims to investigate the microwave radiation response depth of black soil in typical permafrost regions of Northeast China, focusing on its behavior under natural freezing conditions during winter.To address the research gap, this study employed a dual-polarized L-band microwave radiometer with a frequency of 1.414 GHz to perform near-field experiments on black soil samples with different initial moisture contents. The experiments were conducted in winter under natural freezing conditions. The study examined the changes in microwave radiation response depth during and after the freezing process, considering four initial moisture contents: 0%, 10%, 20%, and 30%. By analyzing the experimental results, the study aimed to explore how the initial moisture content affects the microwave radiation response depth and to determine the dominant factors that influence brightness temperature in frozen soil. This approach allowed for a comprehensive understanding of the interactions between soil moisture, freezing processes, and microwave radiation.The results revealed several key findings. During the freezing process, the L-band microwave radiation response depth for soils with 10% and 30% initial moisture content exceeded 5 cm, suggesting that the L-band is capable of detecting soil characteristics at relatively greater depths during freezing. Notably, the soil moisture content remained the dominant factor that influences brightness temperature during this process. After freezing, the initial moisture content continued to impact the microwave radiation response depth by affecting the amount of unfrozen water in the soil. The measured response depths for black soil with an initial moisture content of 0% (frozen soil) and 10% ranged from 100to 105 cm and 50to 60 cm, respectively, following freezing. For soils with higher initial moisture contents of 20% and 30%, the post-freezing microwave radiation response depths between 35to 50 cm and 25 to 35 cm, respectively. These results highlight the significant influence of soil moisture content on the penetration depth of the L-band signal. Furthermore, the study confirmed that under certain conditions, the microwave radiation response depth of frozen soil exceeded the penetration depth calculated using the Ulaby (1981) model, indicating that the actual response depth could be greater than previously estimated for frozen environments.This study provides new insights into the L-band microwave radiation response depth of frozen soil with varying initial moisture contents. The findings demonstrate that initial moisture content plays a significant role in determining the microwave radiation response depth by influencing the unfrozen water content in the soil. Additionally, the observed response depth surpassing the Ulaby model’s predicted penetration depth emphasizes the complexity of microwave interactions with frozen soil. These results have important implications for remote sensing inversion of frozen soil parameters and the use of L-band microwave radiometry in monitoring permafrost and frozen ground. The ability to accurately measure the microwave radiation response depth in these environments can improve our understanding of the physical properties of frozen soils and enhance the accuracy of remote sensing systems designed for frozen soil monitoring and analysis.关键词:Microwave radiometer;Response Depth;L-band;Frozen soil;Black Soil0|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30
摘要:In the detection of frozen soil parameters, the L-band offers stronger penetration capability than other microwave bands do, making it more advantageous for studying soil properties in frozen conditions. However, limited research has been conducted on the microwave radiation response depth of the L-band in such environments. Additionally, the microwave radiation response characteristics of soil under freezing conditions are not fully understood. This study aims to investigate the microwave radiation response depth of black soil in typical permafrost regions of Northeast China, focusing on its behavior under natural freezing conditions during winter.To address the research gap, this study employed a dual-polarized L-band microwave radiometer with a frequency of 1.414 GHz to perform near-field experiments on black soil samples with different initial moisture contents. The experiments were conducted in winter under natural freezing conditions. The study examined the changes in microwave radiation response depth during and after the freezing process, considering four initial moisture contents: 0%, 10%, 20%, and 30%. By analyzing the experimental results, the study aimed to explore how the initial moisture content affects the microwave radiation response depth and to determine the dominant factors that influence brightness temperature in frozen soil. This approach allowed for a comprehensive understanding of the interactions between soil moisture, freezing processes, and microwave radiation.The results revealed several key findings. During the freezing process, the L-band microwave radiation response depth for soils with 10% and 30% initial moisture content exceeded 5 cm, suggesting that the L-band is capable of detecting soil characteristics at relatively greater depths during freezing. Notably, the soil moisture content remained the dominant factor that influences brightness temperature during this process. After freezing, the initial moisture content continued to impact the microwave radiation response depth by affecting the amount of unfrozen water in the soil. The measured response depths for black soil with an initial moisture content of 0% (frozen soil) and 10% ranged from 100to 105 cm and 50to 60 cm, respectively, following freezing. For soils with higher initial moisture contents of 20% and 30%, the post-freezing microwave radiation response depths between 35to 50 cm and 25 to 35 cm, respectively. These results highlight the significant influence of soil moisture content on the penetration depth of the L-band signal. Furthermore, the study confirmed that under certain conditions, the microwave radiation response depth of frozen soil exceeded the penetration depth calculated using the Ulaby (1981) model, indicating that the actual response depth could be greater than previously estimated for frozen environments.This study provides new insights into the L-band microwave radiation response depth of frozen soil with varying initial moisture contents. The findings demonstrate that initial moisture content plays a significant role in determining the microwave radiation response depth by influencing the unfrozen water content in the soil. Additionally, the observed response depth surpassing the Ulaby model’s predicted penetration depth emphasizes the complexity of microwave interactions with frozen soil. These results have important implications for remote sensing inversion of frozen soil parameters and the use of L-band microwave radiometry in monitoring permafrost and frozen ground. The ability to accurately measure the microwave radiation response depth in these environments can improve our understanding of the physical properties of frozen soils and enhance the accuracy of remote sensing systems designed for frozen soil monitoring and analysis.关键词:Microwave radiometer;Response Depth;L-band;Frozen soil;Black Soil0|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30
City and Land
- “介绍了其在湖陆云量差异领域的研究进展,相关专家基于Sentinel-5P云量数据等,分析了中国334个湖泊及其邻近陆地的云量差异在夏秋两季的时空格局、影响因素及物理过程,为湖泊模型驱动数据选择提供参考。”
 摘要:Investigating the spatial–temporal patterns of lake–land cloud fraction difference (ΔCF) and identifying its influencing factors and underlying physical processes are important for quantifying lake–land radiation discrepancies and evaluating the applicability of land-based observations in driving lake numerical models. This paper analyzed the spatiotemporal patterns of ΔCF between 334 lakes and their surrounding lands across five lake zones in summer and autumn by using Sentinel-5P cloud fraction products from 2019 to 2023. The influencing factors of ΔCF and underlying physical processes were explored utilizing ERA5 and ERA5-land reanalysis datasets. The results show that all the five lake zones exhibit lower cloud fraction over lakes than adjacent lands (ΔCF<0) during summer and autumn. Lakes in the Tibetan Plateau Lake (TPL) Zone and the Inner Mongolia–Xinjiang Lake Zone show the most pronounced contrasts. ΔCF demonstrates a strong negative correlation with lake surface area, particularly in Northeast Plain and Mountain Lake Zone (R =-0.95, P<0.01). Only ΔCF in TPL exhibits a significant negative relationship with lake depth (P<0.01). With regard to physical processes, lake breezes amplify the negative ΔCF by suppressing cloud formation over lakes via subsidence, particularly at Selin Co. Lake–land cloud fraction differences intensify during lake breeze occurrences with flow configuration of surface divergence over lakes and convergence over surrounding lands.These results indicate that neglecting the lake–land cloud fraction difference and directly driving lake models by using land-based radiation observations may underestimate lake surface temperature and evaporation rate. The underestimation would be more pronounced in TPL during lake breeze periods.关键词:Sentinel-5P;Lake-land cloud fraction difference;Lake morphological characteristics;Lake breeze;Flow configuration0|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30
摘要:Investigating the spatial–temporal patterns of lake–land cloud fraction difference (ΔCF) and identifying its influencing factors and underlying physical processes are important for quantifying lake–land radiation discrepancies and evaluating the applicability of land-based observations in driving lake numerical models. This paper analyzed the spatiotemporal patterns of ΔCF between 334 lakes and their surrounding lands across five lake zones in summer and autumn by using Sentinel-5P cloud fraction products from 2019 to 2023. The influencing factors of ΔCF and underlying physical processes were explored utilizing ERA5 and ERA5-land reanalysis datasets. The results show that all the five lake zones exhibit lower cloud fraction over lakes than adjacent lands (ΔCF<0) during summer and autumn. Lakes in the Tibetan Plateau Lake (TPL) Zone and the Inner Mongolia–Xinjiang Lake Zone show the most pronounced contrasts. ΔCF demonstrates a strong negative correlation with lake surface area, particularly in Northeast Plain and Mountain Lake Zone (R =-0.95, P<0.01). Only ΔCF in TPL exhibits a significant negative relationship with lake depth (P<0.01). With regard to physical processes, lake breezes amplify the negative ΔCF by suppressing cloud formation over lakes via subsidence, particularly at Selin Co. Lake–land cloud fraction differences intensify during lake breeze occurrences with flow configuration of surface divergence over lakes and convergence over surrounding lands.These results indicate that neglecting the lake–land cloud fraction difference and directly driving lake models by using land-based radiation observations may underestimate lake surface temperature and evaporation rate. The underestimation would be more pronounced in TPL during lake breeze periods.关键词:Sentinel-5P;Lake-land cloud fraction difference;Lake morphological characteristics;Lake breeze;Flow configuration0|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30 - “介绍了其在海洋漂浮藻监测领域的研究进展,相关专家建立了中国东海马尾藻光学遥感估算模型,为解决中国近海马尾藻精准量化和动态监测问题提供了重要参考。”
 摘要:Sargassum, a type of floating macroalgae widely distributed in global oceans, is responsible for mass algae beaching events along the coastal areas of Caribbean Sea and other central western seas of the tropical Atlantic Ocean, causing many severe problems to the production and life of local residents. In recent years, Sargassum has also triggered frequent occurrences of “golden tides” in the marginal sea of China, particularly the East China Sea (ECS), due to its massive proliferation entangled with intricate climate and anthropogenic events. The emergence of golden tide events has had a significant impact on coastal ecosystems and economic activities. Optical satellite remote sensing has become a powerful tool for monitoring algae because of its advantages, such as wide monitoring coverage, rich spectral information, relatively uniform data formats, and easy accessibility. By combining accurate algae-identifying algorithms and algae-estimating quantitative models such as Biomass Per Area (BPA, kg/m2) estimation model, it will enable optical satellite remote sensing to precisely identify and quantitatively estimate Sargassum. Notably, Sargassum in the ECS (SargassumECS), which is primarily composed of S. horneri, exhibits different reflectance spectral characteristics due to species differences compared with Sargassum that inhabits other regions in the Atlantic Ocean, where S. natans and S. fluitans are the dominant species. Many studies that aimed to observe the SargassumECS via remote sensing of optical satellites were mainly qualitative or not based on quantitative estimation models suitable for S. horneri, whose key parameters have not been scientifically and objectively determined due to the lack of measured spectral data from spectrum collecting experiment. Thus, to realize the accurate quantification of SargassumECS via optical remote sensing, this study conducted controlled biomass experiments on S. horneri in the marginal sea of China, acquiring its hyperspectral reflectance dataset, then integrating spectral response functions of multiple optical sensors to simulate the corresponding Rayleigh-corrected reflectance (Rrc), such as the Multispectral Imager (MSI) onboard Sentinel-2A/B, the Coastal Zone Imager onboard HaiYang-1C/D (CZI on HY-1C/D), the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer onboard Aqua/Terra (MODIS on Aqua/Terra), the Operational Land Imager onboard Landsat-8, the Ocean and Land Color Instrument onboard Sentinel-3A/B, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer onboard National Polar-Orbiting Partnership, and the Geostationary Ocean Color Imager-II on board GEO-KOMPSAT-2B, to develop remote sensing estimation models applicable to multisource sensors. In the comparison and validation step of the quantitative models of multisource remote sensing data, CZI and MODIS multispectral images with quantitative estimation results was selected as samples to be compared with the quasi-synchronous MSI quantitative estimation results as reference value. The comparison and validation result showed that the biomass from BPA estimation models that integrate the spatial resolution of pixel, as the most robust quantitative parameter among algae-containing pixels area or algae coverage area, effectively reduces the remote sensing scale effect discrepancies among data from multiple optical sensors, offering higher consistency and less uncertainty in multisource data estimation results. This study, which is based on multisource optical satellite remote sensing data, analyzes Sargassum in the marginal sea of China, providing crucial references for comprehensively and precisely understanding the dynamics of golden tide outbreaks and enhancing the precise quantification and monitoring of floating algae in these areas关键词:golden tides;Sargassum;MSI;CZI/HY-1;MODIS;multi-source optical satellite remote sensing2|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30
摘要:Sargassum, a type of floating macroalgae widely distributed in global oceans, is responsible for mass algae beaching events along the coastal areas of Caribbean Sea and other central western seas of the tropical Atlantic Ocean, causing many severe problems to the production and life of local residents. In recent years, Sargassum has also triggered frequent occurrences of “golden tides” in the marginal sea of China, particularly the East China Sea (ECS), due to its massive proliferation entangled with intricate climate and anthropogenic events. The emergence of golden tide events has had a significant impact on coastal ecosystems and economic activities. Optical satellite remote sensing has become a powerful tool for monitoring algae because of its advantages, such as wide monitoring coverage, rich spectral information, relatively uniform data formats, and easy accessibility. By combining accurate algae-identifying algorithms and algae-estimating quantitative models such as Biomass Per Area (BPA, kg/m2) estimation model, it will enable optical satellite remote sensing to precisely identify and quantitatively estimate Sargassum. Notably, Sargassum in the ECS (SargassumECS), which is primarily composed of S. horneri, exhibits different reflectance spectral characteristics due to species differences compared with Sargassum that inhabits other regions in the Atlantic Ocean, where S. natans and S. fluitans are the dominant species. Many studies that aimed to observe the SargassumECS via remote sensing of optical satellites were mainly qualitative or not based on quantitative estimation models suitable for S. horneri, whose key parameters have not been scientifically and objectively determined due to the lack of measured spectral data from spectrum collecting experiment. Thus, to realize the accurate quantification of SargassumECS via optical remote sensing, this study conducted controlled biomass experiments on S. horneri in the marginal sea of China, acquiring its hyperspectral reflectance dataset, then integrating spectral response functions of multiple optical sensors to simulate the corresponding Rayleigh-corrected reflectance (Rrc), such as the Multispectral Imager (MSI) onboard Sentinel-2A/B, the Coastal Zone Imager onboard HaiYang-1C/D (CZI on HY-1C/D), the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer onboard Aqua/Terra (MODIS on Aqua/Terra), the Operational Land Imager onboard Landsat-8, the Ocean and Land Color Instrument onboard Sentinel-3A/B, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer onboard National Polar-Orbiting Partnership, and the Geostationary Ocean Color Imager-II on board GEO-KOMPSAT-2B, to develop remote sensing estimation models applicable to multisource sensors. In the comparison and validation step of the quantitative models of multisource remote sensing data, CZI and MODIS multispectral images with quantitative estimation results was selected as samples to be compared with the quasi-synchronous MSI quantitative estimation results as reference value. The comparison and validation result showed that the biomass from BPA estimation models that integrate the spatial resolution of pixel, as the most robust quantitative parameter among algae-containing pixels area or algae coverage area, effectively reduces the remote sensing scale effect discrepancies among data from multiple optical sensors, offering higher consistency and less uncertainty in multisource data estimation results. This study, which is based on multisource optical satellite remote sensing data, analyzes Sargassum in the marginal sea of China, providing crucial references for comprehensively and precisely understanding the dynamics of golden tide outbreaks and enhancing the precise quantification and monitoring of floating algae in these areas关键词:golden tides;Sargassum;MSI;CZI/HY-1;MODIS;multi-source optical satellite remote sensing2|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30
Atmosphere and Ocean
- “介绍了其在海浪参数测量领域的研究进展,相关专家提出了一种基于相干X波段雷达的随机森林和线性回归的集成模型的平均波周期估计方法,为提高波周期估计准确性提供了新方案。”
 摘要:Breaking and its evolution lead to some nonlinear features in the wavenumber-frequency spectrum observed by radar, such as group line and higher harmonic energy, accompanied by a decrease in the energy of the dominant wave. Group line is often considered the main reason for the overestimation of mean wave periods obtained by coherent microwave radar. Many methods have attempted to remove part or all the energy from group lines to improve the accuracy of mean wave period estimation. However, a certain degree of bias always occurs when inferring wave periods from the spectrum because of the uncertainty in the energy distribution within the wavenumber-frequency spectrum. The primary objective of this study is to develop a novel, robust method for estimating mean wave periods by using coherent X-band radar data, specifically addressing the challenges posed by these nonlinear features in the wavenumber-frequency spectrum. To address this issue, this paper proposes a mean wave period estimation method based on a random forest and linear regression ensemble model using coherent X-band radar, which estimates mean wave periods directly from the motion characteristics of waves in the spatial–temporal velocity series. The proposed method integrates random forest and linear regression into a powerful ensemble. It first extracts temporal velocity series from the time-Doppler spectrum and conducts comprehensive feature extraction from spatial–temporal data. Utilizing ECMWF data as a reference, the model predicts minimum peak distances to accurately identify wave crests and troughs while estimating the mean wave period on the basis of the fundamental wavelength-period relationship. First, temporal velocity series are derived from the time-Doppler spectrum. Next, features are extracted from the spatial–temporal velocity series, and a model is constructed in conjunction with European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) data to predict the minimum peak distance, identifying the positions of the wave crests and troughs. Finally, the mean wave period is inferred using the relationship between wave wavelength and period, and the method is validated by simulation. In addition, an approximately three-day dataset collected with a coherent X-band radar deployed along the coast of Shandong Province in China is reanalyzed and used to retrieve mean wave period. Compared with the ECMWF data, the mean wave periods retrieved by the proposed method have root-mean-square differences (RMSDs) of 0.15 and 0.22 s for Horizontal-Horizontal and Vertical-Vertical polarizations, respectively, and also have correlation coefficients of 0.96 and 0.89, respectively. Validation of the method using simulations and applied to this dataset shows that the proposed method can invert wave parameters effectively and with high accuracy. Results indicate that the proposed method can achieve real-time estimation of wave parameters from the spatial–temporal velocity series with a reasonable performance. In conclusion, this study presents a new method for estimating mean wave periods that integrates radar data, machine learning, and ECMWF data, addressing the shortcomings of existing approaches. The ensemble model demonstrates excellent performance and generalization capability, making it effective for real-time wave monitoring and forecasting. Future research could focus on expanding the dataset and refining the model to enhance its predictive capabilities in diverse marine environments.关键词:coherent X-band radar;mean wave period;spatial-temporal velocity series;vertical polarization;horizontal polarization;Random Forest;real-time estimation0|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30
摘要:Breaking and its evolution lead to some nonlinear features in the wavenumber-frequency spectrum observed by radar, such as group line and higher harmonic energy, accompanied by a decrease in the energy of the dominant wave. Group line is often considered the main reason for the overestimation of mean wave periods obtained by coherent microwave radar. Many methods have attempted to remove part or all the energy from group lines to improve the accuracy of mean wave period estimation. However, a certain degree of bias always occurs when inferring wave periods from the spectrum because of the uncertainty in the energy distribution within the wavenumber-frequency spectrum. The primary objective of this study is to develop a novel, robust method for estimating mean wave periods by using coherent X-band radar data, specifically addressing the challenges posed by these nonlinear features in the wavenumber-frequency spectrum. To address this issue, this paper proposes a mean wave period estimation method based on a random forest and linear regression ensemble model using coherent X-band radar, which estimates mean wave periods directly from the motion characteristics of waves in the spatial–temporal velocity series. The proposed method integrates random forest and linear regression into a powerful ensemble. It first extracts temporal velocity series from the time-Doppler spectrum and conducts comprehensive feature extraction from spatial–temporal data. Utilizing ECMWF data as a reference, the model predicts minimum peak distances to accurately identify wave crests and troughs while estimating the mean wave period on the basis of the fundamental wavelength-period relationship. First, temporal velocity series are derived from the time-Doppler spectrum. Next, features are extracted from the spatial–temporal velocity series, and a model is constructed in conjunction with European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) data to predict the minimum peak distance, identifying the positions of the wave crests and troughs. Finally, the mean wave period is inferred using the relationship between wave wavelength and period, and the method is validated by simulation. In addition, an approximately three-day dataset collected with a coherent X-band radar deployed along the coast of Shandong Province in China is reanalyzed and used to retrieve mean wave period. Compared with the ECMWF data, the mean wave periods retrieved by the proposed method have root-mean-square differences (RMSDs) of 0.15 and 0.22 s for Horizontal-Horizontal and Vertical-Vertical polarizations, respectively, and also have correlation coefficients of 0.96 and 0.89, respectively. Validation of the method using simulations and applied to this dataset shows that the proposed method can invert wave parameters effectively and with high accuracy. Results indicate that the proposed method can achieve real-time estimation of wave parameters from the spatial–temporal velocity series with a reasonable performance. In conclusion, this study presents a new method for estimating mean wave periods that integrates radar data, machine learning, and ECMWF data, addressing the shortcomings of existing approaches. The ensemble model demonstrates excellent performance and generalization capability, making it effective for real-time wave monitoring and forecasting. Future research could focus on expanding the dataset and refining the model to enhance its predictive capabilities in diverse marine environments.关键词:coherent X-band radar;mean wave period;spatial-temporal velocity series;vertical polarization;horizontal polarization;Random Forest;real-time estimation0|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30 - “卫星遥感技术在大气水汽探测领域应用广泛,但精度有待提升。专家借助机器学习技术,构建了顾及空间邻域特征的MODIS水汽产品神经网络校正模型,显著降低了校正误差,为大气水汽变化研究提供了更精确的数据支持。”
 摘要:Precipitable Water Vapor (PWV) is a crucial indicator for characterizing precipitation potential and serves as a key parameter for predicting extreme weather events and climate change. Fine-scale spatiotemporal distribution information of PWV provides essential data support for scientific and effective analysis. Remote sensing water vapor retrieval technology with high spatial resolution and high-precision Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) water vapor detection technology have become the mainstream methods for detecting PWV. However, both technologies have certain limitations: MODIS PWV products are susceptible to nonlinear factors such as cloud type and land cover type, resulting in limited observational accuracy, and GNSS PWV products cannot effectively reflect the high spatial-resolution information on water vapor distribution due to the distribution of GNSS stations. Therefore, the high-precision GNSS PWV is used as a reference value to calibrate MODIS PWV, and it can effectively improve accuracy. However, existing research has paid little attention to the influence of local spatial correlation of remote sensing water vapor products, leading to limited correction capability. In summary, this paper proposes a new correction model based on the strong local spatial correlation of water vapor products, which can significantly enhance correction accuracy and subsequently reflect fine-scale spatiotemporal information on water vapor distribution.In this paper, correlation analysis of remote sensing water vapor products within a local spatial domain is first conducted to determine an appropriate spatial neighborhood influence scale. Nonlinear influencing factors such as cloud information, land cover type, and sensor spatial orientation within this spatial domain from MOIDS products were taken into account, and a MODIS PWV correction model that considers the aforesaid spatial neighborhood characteristics is constructed. The proposed correction model is based on backpropagation (BP) neural network, with the difference between GNSS PWV and MODIS PWV matched data as the output variable.Taking GNSS PWV as the reference value, the proposed correction model achieves a root mean square error (RMSE) of 2.13 mm. Compared with the uncorrected data (RMSE = 4.97 mm), the correction results of the traditional linear model (RMSE = 3.96 mm), and the point-based matching BP model (RMSE = 2.43 mm), the quality of MODIS PWV is significantly improved, with enhancements of approximately 57.14%, 46.21%, and 12.35%, respectively. In terms of spatial and temporal performance, the proposed model demonstrates stable correction effects. Across the entire spatial domain of the study area, the RMSE of most correction results from the proposed model is below 3 mm, and the RMSE of correction results in different months generally falls within the range of 2.0—2.5 mm, indicating good stability.Four hours is the time threshold, taking the high-precision radiosonde PWV as the reference value and considering the poor spatial resolution of the radiosonde PWV. The RMSE of the corrected MODIS PWV is 2.50 mm, representing a 53.79% improvement over the uncorrected data (RMSE = 5.41 mm). Furthermore, the RMSE of most corrected PWV lies within the range of -3 and 3 mm, which further demonstrates that the correction model can effectively improve the quality of MODIS water vapor products and meet requirements for practical applications.First, the experiment demonstrates that considering the strong local spatial correlation of atmospheric water vapor can effectively improve the correction accuracy of MODIS PWV. Second, the correction results obtained using the proposed model exhibit good stability and can reflect fine-scale spatiotemporal information on water vapor distribution.关键词:MODIS PWV;GNSS PWV;PWV correction;spatial correlation;BP neural network0|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30
摘要:Precipitable Water Vapor (PWV) is a crucial indicator for characterizing precipitation potential and serves as a key parameter for predicting extreme weather events and climate change. Fine-scale spatiotemporal distribution information of PWV provides essential data support for scientific and effective analysis. Remote sensing water vapor retrieval technology with high spatial resolution and high-precision Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) water vapor detection technology have become the mainstream methods for detecting PWV. However, both technologies have certain limitations: MODIS PWV products are susceptible to nonlinear factors such as cloud type and land cover type, resulting in limited observational accuracy, and GNSS PWV products cannot effectively reflect the high spatial-resolution information on water vapor distribution due to the distribution of GNSS stations. Therefore, the high-precision GNSS PWV is used as a reference value to calibrate MODIS PWV, and it can effectively improve accuracy. However, existing research has paid little attention to the influence of local spatial correlation of remote sensing water vapor products, leading to limited correction capability. In summary, this paper proposes a new correction model based on the strong local spatial correlation of water vapor products, which can significantly enhance correction accuracy and subsequently reflect fine-scale spatiotemporal information on water vapor distribution.In this paper, correlation analysis of remote sensing water vapor products within a local spatial domain is first conducted to determine an appropriate spatial neighborhood influence scale. Nonlinear influencing factors such as cloud information, land cover type, and sensor spatial orientation within this spatial domain from MOIDS products were taken into account, and a MODIS PWV correction model that considers the aforesaid spatial neighborhood characteristics is constructed. The proposed correction model is based on backpropagation (BP) neural network, with the difference between GNSS PWV and MODIS PWV matched data as the output variable.Taking GNSS PWV as the reference value, the proposed correction model achieves a root mean square error (RMSE) of 2.13 mm. Compared with the uncorrected data (RMSE = 4.97 mm), the correction results of the traditional linear model (RMSE = 3.96 mm), and the point-based matching BP model (RMSE = 2.43 mm), the quality of MODIS PWV is significantly improved, with enhancements of approximately 57.14%, 46.21%, and 12.35%, respectively. In terms of spatial and temporal performance, the proposed model demonstrates stable correction effects. Across the entire spatial domain of the study area, the RMSE of most correction results from the proposed model is below 3 mm, and the RMSE of correction results in different months generally falls within the range of 2.0—2.5 mm, indicating good stability.Four hours is the time threshold, taking the high-precision radiosonde PWV as the reference value and considering the poor spatial resolution of the radiosonde PWV. The RMSE of the corrected MODIS PWV is 2.50 mm, representing a 53.79% improvement over the uncorrected data (RMSE = 5.41 mm). Furthermore, the RMSE of most corrected PWV lies within the range of -3 and 3 mm, which further demonstrates that the correction model can effectively improve the quality of MODIS water vapor products and meet requirements for practical applications.First, the experiment demonstrates that considering the strong local spatial correlation of atmospheric water vapor can effectively improve the correction accuracy of MODIS PWV. Second, the correction results obtained using the proposed model exhibit good stability and can reflect fine-scale spatiotemporal information on water vapor distribution.关键词:MODIS PWV;GNSS PWV;PWV correction;spatial correlation;BP neural network0|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30 - “针对高光谱图像HSI分类难题,专家提出基于解耦置信原型网络的跨域小样本分类方法,为提升分类性能提供新思路。”
 摘要:Few-shot learning based methods have gained significant attention because of the difficulty in acquiring labeled hyperspectral images (HSIs). Common few-shot learning methods often assume that the distributions of training and testing sample are consistent. However, due to factors such as varied shooting conditions, distribution differences often exist between different HSIs, limiting the performance of conventional few-shot learning approaches in achieving high classification accuracy.In this paper, we propose a novel cross-domain few-shot classification method for HSI that is based on a Disentangled Confidential Prototype Network (DCPN). Initially, a 3D residual convolutional network is used to extract deep embedded features from samples, thereby fully exploiting the spatial–spectral information of HSIs. Then, with the help of the disentangled network, these deep features undergo feature separation, enabling more focused representation of domain-invariant and domain-specific features. Additionally, a confidential prototype network is used to select high-confidence query set samples for recalculating more reliable class prototypes. More accurate few-shot classification is achieved by combining high-confidence class prototypes with original class prototypes. Experimental results on multiple real hyperspectral datasets validate the effectiveness of the proposed method.Six real HSI datasets, namely, University of Pavia, Pavia Center, Salinas, Indian Pines, WHU Hi LongKou, and Chikusei, were selected for the experiment to validate the effectiveness of the method. Chikusei, which has the largest number of feature classes, was selected as the source domain, and the remaining five datasets were used as the target domains. DCPN achieves the best overall classification accuracy on all datasets and produces significantly fewer noise points and smoother classification maps than other methods do.In this paper, we propose a cross-domain few-shot classification method for hyperspectral images based on the disentangled confidential prototype network. The method has the following advantages: (1) Domain-invariant features and domain-specific features are extracted by the DCPN, and only domain-invariant features are used for the few-shot classification task to reduce the negative impact from domain-specific feature information; (2) A confidential prototype network is proposed, which assigns corresponding weights to the unlabeled query set to recalculate the prototypes of each class and collaborates with the original support set class centers to jointly perform a high-quality few-shot classification task. Experimental results on six real HSI datasets show that the proposed method can achieve higher cross-domain classification accuracy and obtain smoother, more detailed classification results. Given that HSIs are often affected by atmospheric conditions, acquisition equipment, and other factors, how to obtain more robust domain-general and domain-specific features on the basis of our method remains a worthy topic for future work.关键词:hyperspectral image;classification;few-shot learning;disentangled network;domain adaptation;class prototypes;convolutional neural network;transfer learning0|1|0更新时间:2026-01-30
摘要:Few-shot learning based methods have gained significant attention because of the difficulty in acquiring labeled hyperspectral images (HSIs). Common few-shot learning methods often assume that the distributions of training and testing sample are consistent. However, due to factors such as varied shooting conditions, distribution differences often exist between different HSIs, limiting the performance of conventional few-shot learning approaches in achieving high classification accuracy.In this paper, we propose a novel cross-domain few-shot classification method for HSI that is based on a Disentangled Confidential Prototype Network (DCPN). Initially, a 3D residual convolutional network is used to extract deep embedded features from samples, thereby fully exploiting the spatial–spectral information of HSIs. Then, with the help of the disentangled network, these deep features undergo feature separation, enabling more focused representation of domain-invariant and domain-specific features. Additionally, a confidential prototype network is used to select high-confidence query set samples for recalculating more reliable class prototypes. More accurate few-shot classification is achieved by combining high-confidence class prototypes with original class prototypes. Experimental results on multiple real hyperspectral datasets validate the effectiveness of the proposed method.Six real HSI datasets, namely, University of Pavia, Pavia Center, Salinas, Indian Pines, WHU Hi LongKou, and Chikusei, were selected for the experiment to validate the effectiveness of the method. Chikusei, which has the largest number of feature classes, was selected as the source domain, and the remaining five datasets were used as the target domains. DCPN achieves the best overall classification accuracy on all datasets and produces significantly fewer noise points and smoother classification maps than other methods do.In this paper, we propose a cross-domain few-shot classification method for hyperspectral images based on the disentangled confidential prototype network. The method has the following advantages: (1) Domain-invariant features and domain-specific features are extracted by the DCPN, and only domain-invariant features are used for the few-shot classification task to reduce the negative impact from domain-specific feature information; (2) A confidential prototype network is proposed, which assigns corresponding weights to the unlabeled query set to recalculate the prototypes of each class and collaborates with the original support set class centers to jointly perform a high-quality few-shot classification task. Experimental results on six real HSI datasets show that the proposed method can achieve higher cross-domain classification accuracy and obtain smoother, more detailed classification results. Given that HSIs are often affected by atmospheric conditions, acquisition equipment, and other factors, how to obtain more robust domain-general and domain-specific features on the basis of our method remains a worthy topic for future work.关键词:hyperspectral image;classification;few-shot learning;disentangled network;domain adaptation;class prototypes;convolutional neural network;transfer learning0|1|0更新时间:2026-01-30 -
A fine-grained obect detection method for remote sensing images based on dual classification head AI导读
“遥感图像目标精细化检测领域迎来新突破,相关专家提出基于双分类头的检测方法,有效解决相似数据利用不足、错误标签干扰及相似类别区分难等问题,显著提升检测精度与鲁棒性。” 摘要:With the availability of remote sensing images improved, fine-grained object detection in remote sensing images has become an important research topic in the field of remote sensing and computer vision, and a large number of remote sensing image object detection datasets have been published. However, the current fine-grained object detection method cannot effectively use these publicized datasets, although they have similar image scenes and similar categories with the fine-grained object detection datasets, which will greatly affect the accuracy of the detectors. To solve the problem of insufficient utilization of similar data, incorrect labels affecting model accuracy, and difficulty in distinguishing similar categories, a fine-grained object detection method based on a dual classification head is proposed in this paper. Firstly, to solve the problem of similar data not being able to be used effectively in fine-grained object detection in remote sensing images, a dual classified detection head is proposed in this paper. This head uses different classified branches to train different datasets and allow similar data with varying definitions of category to participate in the training, which can effectively use similar data and significantly improve the accuracy of the model. Secondly, to solve the problem of noise labels in training data in fine-grained object detection, an error label filtering module based on prediction is proposed to reduce the impact of error labels. The category and confidence score of the object were obtained by an additional SoftMax operation in training. If the predicted category is different from the ground truth label and the confidence score is higher than a certain threshold, the label is considered to be incorrect. Finally, to solve the problem of large intra-class distance and small inter-class distance in fine-grained object detection in high-resolution remote sensing images, a margin cross-entropy loss function is designed to increase the classification boundary. The detection accuracy was improved by increasing the classification boundary of different categories. The Margin cross-entropy loss function calculates the loss by artificially subtracting the constant term from the network-predicted value of the positive sample and the detection accuracy was improved by increasing the classification boundary of different categories. Experiments on remote sensing fine-grained object detection datasets and FAIR1M datasets show that the proposed method improves the accuracy and robustness of fine-grained object detectors significantly in remote sensing images. The code is open source athttps://github.com/zf020114/DCH.关键词:remote sensing;deep learning;fine-grained object detection;rotated object detection;dual classification heads;error label filtering module;margin cross-entropy loss5|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30
摘要:With the availability of remote sensing images improved, fine-grained object detection in remote sensing images has become an important research topic in the field of remote sensing and computer vision, and a large number of remote sensing image object detection datasets have been published. However, the current fine-grained object detection method cannot effectively use these publicized datasets, although they have similar image scenes and similar categories with the fine-grained object detection datasets, which will greatly affect the accuracy of the detectors. To solve the problem of insufficient utilization of similar data, incorrect labels affecting model accuracy, and difficulty in distinguishing similar categories, a fine-grained object detection method based on a dual classification head is proposed in this paper. Firstly, to solve the problem of similar data not being able to be used effectively in fine-grained object detection in remote sensing images, a dual classified detection head is proposed in this paper. This head uses different classified branches to train different datasets and allow similar data with varying definitions of category to participate in the training, which can effectively use similar data and significantly improve the accuracy of the model. Secondly, to solve the problem of noise labels in training data in fine-grained object detection, an error label filtering module based on prediction is proposed to reduce the impact of error labels. The category and confidence score of the object were obtained by an additional SoftMax operation in training. If the predicted category is different from the ground truth label and the confidence score is higher than a certain threshold, the label is considered to be incorrect. Finally, to solve the problem of large intra-class distance and small inter-class distance in fine-grained object detection in high-resolution remote sensing images, a margin cross-entropy loss function is designed to increase the classification boundary. The detection accuracy was improved by increasing the classification boundary of different categories. The Margin cross-entropy loss function calculates the loss by artificially subtracting the constant term from the network-predicted value of the positive sample and the detection accuracy was improved by increasing the classification boundary of different categories. Experiments on remote sensing fine-grained object detection datasets and FAIR1M datasets show that the proposed method improves the accuracy and robustness of fine-grained object detectors significantly in remote sensing images. The code is open source athttps://github.com/zf020114/DCH.关键词:remote sensing;deep learning;fine-grained object detection;rotated object detection;dual classification heads;error label filtering module;margin cross-entropy loss5|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30 - “介绍了其在建筑物屋顶特征线提取领域的研究进展,相关专家提出了一种联合边界三角形检测与双向叠加平移的提取方法,为解决现有方法复杂、鲁棒性低等问题提供了新方案。”
 摘要:Roof feature lines are among the most important structural features of building surfaces and are widely used in 3D building model reconstruction. To address the issues in existing roof feature line extraction methods, such as high complexity, low robustness, and reliance on the accuracy of roof surface segmentation, this study proposes a novel method that combines boundary triangle detection with bidirectional superimposed translation. First, this study adopts Delaunay triangulation to establish the triangular mesh model of the roof point clouds, and an Equi-deep forest data structure is created to quickly store and search the neighborhood information of each triangle. Second, according to the adjacency relationship of each triangle provided by the equi-deep forest, the independent edges in the triangular mesh model are queried to determine the boundary points, and the center points of each triangle are translated upward and downward along their respective normal vectors. The intersecting lines of adjacent roof patches after projection are determined by counting the number of point sections in each point sphere domain after translation, and the points on the intersecting lines are translated in the opposite direction of the normal vector to obtain the ridge line points. Finally, the Ramer–Douglas–Peucker algorithm was used to simplify the closed independent edges to generate the boundary lines of the roof components, including the contours and step structures. The least squares fitting algorithm was used to vectorize the ridge points to generate the ridge lines. Combined with the plane coordinates of the intersection points of the multifeature lines and the elevation of the local original points, the endpoints of each feature line were refined, and feature line extraction free from roof surface segmentation was completed. To verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm, this study selected 12 groups of building roof point clouds with typical roof structure features from the Building3D and Vaihingen datasets for testing and compared them qualitatively and quantitatively with existing roof feature line extraction methods. Results showed that the average coordinate deviation of the feature line endpoints extracted by the proposed method was approximately one times the average point spacing, and the line similarity measure was higher than 85%, which was generally higher than that of the two comparison methods. In addition, compared with the half-edge data structure, the proposed equi-deep forest data structure demonstrates higher efficiency and a smaller memory footprint for storing triangular mesh models, which can alleviate the difficulty of calling the triangle adjacency relationship to a certain extent. Overall, the proposed method is suitable for extracting roof ridge lines from dense mesh models. It demonstrates stable performance and strong robustness and meets the requirements for extracting roof feature lines in the vast majority of building cases, thereby providing a novel approach for roof feature line extraction.关键词:feature line extraction;bidirectional superimposed translation;triangular mesh model;D-P algorithm;DBSCAN algorithm0|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30
摘要:Roof feature lines are among the most important structural features of building surfaces and are widely used in 3D building model reconstruction. To address the issues in existing roof feature line extraction methods, such as high complexity, low robustness, and reliance on the accuracy of roof surface segmentation, this study proposes a novel method that combines boundary triangle detection with bidirectional superimposed translation. First, this study adopts Delaunay triangulation to establish the triangular mesh model of the roof point clouds, and an Equi-deep forest data structure is created to quickly store and search the neighborhood information of each triangle. Second, according to the adjacency relationship of each triangle provided by the equi-deep forest, the independent edges in the triangular mesh model are queried to determine the boundary points, and the center points of each triangle are translated upward and downward along their respective normal vectors. The intersecting lines of adjacent roof patches after projection are determined by counting the number of point sections in each point sphere domain after translation, and the points on the intersecting lines are translated in the opposite direction of the normal vector to obtain the ridge line points. Finally, the Ramer–Douglas–Peucker algorithm was used to simplify the closed independent edges to generate the boundary lines of the roof components, including the contours and step structures. The least squares fitting algorithm was used to vectorize the ridge points to generate the ridge lines. Combined with the plane coordinates of the intersection points of the multifeature lines and the elevation of the local original points, the endpoints of each feature line were refined, and feature line extraction free from roof surface segmentation was completed. To verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm, this study selected 12 groups of building roof point clouds with typical roof structure features from the Building3D and Vaihingen datasets for testing and compared them qualitatively and quantitatively with existing roof feature line extraction methods. Results showed that the average coordinate deviation of the feature line endpoints extracted by the proposed method was approximately one times the average point spacing, and the line similarity measure was higher than 85%, which was generally higher than that of the two comparison methods. In addition, compared with the half-edge data structure, the proposed equi-deep forest data structure demonstrates higher efficiency and a smaller memory footprint for storing triangular mesh models, which can alleviate the difficulty of calling the triangle adjacency relationship to a certain extent. Overall, the proposed method is suitable for extracting roof ridge lines from dense mesh models. It demonstrates stable performance and strong robustness and meets the requirements for extracting roof feature lines in the vast majority of building cases, thereby providing a novel approach for roof feature line extraction.关键词:feature line extraction;bidirectional superimposed translation;triangular mesh model;D-P algorithm;DBSCAN algorithm0|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30 - “遥感图像去噪领域迎来新突破,相关专家提出基于特征增强与对比学习的自监督去噪算法,有效解决复杂纹理图像去噪时细节丢失和背景模糊问题,为提升遥感图像质量开辟新路径。”
 摘要:Optical remote sensing images are often disturbed by noise during transmission or storage, which affects the processing accuracy of downstream tasks. Thus, effectively removing noise from images is important. Obtaining clean and noisy image pairs in the same scene for optical remote sensing images is difficult, which is why many researchers have proposed self-supervised image denoising methods. Among them, convolutional autoencoders are a common self-supervised learning paradigm that requires no external labels. However, their current designs are often simplistic, limiting their ability to preserve fine textures in optical remote sensing images. Additionally, existing denoising methods often lack an effective perceptual loss function, which can result in over-smoothing after noise removal, with background blurring and artifacts.To this end, this paper proposes a self-supervised remote sensing image denoising algorithm based on feature enhancement and contrastive learning, including two core parts: the denoising branch and the contrastive branch. First, in the denoising branch, this paper constructs a feature-enhanced convolutional autoencoder denoising network, which acquires shallow contour features at different scales by using a global feature extraction module. Then, a lightweight attention mechanism is introduced in the attention extraction module, which can effectively focus complex texture features from remote sensing images. Next, the dynamic enhancement module is used to dynamically expand the sensory field to incorporate more spatially structured information. Finally, a dynamic adaptive mix-up operation is introduced in the image reconstruction module to encourage the shallow feature information in the downsampled part to flow adaptively to the deeper features in the upsampled part and thus effectively preserve the detailed features. In addition, in the contrastive branch, this paper utilizes the feature information carried by the noisy images to construct positive and negative sample pairs by using different data enhancement strategies to compute a new contrastive perceptual loss. This loss forms two opposite forces in the feature space: pulling the denoised image closer to the clean image and pushing it away from the noisy one. Meanwhile, total variation loss is applied to reduce pixel variations and thus better preserve edge details. Finally, reconstruction loss, total variation loss, and contrastive perception loss are used as a joint loss function to guide the network training to achieve the best denoising effect.Experimental results show that on the NWPU-RESISC45 and UC Merced Land Use datasets, the proposed method improves the average PSNR on Gaussian noise by 1.47—4.34 and 2.06—4.95 dB, and the average SSIM by 2.3%—11.8% and 2.6%—11.5% compared with other denoising methods. In addition, the proposed method achieves satisfactory denoising results on Speckle noise, Stripe noise, and real noisy remote sensing images.Whether on synthetic or real noise experiments, the proposed method can retain richer detail features after removing noise and avoid background blurring and artefacts. In addition, the proposed method has good generalizability and can handle Gaussian noise, speckle noise, and stripe noise.关键词:remote sensing;image denoising;deep learning;self-supervised learning;autoencoder;contrastive learning;contrastive perception loss;detail preservation0|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30
摘要:Optical remote sensing images are often disturbed by noise during transmission or storage, which affects the processing accuracy of downstream tasks. Thus, effectively removing noise from images is important. Obtaining clean and noisy image pairs in the same scene for optical remote sensing images is difficult, which is why many researchers have proposed self-supervised image denoising methods. Among them, convolutional autoencoders are a common self-supervised learning paradigm that requires no external labels. However, their current designs are often simplistic, limiting their ability to preserve fine textures in optical remote sensing images. Additionally, existing denoising methods often lack an effective perceptual loss function, which can result in over-smoothing after noise removal, with background blurring and artifacts.To this end, this paper proposes a self-supervised remote sensing image denoising algorithm based on feature enhancement and contrastive learning, including two core parts: the denoising branch and the contrastive branch. First, in the denoising branch, this paper constructs a feature-enhanced convolutional autoencoder denoising network, which acquires shallow contour features at different scales by using a global feature extraction module. Then, a lightweight attention mechanism is introduced in the attention extraction module, which can effectively focus complex texture features from remote sensing images. Next, the dynamic enhancement module is used to dynamically expand the sensory field to incorporate more spatially structured information. Finally, a dynamic adaptive mix-up operation is introduced in the image reconstruction module to encourage the shallow feature information in the downsampled part to flow adaptively to the deeper features in the upsampled part and thus effectively preserve the detailed features. In addition, in the contrastive branch, this paper utilizes the feature information carried by the noisy images to construct positive and negative sample pairs by using different data enhancement strategies to compute a new contrastive perceptual loss. This loss forms two opposite forces in the feature space: pulling the denoised image closer to the clean image and pushing it away from the noisy one. Meanwhile, total variation loss is applied to reduce pixel variations and thus better preserve edge details. Finally, reconstruction loss, total variation loss, and contrastive perception loss are used as a joint loss function to guide the network training to achieve the best denoising effect.Experimental results show that on the NWPU-RESISC45 and UC Merced Land Use datasets, the proposed method improves the average PSNR on Gaussian noise by 1.47—4.34 and 2.06—4.95 dB, and the average SSIM by 2.3%—11.8% and 2.6%—11.5% compared with other denoising methods. In addition, the proposed method achieves satisfactory denoising results on Speckle noise, Stripe noise, and real noisy remote sensing images.Whether on synthetic or real noise experiments, the proposed method can retain richer detail features after removing noise and avoid background blurring and artefacts. In addition, the proposed method has good generalizability and can handle Gaussian noise, speckle noise, and stripe noise.关键词:remote sensing;image denoising;deep learning;self-supervised learning;autoencoder;contrastive learning;contrastive perception loss;detail preservation0|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30 - “介绍了其在高光谱图像解混领域的研究进展,相关专家提出了一种新的基于Mamba模型的高光谱图像解混框架PSAMN,为解决现有解混技术的局限性问题提供了有效方案。”
 摘要:In recent years, the linear mixture model (LMM) has emerged as an important methodology in hyperspectral image unmixing, attracting considerable attention because of its computational efficiency, conceptual simplicity, and interpretability. LMM provides straightforward computations, scalability, and clear physical insights into the unmixing process, thus making it a good option for researchers and practitioners. Among the various linear unmixing techniques, autoencoder-based approaches have demonstrated notable advantages in data fitting capabilities and deep feature extraction. These methods use neural networks to capture complex patterns in hyperspectral data, thereby enabling more precise and robust unmixing outcomes. However, despite their strengths, these methodologies have limitations. A critical issue is the presence of noise within input data, which can affect the model’s generalizability during processing. Noise introduces uncertainty that propagates through the network, thus degrading performance in real-world applications. Furthermore, redundancy often occurs when addressing multiscale features, which are commonly associated with hyperspectral images, thus complicating the learning process and potentially reducing the overall efficacy of the model. Another major issue is the need to maintain long-range dependencies while ensuring computational efficiency. This balance can be achieved by understanding the spatial and spectral characteristics, which is a complicated task in high-dimensional datasets such as hyperspectral images. These challenges become even more pronounced when incorporating advanced architectures such as Mamba blocks, which aim to handle global interactions and require sophisticated design strategies. To address these issues, this study proposes a novel framework that integrates an attention module specifically tailored for denoising hyperspectral images. Furthermore, we introduce MambaHSI, a new hyperspectral image model based on the Mamba framework. This proposed model incorporates two key innovations: a spatial Mamba block and a spectral Mamba block. The spatial Mamba block is designed to simulate global interactions across the entire image at the pixel level, capturing complex relationships between pixels over extensive spatial extents. Meanwhile, the spectral Mamba block partitions spectral vectors into multiple groups, enabling the exploration of inter-group relationships and the extraction of meaningful spectral features. By grouping spectral vectors, the model reduces redundancy and enhances its capacity to effectively represent different spectral patterns. These components are integrated into a multistage convolutional autoencoder network, forming the multistage Mamba attention unmixing framework (PSAMN). PSAMN combines the strengths of spatial and spectral modeling with the power of attention mechanisms, thereby comprehensively addressing the aforementioned challenges. The attention module plays a key role in mitigating the impact of noise by emphasizing relevant features and suppressing irrelevant ones, thereby enhancing the model’s robustness. The multistage architecture ensures that the model can progressively refine its representations, achieving superior accuracy in unmixing tasks. To validate the efficacy of the proposed framework, we conducted extensive comparative experiments on synthetic and real hyperspectral datasets. Results demonstrate that PSAMN outperforms existing state-of-the-art algorithms in terms of unmixing accuracy, robustness, and computational efficiency. On synthetic datasets, PSAMN achieves superior performance metrics, including lower reconstruction errors and higher endmember extraction precision. On real-world datasets, the framework exhibits strong adaptability to varying noise levels and complex spectral–spatial structures, thus being highly competitive in practical applications. In summary, the proposed PSAMN framework is a significant advancement in the field of hyperspectral image unmixing. By addressing key challenges such as noise sensitivity, redundancy in multiscale features, and the need for efficient long-range dependency modeling, PSAMN establishes a new benchmark for future research. Its innovative integration of spatial and spectral Mamba blocks, coupled with an attention-driven denoising module, provides a comprehensive solution to the inherent complexities of hyperspectral data analysis. With the growing application of hyperspectral imaging in remote sensing, environmental monitoring, and medical imaging, frameworks such as PSAMN will play a crucial role in unlocking the full potential of hyperspectral data.关键词:hyperspectral unmixing;deep learning;Mamba model;Self-Attention Module;Mamba Block0|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30
摘要:In recent years, the linear mixture model (LMM) has emerged as an important methodology in hyperspectral image unmixing, attracting considerable attention because of its computational efficiency, conceptual simplicity, and interpretability. LMM provides straightforward computations, scalability, and clear physical insights into the unmixing process, thus making it a good option for researchers and practitioners. Among the various linear unmixing techniques, autoencoder-based approaches have demonstrated notable advantages in data fitting capabilities and deep feature extraction. These methods use neural networks to capture complex patterns in hyperspectral data, thereby enabling more precise and robust unmixing outcomes. However, despite their strengths, these methodologies have limitations. A critical issue is the presence of noise within input data, which can affect the model’s generalizability during processing. Noise introduces uncertainty that propagates through the network, thus degrading performance in real-world applications. Furthermore, redundancy often occurs when addressing multiscale features, which are commonly associated with hyperspectral images, thus complicating the learning process and potentially reducing the overall efficacy of the model. Another major issue is the need to maintain long-range dependencies while ensuring computational efficiency. This balance can be achieved by understanding the spatial and spectral characteristics, which is a complicated task in high-dimensional datasets such as hyperspectral images. These challenges become even more pronounced when incorporating advanced architectures such as Mamba blocks, which aim to handle global interactions and require sophisticated design strategies. To address these issues, this study proposes a novel framework that integrates an attention module specifically tailored for denoising hyperspectral images. Furthermore, we introduce MambaHSI, a new hyperspectral image model based on the Mamba framework. This proposed model incorporates two key innovations: a spatial Mamba block and a spectral Mamba block. The spatial Mamba block is designed to simulate global interactions across the entire image at the pixel level, capturing complex relationships between pixels over extensive spatial extents. Meanwhile, the spectral Mamba block partitions spectral vectors into multiple groups, enabling the exploration of inter-group relationships and the extraction of meaningful spectral features. By grouping spectral vectors, the model reduces redundancy and enhances its capacity to effectively represent different spectral patterns. These components are integrated into a multistage convolutional autoencoder network, forming the multistage Mamba attention unmixing framework (PSAMN). PSAMN combines the strengths of spatial and spectral modeling with the power of attention mechanisms, thereby comprehensively addressing the aforementioned challenges. The attention module plays a key role in mitigating the impact of noise by emphasizing relevant features and suppressing irrelevant ones, thereby enhancing the model’s robustness. The multistage architecture ensures that the model can progressively refine its representations, achieving superior accuracy in unmixing tasks. To validate the efficacy of the proposed framework, we conducted extensive comparative experiments on synthetic and real hyperspectral datasets. Results demonstrate that PSAMN outperforms existing state-of-the-art algorithms in terms of unmixing accuracy, robustness, and computational efficiency. On synthetic datasets, PSAMN achieves superior performance metrics, including lower reconstruction errors and higher endmember extraction precision. On real-world datasets, the framework exhibits strong adaptability to varying noise levels and complex spectral–spatial structures, thus being highly competitive in practical applications. In summary, the proposed PSAMN framework is a significant advancement in the field of hyperspectral image unmixing. By addressing key challenges such as noise sensitivity, redundancy in multiscale features, and the need for efficient long-range dependency modeling, PSAMN establishes a new benchmark for future research. Its innovative integration of spatial and spectral Mamba blocks, coupled with an attention-driven denoising module, provides a comprehensive solution to the inherent complexities of hyperspectral data analysis. With the growing application of hyperspectral imaging in remote sensing, environmental monitoring, and medical imaging, frameworks such as PSAMN will play a crucial role in unlocking the full potential of hyperspectral data.关键词:hyperspectral unmixing;deep learning;Mamba model;Self-Attention Module;Mamba Block0|0|0更新时间:2026-01-30
Models and Methods
0

